Interrupts and Exceptions
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 5-5
5.3 Interrupt Registers
Table 5-2 summarizes registers used for interrupt handling.
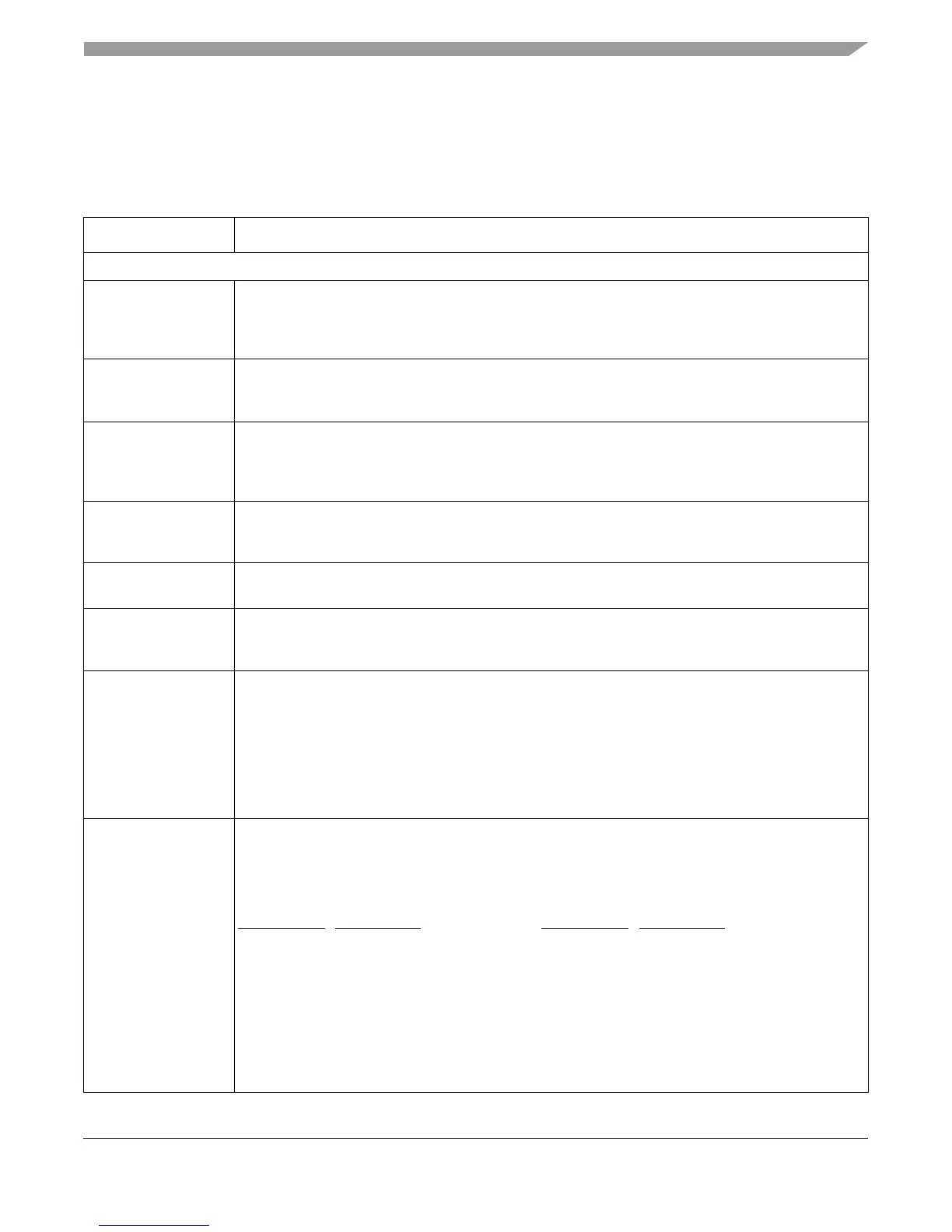
Table 5-2. Interrupt Registers Defined by the PowerPC Architecture
Register Description
Book E Interrupt Registers
Save/restore register 0
(SRR0)
On a noncritical interrupt, SRR0 is set to the current or next instruction address. When rfi is executed,
instruction execution continues at the address in SRR0. In general, SRR0 contains the address of the
instruction that caused the noncritical interrupt or the address of the instruction to return to after a
noncritical interrupt is serviced.
Save/restore register 1
(SRR1)
When a noncritical interrupt is taken, MSR contents are placed into SRR1. When rfi is executed, SRR1
contents are placed into the MSR. SRR1 bits that correspond to reserved MSR bits are also reserved.
Note that an MSR bit that is reserved may be altered by rfi.
Critical save/restore
register 0 (CSRR0)
When a critical interrupt is taken, CSRR0 is set to the current or next instruction address. When rfci is
executed, instruction execution continues at the address in CSRR0. In general, CSRR0 contains the
address of the instruction that caused the critical interrupt, or the address of the instruction to return to
after a critical interrupt is serviced.
Critical save/restore
register 1 (CSRR1)
When a critical interrupt is taken, MSR contents are placed into CSRR1. When rfci is executed, CSRR1
contents are placed into the MSR. CSRR1 bits that correspond to reserved MSR bits are also reserved.
Note that an MSR bit that is reserved may be altered by rfci.
Data exception address
register (DEAR)
DEAR contains the address referenced by a load, store, or cache management instruction that caused
an alignment, data TLB miss, or data storage interrupt.
Interrupt vector prefix
register (IVPR)
IVPR[32–47] provides the high-order 48 bits of the address of the interrupt handling routine for each
interrupt type. The 16-bit vector offsets are concatenated to the right of IVPR to form the address of the
interrupt handling routine. IVPR[48–63] are reserved.
Exception syndrome
register (ESR)
Provides a syndrome to differentiate between exceptions that can generate the same interrupt type.
When one of these types of interrupts is generated, bits corresponding to the specific exception that
generated the interrupt are set and all other ESR bits are cleared. Other interrupt types do not affect
the ESR. ESR does not need to be cleared by software. Table 5-3 shows ESR bit definitions.
The EIS defines ESR[56] as the SPE exception bit (SPE). It is set when the processor reports an
exception related to the execution of an embedded floating-point or SPE instruction. Note that the EIS
definition of the machine check interrupt uses the machine check syndrome register (MCSR) rather
than the ESR.
Interrupt vector offset
registers (IVORs)
Holds the quad-word index from the base address provided by the IVPR for each interrupt type.
IVOR0–IVOR15 are provided for defined interrupt types. SPR numbers corresponding to
IVOR16–IVOR31 are reserved. IVOR[32–47,60–63] are reserved. SPR numbers for IVOR32–IVOR63
are allocated for implementation-dependent use. (IVOR32–IVOR34 (SPR 528–530) are used by
interrupts defined by the EIS.) IVOR assignments are shown below.
IVOR Number
Interrupt Type
IVOR0 Critical input
IVOR1 Machine check
IVOR2 Data storage
IVOR3 Instruction storage
IVOR4 External input
IVOR5 Alignment
IVOR6 Program
IVOR8 System call
IVOR10 Decrementer
IVOR Number
Interrupt Type
IVOR11 Fixed-interval timer interrupt
IVOR12 Watchdog timer interrupt
IVOR13 Data TLB error
IVOR14 Instruction TLB error
IVOR15 Debug
VOR32 SPE APU unavailable
IVOR33 Embedded floating-point data
IVOR34 Embedded floating-point round
IVOR35 Performance monitor
 Loading...
Loading...