Performance Monitor
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 7-7
PMLCb registers are shown in Figure 7-3.
PMLCb is cleared by a hard reset. Table 7-5 describes PMLCb fields.
7.2.6 User Local Control B Registers (UPMLCb0–UPMLCb3)
The contents of PMLCb0–PMLCb3 are reflected to UPMLCb0–UPMLCb3, which can be read by
user-level software with mfpmr using PMR numbers in Table 7-2.
PMLCb0 (PMR272)
PMLCb1 (PMR273)
PMLCb2 (PMR274)
PMLCb3 (PMR275)
UPMLCb0 (PMR256)
UPMLCb1 (PMR257)
UPMLCb2 (PMR258)
UPMLCb3 (PMR259)
Access: PMLCb0–PMLCb3: Supervisor-only
UPMLCb0–UPMLCb3: Supervisor/user read-only
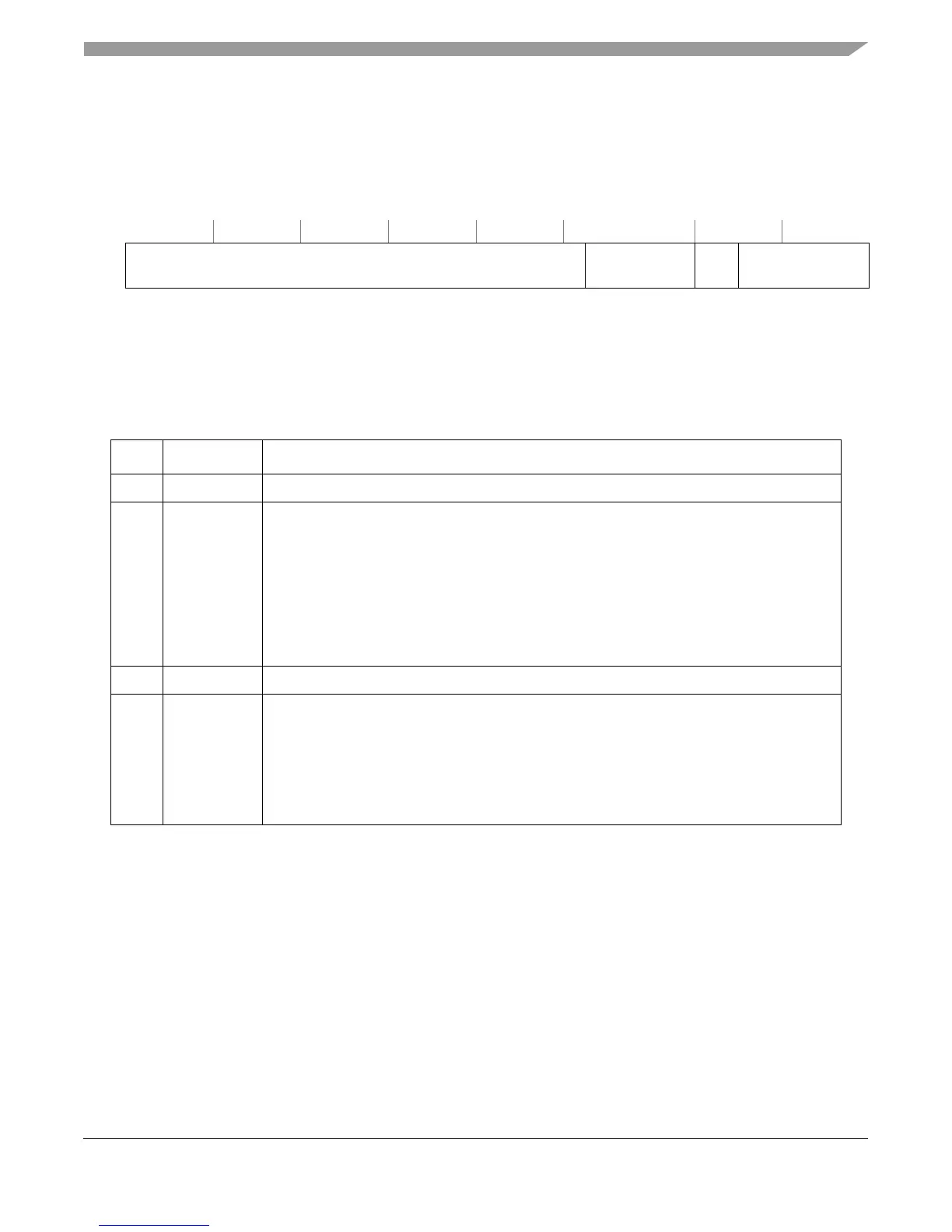
32 51 52 53 55 56 57 58 63
R
— THRESHMUL — THRESHOLD
W
Reset All zeros
Figure 7-3. Local Control B Registers (PMLCb0–PMLCb3)/
User Local Control B Registers (UPMLCb0–UPMLCb3)
Table 7-5. PMLCb0–PMLCb3 Field Descriptions
Bits Name Description
32–52 — Reserved, should be cleared.
53–55 THRESHMUL Threshold multiple.
000 Threshold field is multiplied by 1 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 1)
001 Threshold field is multiplied by 2 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 2)
010 Threshold field is multiplied by 4 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 4)
011 Threshold field is multiplied by 8 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 8)
100 Threshold field is multiplied by 16 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 16)
101 Threshold field is multiplied by 32 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 32)
110 Threshold field is multiplied by 64 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 64)
111 Threshold field is multiplied by 128 (PMLCb
n
[THRESHOLD] × 128)
56–57 — Reserved, should be cleared.
58–63 THRESHOLD Threshold. Only events that exceed this value are counted. Events to which a threshold value
applies are implementation dependent, as are the unit (for example duration in cycles) and the
granularity with which the threshold value is interpreted.
By varying the threshold value, software can obtain a profile of the event characteristics
subject to thresholding. For example, if PMC1 is configured to count cache misses that exceed
the threshold value, software can measure the distribution of cache miss durations for a given
program by monitoring the program repeatedly using a different threshold value each time.
 Loading...
Loading...