Execution Timing
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 4-49
4.7.6.3.2 Misalignment Effects
Misalignment, particularly the back-to-back misalignment of loads, can cause strange
performance effects. The e500 splits misaligned transactions into two transactions, so misaligned
load latency is at least 1 cycle greater than the default latency.
For loads that hit in the cache, the throughput of the LSU degrades to one misaligned load every
3 cycles. Similarly, stores can be translated at a rate of one store per 3 cycles. Additionally, after
translation, each misaligned store is treated as two separate store queue entries, each requiring a
cache access.
A word or half-word storage access requires multiple accesses if it crosses a double-word
boundary. Extended vector loads and stores cause alignment exceptions if they cross their natural
alignment boundaries (as show in Figure 4-9).
Frequent unaligned accesses are discouraged because of the impact on performance.
Note the following:
• Accesses that cross a translation boundary may be restarted—that is, a misaligned access
that crosses a page boundary is entirely restarted if the second portion of the access causes
a TLB miss. This may result in the first portion being accessed twice.
• Accesses that cross a translation boundary where the endianness changes cause a
byte-ordering DSI exception.
• Future generations of high-performance microprocessors that implement the PowerPC
architecture may experience greater misalignment penalties.
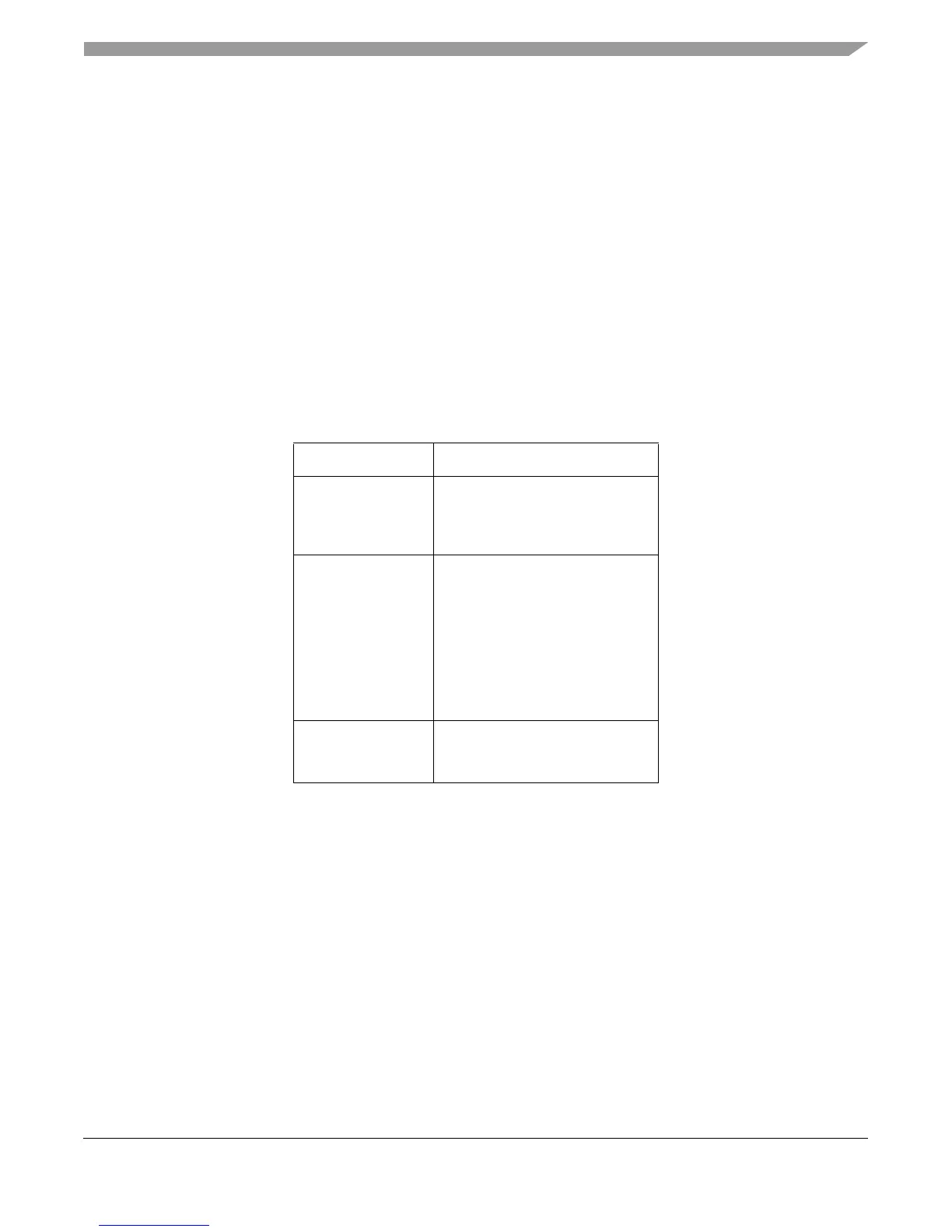
Table 4-9. Natural Alignment Boundaries for Extended Vector Instructions
Instruction Boundary
evld{d,w,h}
evld{d,w,h}x
evstd{d,w,h}
evstd{d,w,h}x
Double-word
evlwwsplat{x}
evlwhe{x}
evlwhou{x}
evlwhos{x}
evlwhsplat{x}
evstwwe{x}
evstwwo{x}
evstwhe{x}
evstwho{x}
Word
evlhhesplat{x}
evlhhousplat{x}
evlhhossplat{x}
Half
 Loading...
Loading...