Auxiliary Processing Units (APUs)
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 10-5
are handled. Mode 0 defines a real-time, default results–oriented mode that saturates results. No
other modes are currently defined.
10.4.2.2 Floating-Point Data Formats
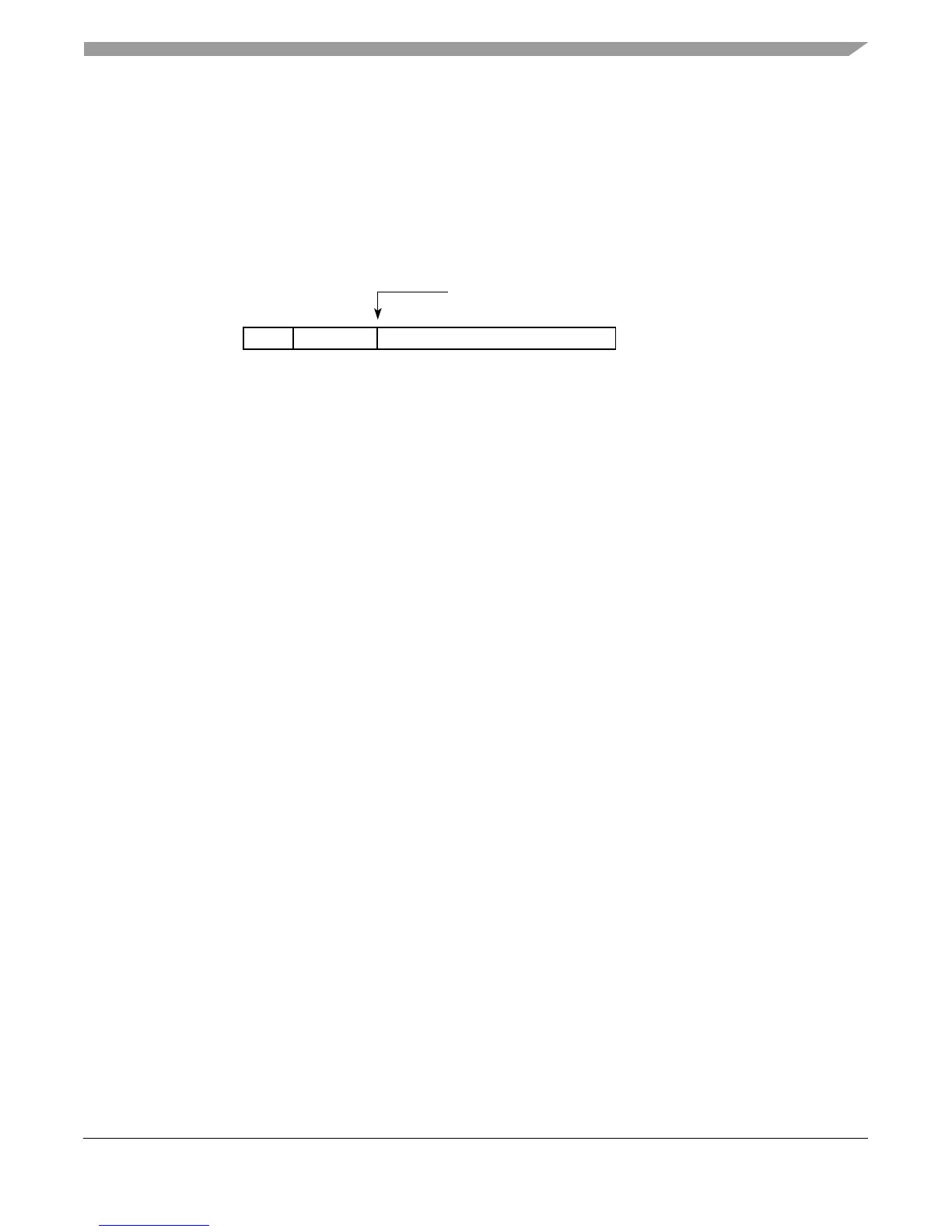
As shown in Figure 10-2, double-precision floating-point data elements are 64 bits wide with 1
sign bit (s), 11 bits of biased exponent (e) and 52 bits of fraction (f).
Figure 10-2. Floating-Point Data Format
For double-precision normalized numbers, the biased exponent value ‘e’ lies in the range of 1 to
2046 corresponding to an actual exponent value E in the range -1022 to +1023. With the hidden
bit implied to be ‘1’ (for normalized numbers), the value of the number is interpreted as follows:
where E is the unbiased exponent and 1.fraction is the mantissa (or significand) consisting of a
leading ‘1’ (the hidden bit) and a fractional part (fraction field). The maximum positive normalized
number (pmax) is represented by the encoding 0x7FEF_FFFF_FFFF_FFFF which is
approximately 1.8E+307 ( ), and the minimum positive normalized value (pmin) is
represented by the encoding 0x0010_0000_0000_0000, approximately 2.2E-308 ( )
Biased exponent values 0 and 2047 are reserved for encoding special values of +0, -0, +infinity,
-infinity, and NaNs.
Zeros of both positive and negative sign are represented by a biased exponent value e of zero and
a fraction f which is zero.
Infinities of both positive and negative sign are represented by a maximum exponent field value
(2047) and a fraction which is zero.
Denormalized numbers of both positive and negative sign are represented by a biased exponent
value e of 0 and a fraction f, which is non-zero. For these numbers, the hidden bit is defined by the
IEEE 754 standard to be ‘0’. This number type is not directly supported in hardware. Instead,
either a software interrupt handler is invoked, or a default value is defined.
Double-precision not-a-Numbers (NaNs) are represented by a maximum exponent field value
(2047) and a fraction f which is non-zero.
fraction
0
exp
6311
s
112
Hidden bit
Double-precision
s—sign bit; 0 = positive; 1 = negative
exp—biased exponent field
fraction—fractional portion of number
1–()
s
2
E
× 1.fraction()×
2
2
102
–
 Loading...
Loading...