PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
12-26 Freescale Semiconductor
Memory Management Units
12.7.1 e500 MAS Registers
The core complex uses seven special purpose registers (MAS0, MAS1, MAS2, MAS3, MAS4,
MAS6, and MAS7) to facilitate reading, writing, and searching the TLBs. The MAS registers can
be read or written using the mfspr and mtspr instructions. The core complex does not implement
the MAS5 register, because the tlbsx instruction on the e500 only searches based on a single PID
value (the value of MAS6[SPID0]).
For the core complex, TLB0 is 2 (e500v1) or 4 (e500v2)-way set associative, so bits 45–51 of the
effective address are used to index into TLB0 when it is accessed. For TLB0, ESEL is defined as
a 2-bit field (bits 46–47) that identifies which of the indexed entries is to be referenced by the TLB
operation (ESEL selects the way). For TLB1, ESEL selects one of the 16 entries in the array.
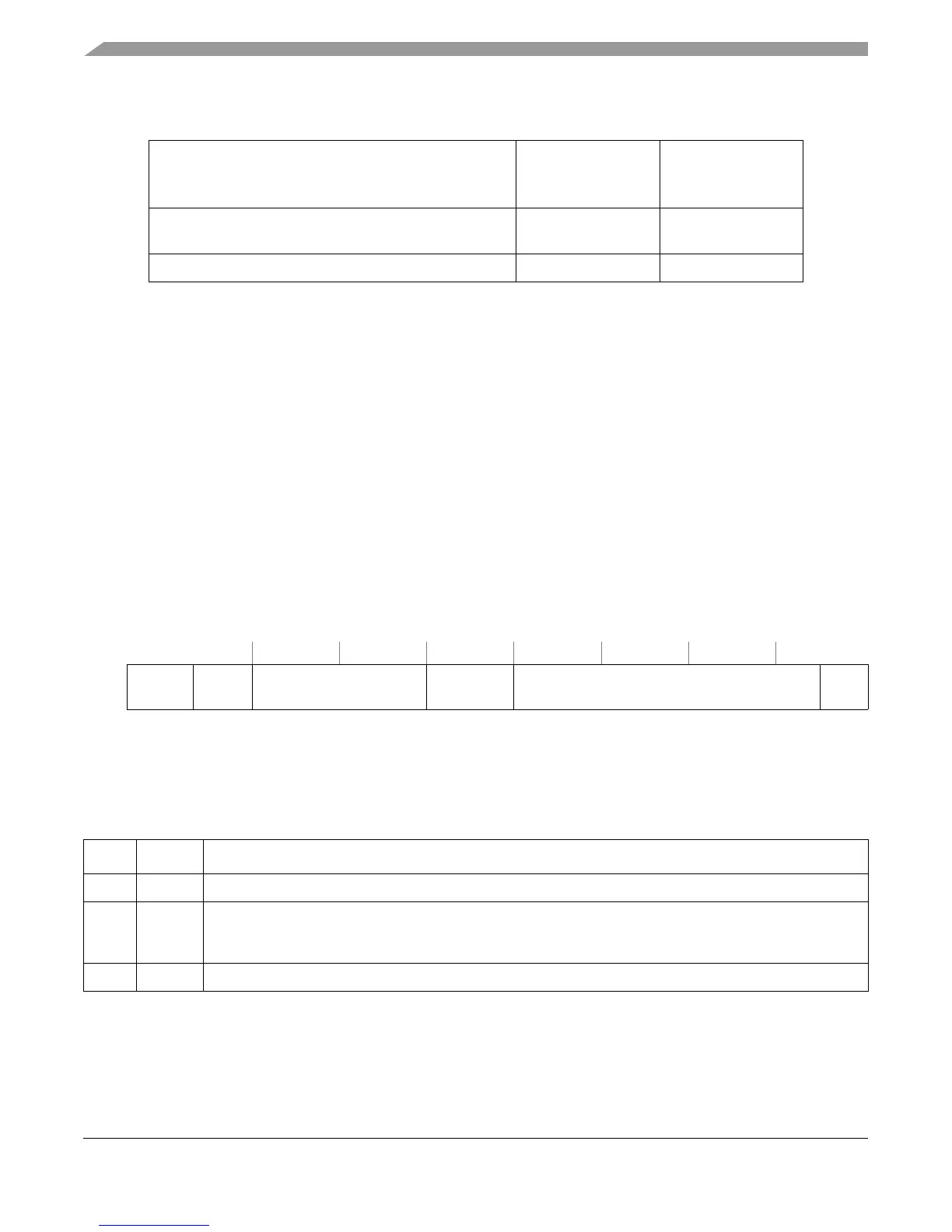
Figure 12-11 describes the format of MAS0 on the e500 core complex.
Table 12-8 shows the core complex MAS0 bit definitions.
MMU assist registers (MAS0–MAS4, MAS6 (and MAS7 for
the e500v2))
2.12.5/2-39 12.7.1/12-26
Data exception address register (DEAR) 2.7.1.3/2-18 —
SPR 624 Access: Supervisor-only
32 34 35 36 43 44 47 48 61 62 63
R
— TLBSEL — ESEL — NV
W
Reset All zeros
Figure 12-11. MAS Register 0 (MAS0)
Table 12-8. MAS0 Field Descriptions—MMU Read/Write and Replacement Control
Bits Name Descriptions
32–34 — Reserved, should be cleared.
35 TLBSEL Selects TLB for access
0TLB0
1TLB1
36–43 — Reserved, should be cleared.
Table 12-7. Registers Used for MMU Functions (continued)
Registers
Comprehensive
Reference
(Section/Page)
Additional
e500-Only Reference
(Section/Page)
 Loading...
Loading...