PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
12-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Memory Management Units
12.2 Effective-to-Real Address Translation
The core complex fetch and load/store units generate 32-bit effective addresses. The MMU
translates each of these addresses to 32-bit real addresses, (36 bits for the e500v2) which are then
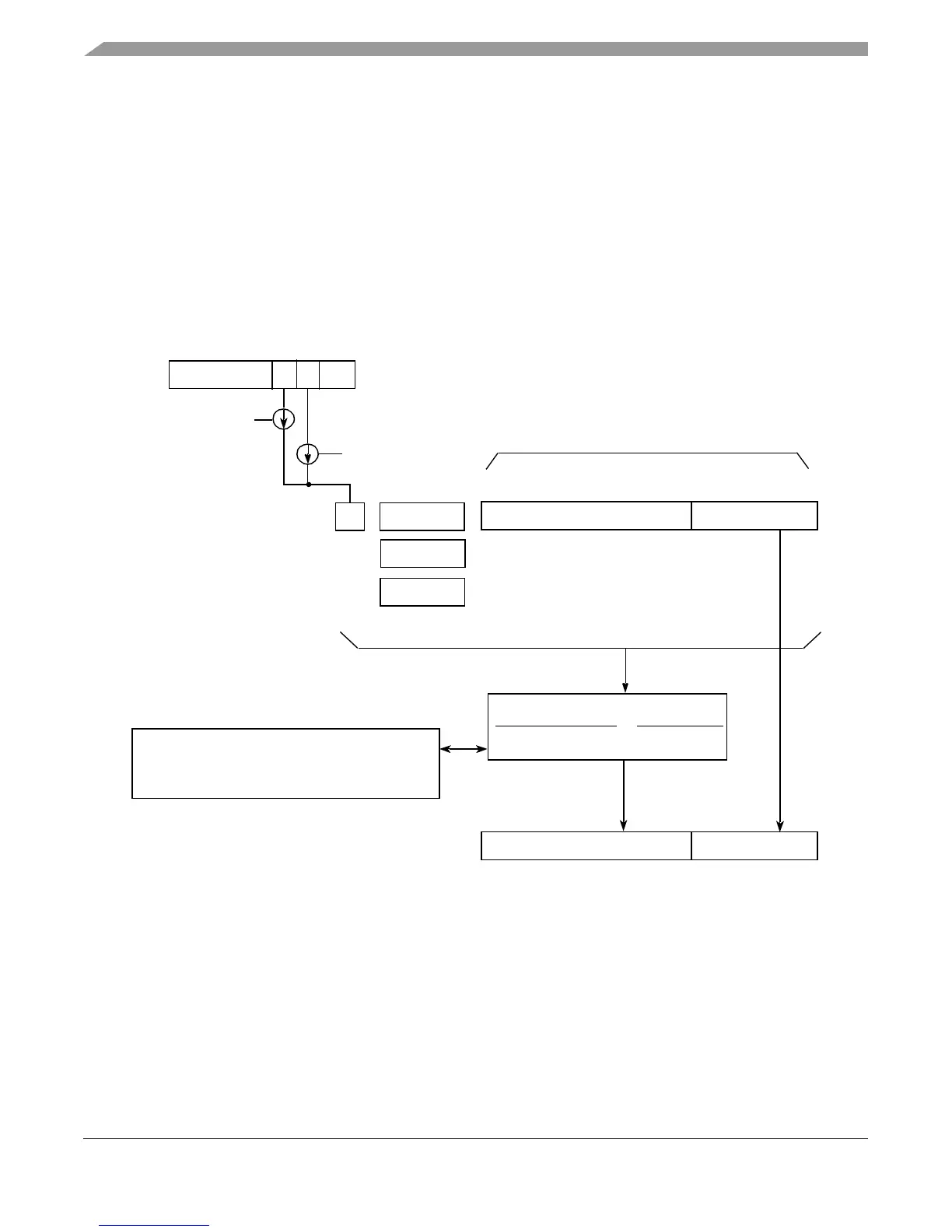
used for memory bus accesses. Figure 12-1 illustrates the high-level translation flow with 32-bit
real addressing for the e500v1core, showing that because the smallest page size supported by the
e500 core complex is 4 Kbytes, the least-significant 12 bits always index within the page and are
untranslated. The appropriate L1 MMU (instruction or data) is checked for a matching address
translation first. If it misses, the request for translation is forwarded to the unified (instruction and
data) L2 MMU.
Figure 12-1. Effective-to-Real Address Translation Flow (e500v1)
Effective Page Number Byte Address
Real Page Number Byte Address
32-bit Effective Address (EA)
32-bit Real Address
4–20 bits* 12–28 bits*
4–20 bits* 12–28 bits*
L2 MMU (unified)
Three 41-bit Virtual Addresses (VAs)
8 bits
MSR
••• IS DS •••
Instruction Access
Data Access
AS
PID0
PID1
PID2
L1 MMUs
Instruction L1 MMU
Data L1 MMU
2 TLBs 2 TLBs
* Number of bits depends on page size
(4 Kbytes–256 Mbytes)
16-Entry Fully-Assoc. VSP Array (TLB1)
256-Entry 2-Way Set Assoc. Array (TLB0)
 Loading...
Loading...