PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
12-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Memory Management Units
Note that when a TID value in a TLB entry is all zeros, it causes a match in the PID compare
(effectively ignoring the values of the PID registers). Thus, the operating system can set the values
of all the TIDs to zero, effectively eliminating the PID values from all translation comparisons.
The simplest method of using multiple PID registers is to use one PID register for each protected
process address space, and a second PID register if the operating system wishes to share TLB
entries that map shared memory among different address spaces.
12.2.2 Variable-Sized Pages
There are two kinds of TLBs on the e500 core complex as follows:
• TLBs that translate addresses for 4-Kbyte pages only. These TLBs are set-associative based
on the page number (page address).
• TLBs that translate addresses for variable-sized pages. These TLBs are fully-associative.
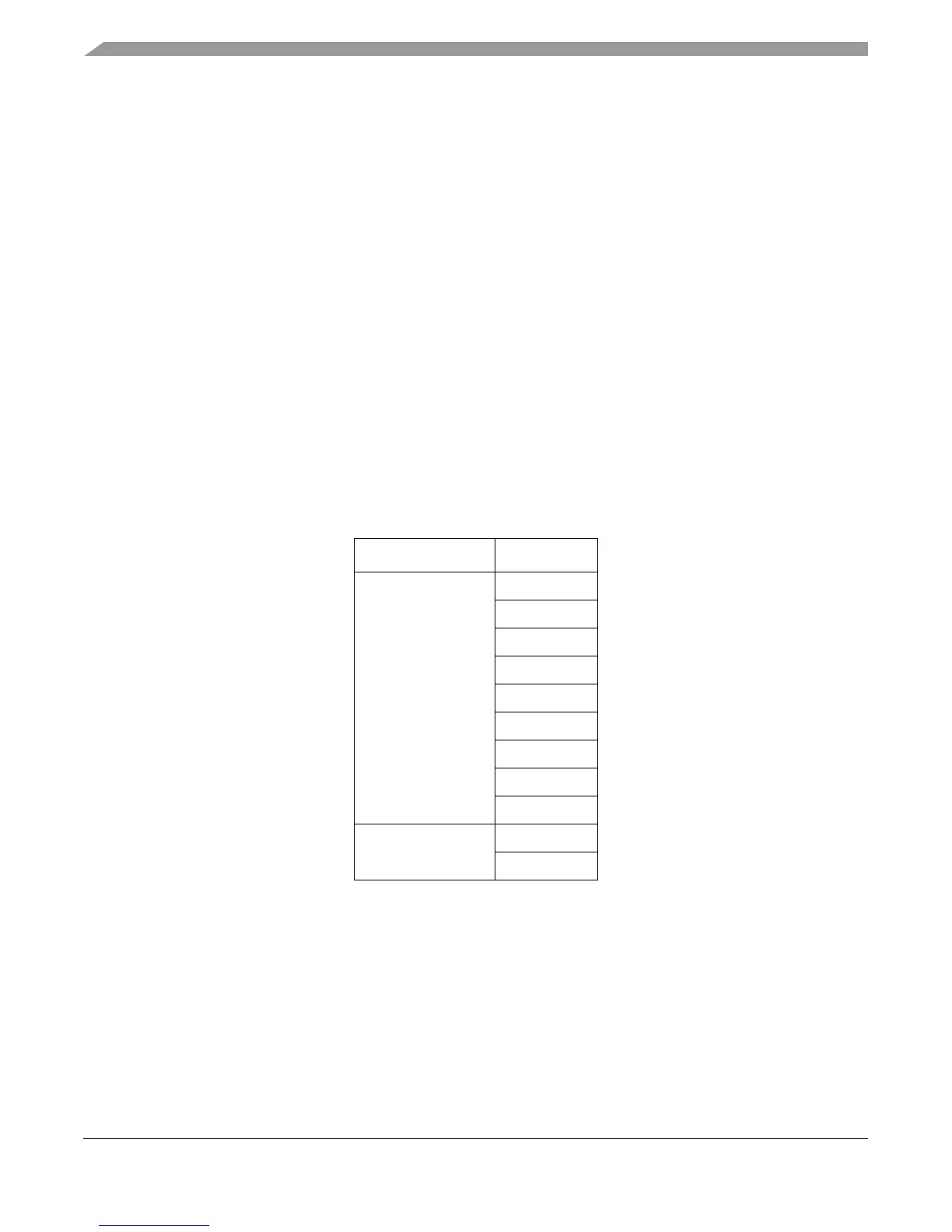
Table 12-2 shows the nine (e500v1) or eleven (e500v2) page sizes supported by the
fully-associative TLBs that support variable-sized pages (VSPs) on the e500 core complex.
For more information on the bit ranges of effective page numbers and offsets that are translated
for these pages sizes, see the EREF.
Table 12-2. Page Sizes for L1VSPs and TLB1 (L2 MMU) on the e500 Core
Core Page Sizes
e500 (both e500v1
and e500v2)
4 Kbyte
16 Kbyte
64 Kbyte
256 Kbyte
1 Mbyte
4 Mbyte
16 Mbyte
64 Mbyte
256 Mbyte
e500v2 1 Gbyte
4 Gbyte
 Loading...
Loading...