Core Complex Overview
PowerPC e500 Core Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 1-23
Each interrupt has an associated interrupt vector address, obtained by concatenating the IVPR value
with the address index in the associated IVOR (that is, IVPR[32–47] || IVORn[48–59] || 0b0000).
The resulting address is that of the instruction to be executed when that interrupt occurs. IVPR and
IVOR values are indeterminate on reset, and must be initialized by the system software using
mtspr. Table 1-7 lists IVOR registers implemented on the e500 and the associated interrupts. For
more information, see Chapter 5, “Interrupts and Exceptions.”
Machine Check Interrupt Registers
MCSRR0 Machine check save/restore register 0—Used to store the address of the instruction that will execute after
an rfmci instruction is executed.
MCSRR1 Machine check save/restore register 1—Holds machine state on machine check interrupts and restores
machine state (if recoverable) after an rfmci instruction is executed.
MCAR Machine check address register—Holds the address of the data or instruction that caused the machine
check interrupt. MCAR contents are not meaningful if a signal triggered the machine check interrupt.
Syndrome Registers
MCSR Machine check syndrome register—Holds machine state information on machine check interrupts and
restores machine state after an rfmci instruction is executed.
ESR Exception syndrome register—Provides a syndrome to differentiate between the different kinds of
exceptions that generate the same interrupt type. Upon generation of a specific exception type, the
associated bit is set and all other bits are cleared.
SPE APU Interrupt Registers
SPEFSCR Signal processing and embedded floating-point status and control register—Provides interrupt control and
status as well as various condition bits associated with the operations performed by the SPE APU.
Other Interrupt Registers
DEAR Data exception address register—Holds the address that was referenced by a load, store, or cache
management instruction that caused an alignment, data TLB miss, or data storage interrupt.
IVPR
IVORs
Together, IVPR[32–47] || IVOR
n
[48–59] || 0b0000 define the address of an interrupt-processing routine.
See Table 1 -7 and the EREF for more information.
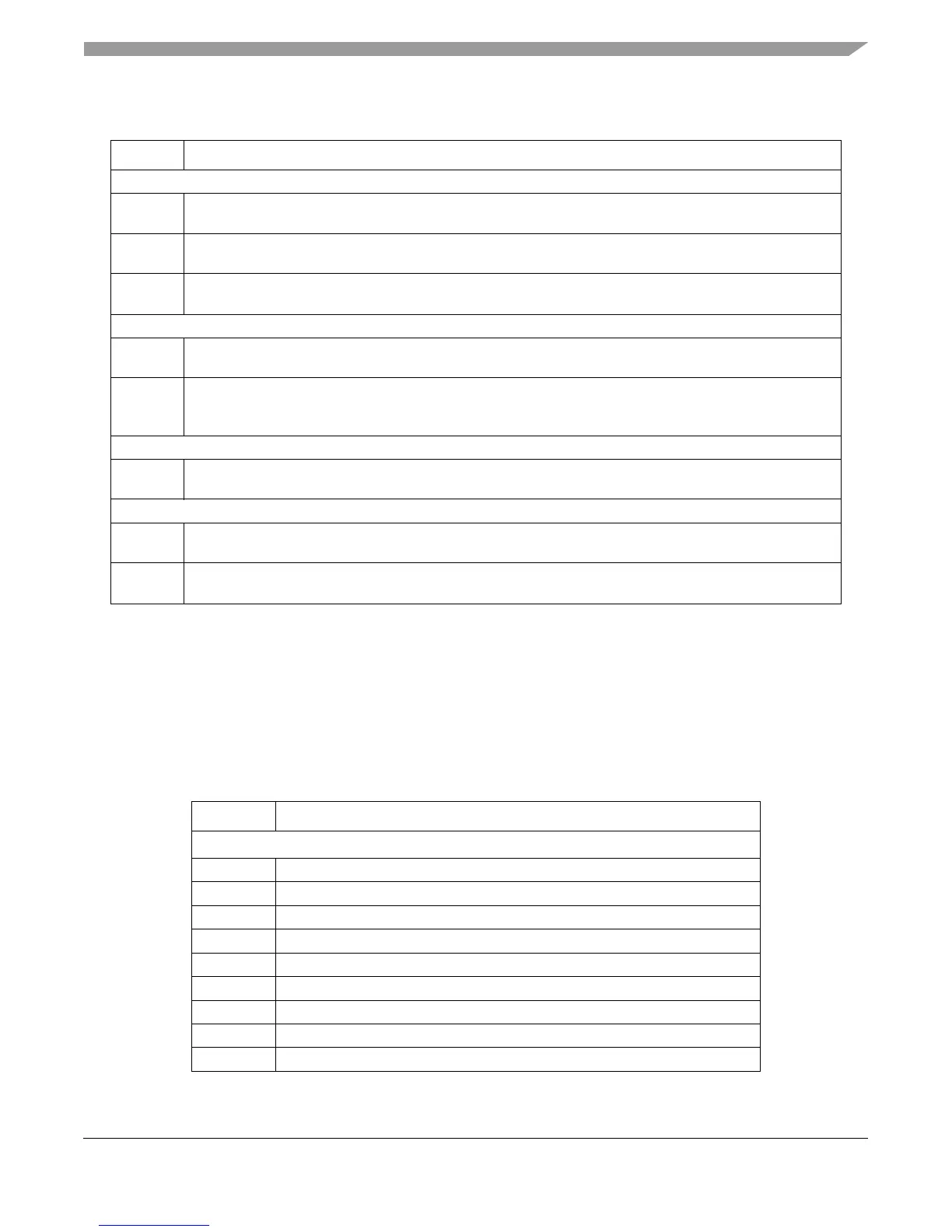
Table 1-7. Interrupt Vector Registers and Exception Conditions
Register Interrupt
Book E–Defined IVORs
IVOR0 Critical input
IVOR1 Machine check interrupt offset
IVOR2 Data storage interrupt offset
IVOR3 Instruction storage interrupt offset
IVOR4 External input interrupt offset
IVOR5 Alignment interrupt offset
IVOR6 Program interrupt offset
IVOR7 Floating-point unavailable interrupt offset (not supported on the e500)
IVOR8 System call interrupt offset
Table 1-6. Interrupt Registers (continued)
Register Description
 Loading...
Loading...