PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
1-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Core Complex Overview
• Two simple units (SU1 and SU2)
— Add and subtract
— Shift and rotate
— Logical operations
— Support for 64-bit SPE APU instructions in SU1
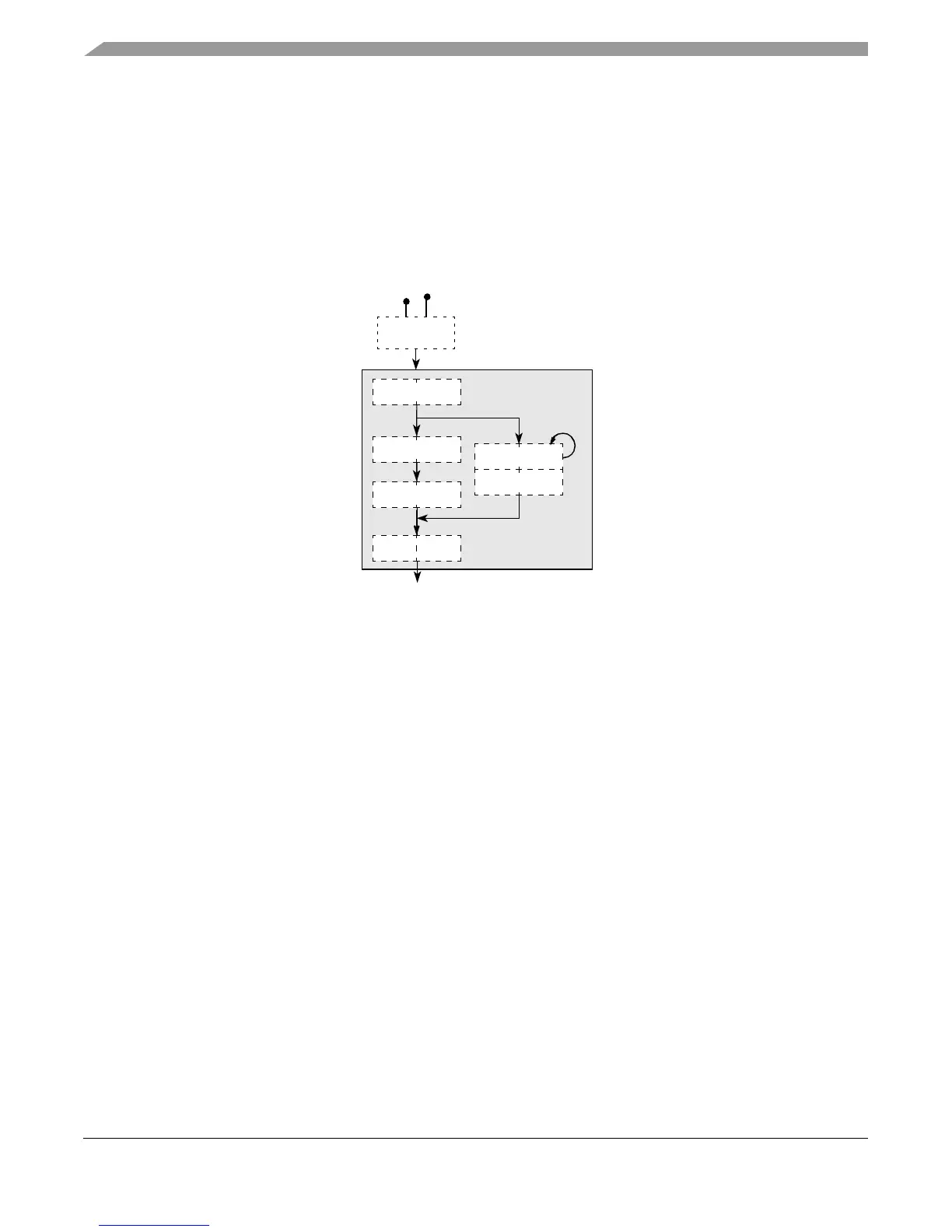
• Multiple-cycle unit (MU)—The MU is shown in Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3. Four-Stage MU Pipeline, Showing Divide Bypass
The MU has the following features:
— Four-cycle latency for all multiplication, including SPE integer and fractional multiply
instructions and embedded scalar and vector floating-point multiply instructions
— Variable-latency divide: 4, 11, 19, and 35 cycles for all integer divide instructions. If rA
or rB is zero, floating-point divide instructions take 4 cycles; all others take 29. Note
that although most divide instructions take more than 4 cycles to execute, the MU
allows subsequent multiply instructions to execute through all four MU stages in
parallel with the divide.
— 4-cycle floating-point add and subtract
• The load/store unit (LSU) is shown in Figure 1-4.
The LSU has the following features:
— 3-cycle load latency
— Fully pipelined
— Load miss queue allows up to four load misses before stalling (up to nine load misses
in the e500v2).
— Load hits can continue to be serviced when the load miss queue is full.
— The seven-entry L1 store queue allows full pipelining of stores.
Upper Lower
MU-3
MU-1
MU-2
Divide Bypass Path
Postdivide
Divide
Reservation
Station
From GIQ0 or GIQ1
MU-4
 Loading...
Loading...