Register Model
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 2-27
2.10 Hardware Implementation-Dependent Registers
This section describes the e500-specific HID0 and HID1 registers.
2.10.1 Hardware Implementation-Dependent Register 0 (HID0)
This section describes the HID0 register, shown in Figure 2-18, as it is defined by the e500 core.
NOTE
Note that some HID fields may not be implemented in a device that
incorporates the e500 core and that some fields may be defined more
specifically by the incorporating device. For specific details it is
important to refer to the “Register Summary” chapter in the device’s
reference manual.
HID0 is used for configuration and control. Writing to HID0 requires synchronization, as
described in Section 2.16, “Synchronization Requirements for SPRs.”
Table 2-14 describes the HID0 fields.
SPR 1008 Access: Supervisor-only
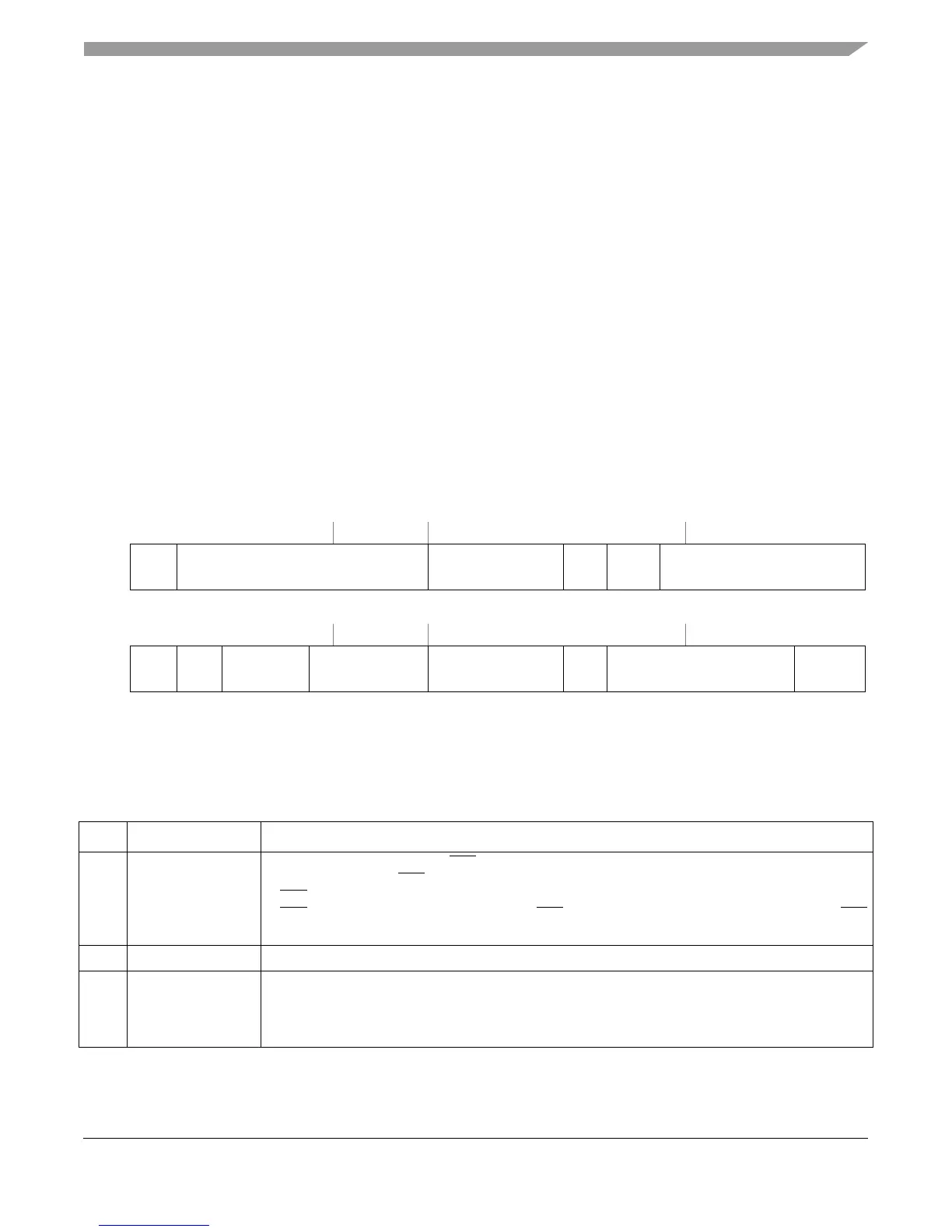
32 33 39 40 41 42 43 47
R
EMCP — DOZE NAP SLEEP —
W
Reset All zeros
48 49 50 51 55 56 57 58 62 63
R
— TBEN SEL_TBCLK — EN_MAS7_UPDATE DCFA — NOPTI
W
Reset All zeros
Figure 2-18. Hardware Implementation-Dependent Register 0 (HID0)
Table 2-14. HID0 Field Descriptions
Bits Name Description
32 EMCP Enable machine check signal, mcp
. Used to mask out further machine check exceptions caused by
asserting the internal mcp
signal.
0mcp
is disabled.
1mcp
is enabled. If MSE[ME] = 0, asserting mcp causes checkstop. If MSR[ME] = 1, asserting mcp
causes a machine check exception.
33–39 — Reserved, should be cleared.
40 DOZE Doze power management mode. If MSR[WE] is set, this bit controls the
doze
output signal.
Interpretation of this bit is handled by integrated system logic.
0
doze
is not asserted.
1
doze
is asserted.
 Loading...
Loading...