Interrupts and Exceptions
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 5-23
write-through-required location may either cause an alignment or data storage interrupt or may
correctly execute the instruction. For all other cases listed above, an implementation may execute
the instruction correctly instead of causing an alignment interrupt. For dcbz, correct execution
means clearing each byte of the block in main memory.
NOTE
Book E does not support use of a misaligned effective address by load
and reserve and store conditional instructions. If a misaligned
effective address is specified, the alignment interrupt handler should
treat the instruction as a programming error and must not attempt to
emulate the instruction.
When an alignment interrupt occurs, the processor suppresses the execution of the instruction
causing the alignment exception.
SRR0, SRR1, MSR, DEAR, and ESR are updated as shown in Table 5-16.
Instruction execution resumes at address IVPR[32–47] || IVOR5[48–59] || 0b0000.
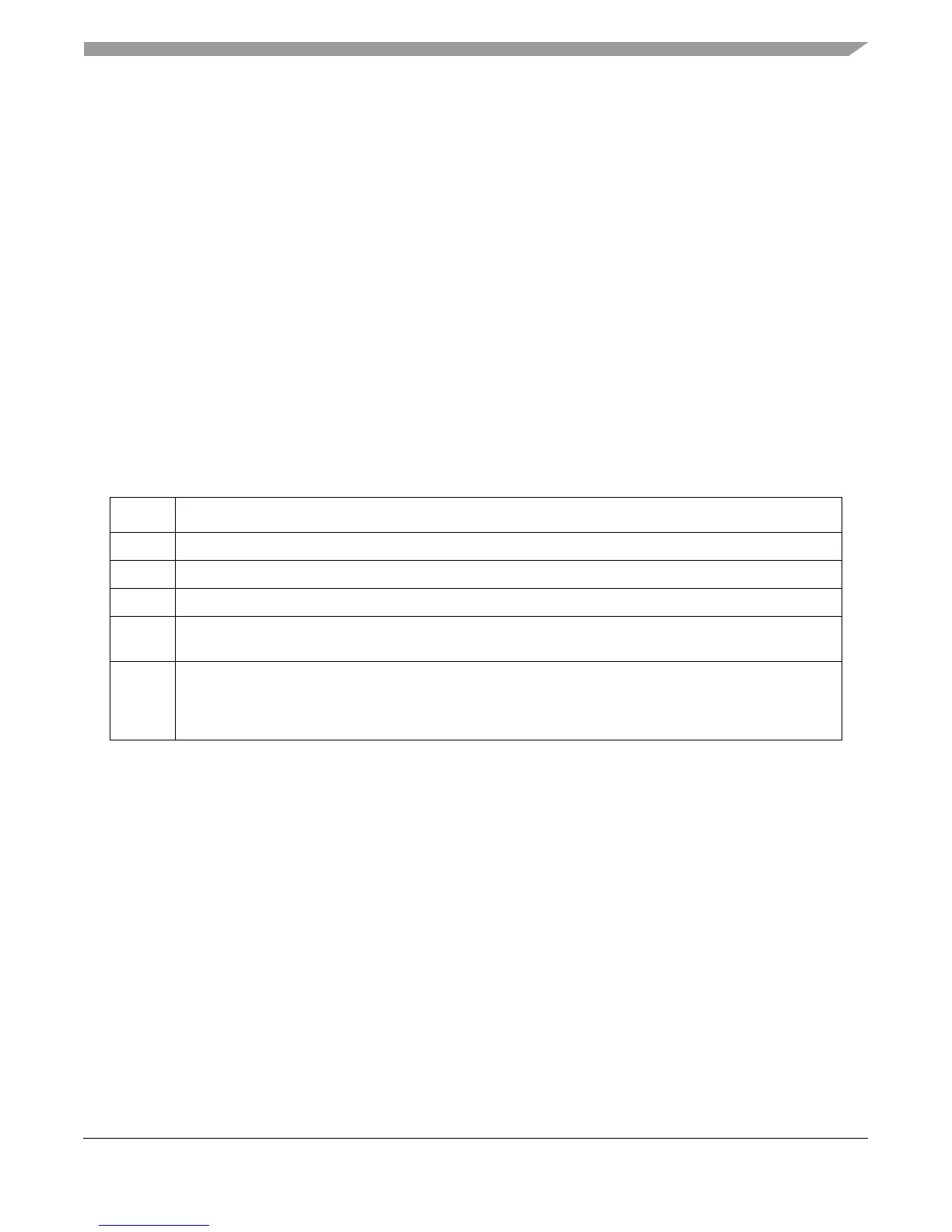
Table 5-16. Alignment Interrupt Register Settings
Register Setting
SRR0 Set to the effective address of the instruction causing the alignment interrupt
SRR1 Set to the MSR contents at the time of the interrupt
MSR CE, ME, and DE are unchanged. All other MSR bits are cleared.
DEAR Set to the EA of a byte that is both within the range of the bytes being accessed by the memory access or
cache management instruction, and within the page whose access caused the alignment exception
ESR The following bits may be affected for vector alignment exception conditions:
SPE Set
ST Set only if the instruction causing the exception is a store and is cleared for a load
All other defined ESR bits are cleared.
 Loading...
Loading...