Register Model
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 2-25
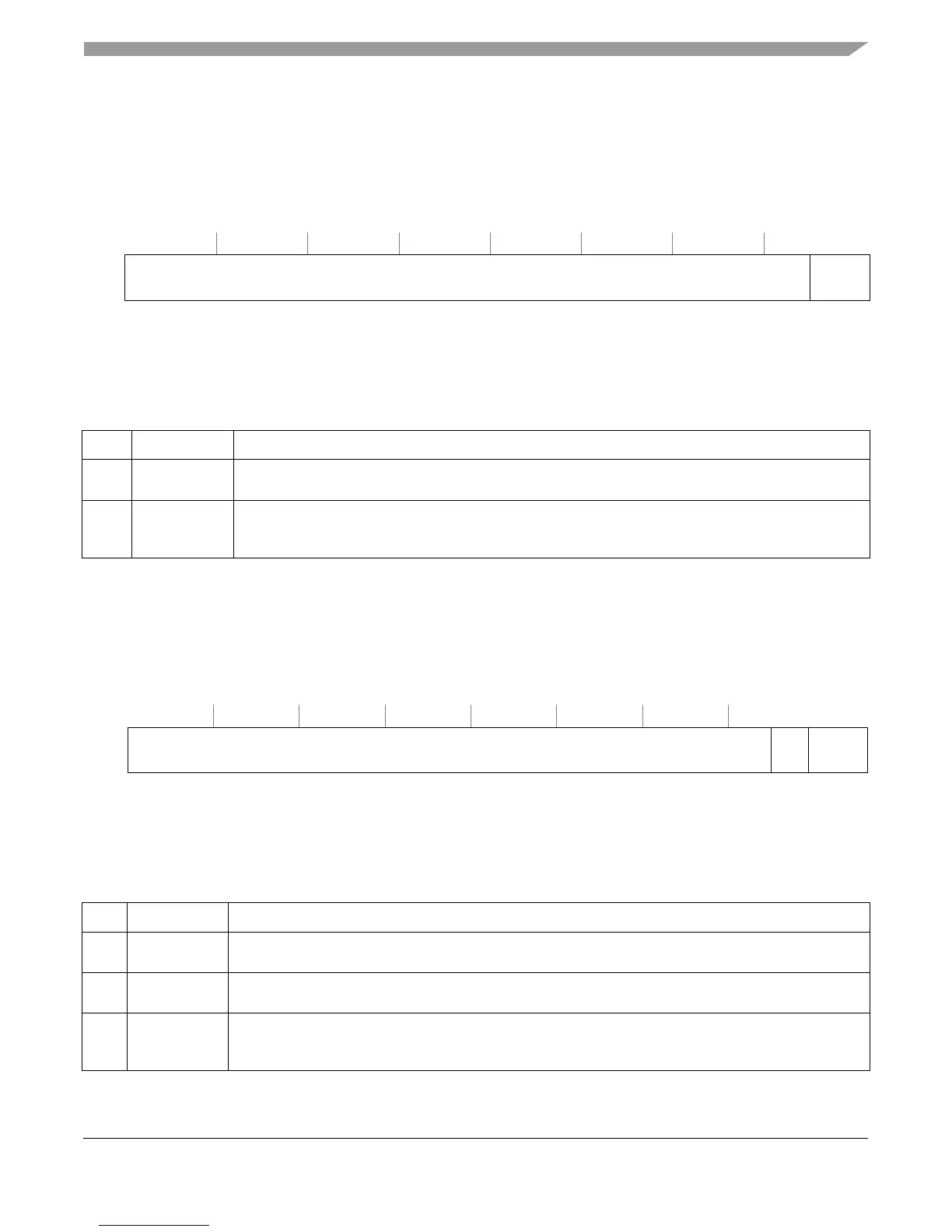
2.9.1 Branch Buffer Entry Address Register (BBEAR)
BBEAR is shown in Figure 2-15. Writing to BBEAR requires synchronization, as described in
Section 2.16, “Synchronization Requirements for SPRs.”
Table 2-12 describes the BBEAR fields.
2.9.2 Branch Buffer Target Address Register (BBTAR)
Figure 2-16 shows the BBTAR. Writing to BBTAR requires synchronization, as described in
Section 2.16, “Synchronization Requirements for SPRs.”
Table 2-12 describes BBTAR fields.
SPR 513 Access: Supervisor/user
32 61 62 63
R
Branch buffer entry address IAB[0–1]
W
Reset All zeros
Figure 2-15. Branch Buffer Entry Address Register (BBEAR)
Table 2-11. BBEAR Field Descriptions
Bits Name Description
32–61 Branch buffer
entry address
Branch buffer effective entry address bits 0–29
62–63 IAB[0–1] Instruction after branch (with BBTAR[62]). 3-bit pointer that points to the instruction in the cache block
after the branch. If the branch is the last instruction in the cache block, IAB = 000, to indicate the next
sequential instruction, which resides in the zeroth position of the next cache block.
SPR 513 Access: Supervisor/user
32 61 62 63
R
Branch buffer target address IAB2 BDIRPR
W
Reset All zeros
Figure 2-16. Branch Buffer Target Address Register (BBTAR)
Table 2-12. BBTAR Field Descriptions
Bits Name Description
32–61 Branch buffer
target address
Branch buffer target address bits 0–29
62 IAB2 Instruction after branch bit 2 (with BBEAR[62–63]). IAB is a 3-bit pointer that points to the instruction in
the cache block after the branch. See the bblels instruction description.
63 BDIRPR Branch direction prediction. The user can pick the direction of the predicted branch.
0 The locked address is always predicted as not taken.
1 The locked address is always predicted as taken.
 Loading...
Loading...