PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
4-28 Freescale Semiconductor
Execution Timing
4.4.3.1 MU Divide Execution
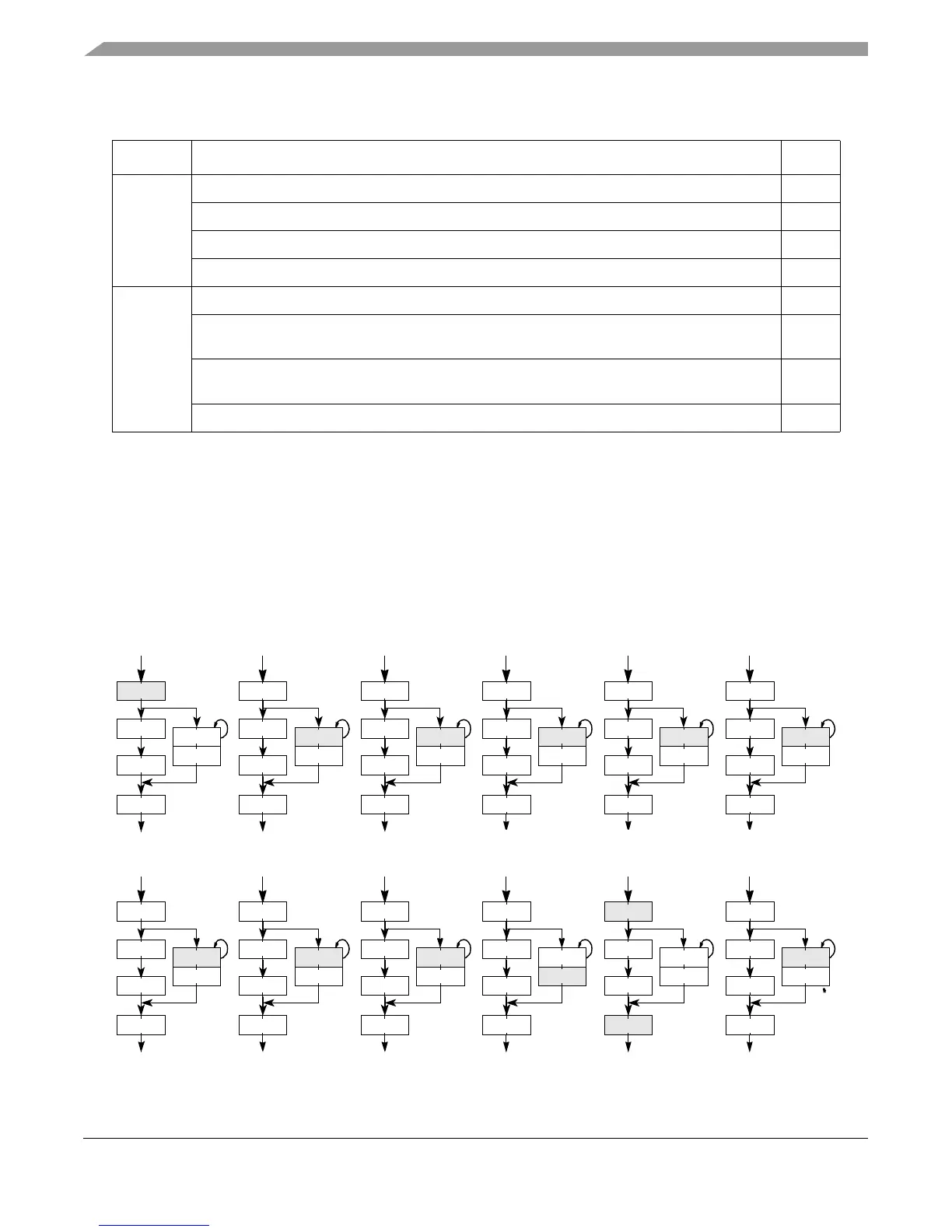
The MU provides a bypass path for divides, as shown in Figure 4-11, so the iterative portion of
divide execution is performed outside of the MU pipeline, allowing subsequent instructions
(except other divides) to execute in the main MU pipeline. Figure 4-11 shows the path that integer
divides and both scalar and vector single-precision divide instructions take. The double-precision
portion of the MU has a six-stage pipeline, but has a similar divide bypass that splits from the main
path after the first stage and before the last.
Figure 4-11. MU Divide Bypass Path (Showing an 11-Cycle Divide)
divw
x
rA or rB is 0 4
rA representable in 8 bits 11
rA representable in 16 bits 19
All other cases 35
evdivw
x
Both the lower and upper words match the criteria described above for the divw
x
4-cycle case. 4
Assuming the 4-cycle evdivw
x
case does not apply, the lower and upper words match the
criteria described above for the divw
x
4- or 11-cycle case.
11
Assuming neither the 4- or 11-cycle evdivw
x
cases apply, the lower and upper words match the
criteria described above for the divw
x
4-, 11-, or 19-cycle case.
19
All other cases 35
Table 4-2. The Effect of Operand Size on Divide Latency (continued)
Instruction Condition Latency
divw 1
Bypass
Path
mulli 1
divw 1
mulli 2
mulli 1
divw 1
mulli 1
mulli 3
mulli 2
divw 1
mulli 2
mulli 4
mulli 1
mulli 3
divw 1
mulli 3
mulli 5
mulli 2
mulli 4
divw 1
Clock 0 Clock 5 Clock 1 Clock 2 Clock 3 Clock 4
mulli 4
mulli 6
mulli 3
mulli 5
divw 1
mulli 5
mulli 4
mulli 7
divw 1
mulli 8
mulli 5
divw 1
mulli 8
mulli 6
mulli 7
divw 1
mulli 7
divw 2
divw 1
mulli 8
mulli 8
mulli 9
mulli 7
divw 2
Clock 6 Clock 11 Clock 7 Clock 8 Clock 9 Clock 10
mulli 7mulli 6
mulli 6
 Loading...
Loading...