Register Model
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 2-9
2.3 Registers for Integer Operations
The following sections describe registers defined for integer computational instructions.
2.3.1 General-Purpose Registers (GPRs)
Book E implementations provide 32 GPRs (GPR0–GPR31) for integer operations. The instruction
formats provide 5-bit fields for specifying the GPRs to be used in the execution of the instruction.
Each GPR is a 64-bit register and can be used to contain address and integer data, although all
instructions except SPE APU instructions, double-precision embedded floating-point instructions
(e500v2 only), and single-precision embedded vector floating-point instructions use and return
32-bit values in GPR bits 32–63.
2.3.2 Integer Exception Register (XER)
Bits in the integer exception register (XER) are set based on the operation of an instruction
considered as a whole, not on intermediate results. (For example, the Subtract from Carrying
instruction (subfc), the result of which is specified as the sum of three values, sets bits in the XER
based on the entire operation, not on an intermediate sum.)
The e500 implements the XER as it is defined by Book E.
2.4 Registers for Branch Operations
This section describes registers used by Book E branch and CR operations.
2.4.1 Condition Register (CR)
The e500 implements the CR as it is defined by Book E for integer instructions. Note that the
embedded floating-point instructions do not use the CR.
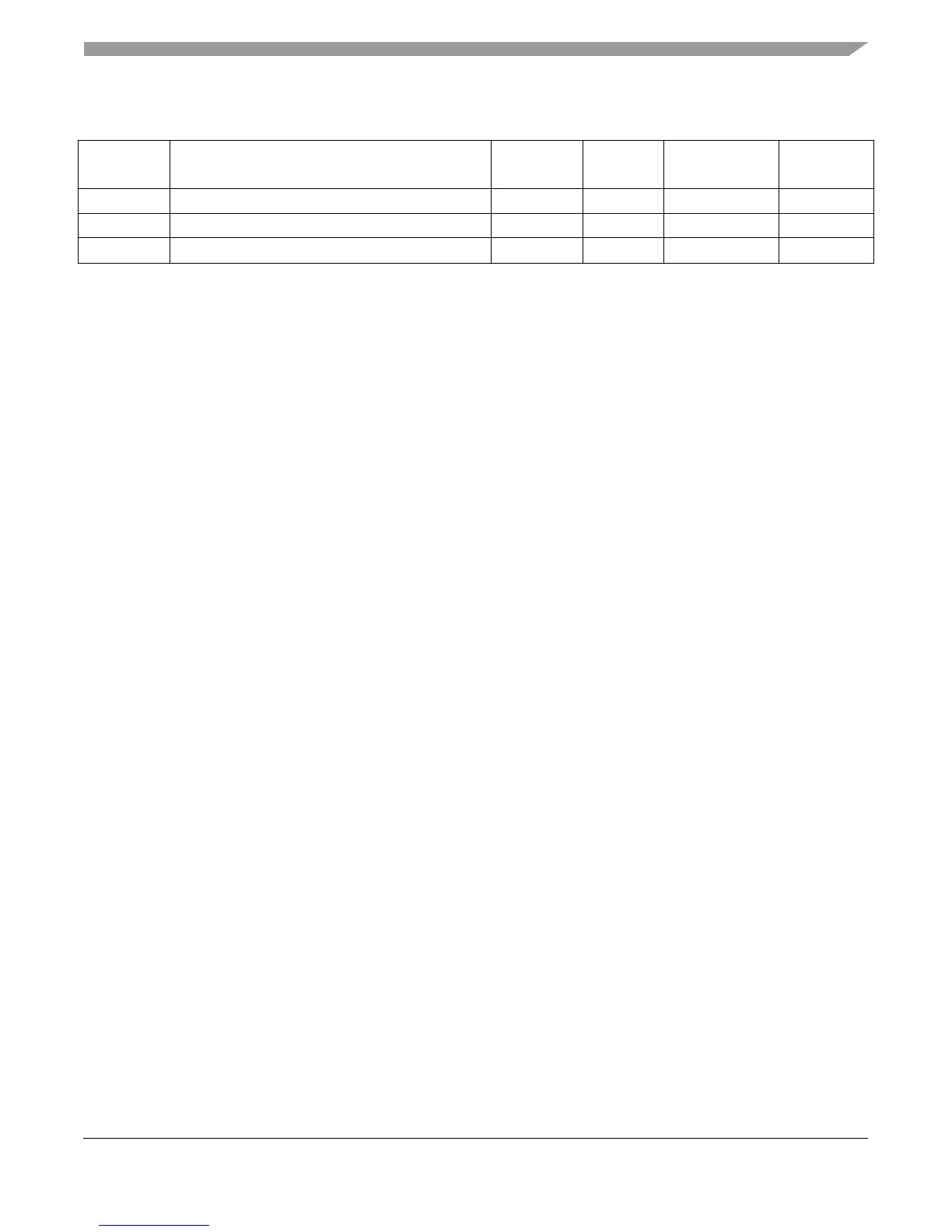
SVR System version register 1023 Read-only Yes 2.5.4/2-13
TLB0CFG TLB configuration register 0 688 Read-only Yes 2.12.4/2-37
TLB1CFG TLB configuration register 1 689 Read-only Yes 2.12.4.2/2-39
1
Writing to these registers requires synchronization, as described in Section 2.16, “Synchronization Requirements for SPRs.”
Table 2-2. Implementation-Specific SPRs (by SPR Abbreviation) (continued)
SPR
Abbreviation
Name SPR Number Access Supervisor Only Section/Page
 Loading...
Loading...