PROGRAM > AL-1: OSC/Pitch 4–2: OSC Sub
147
4–2: OSC Sub
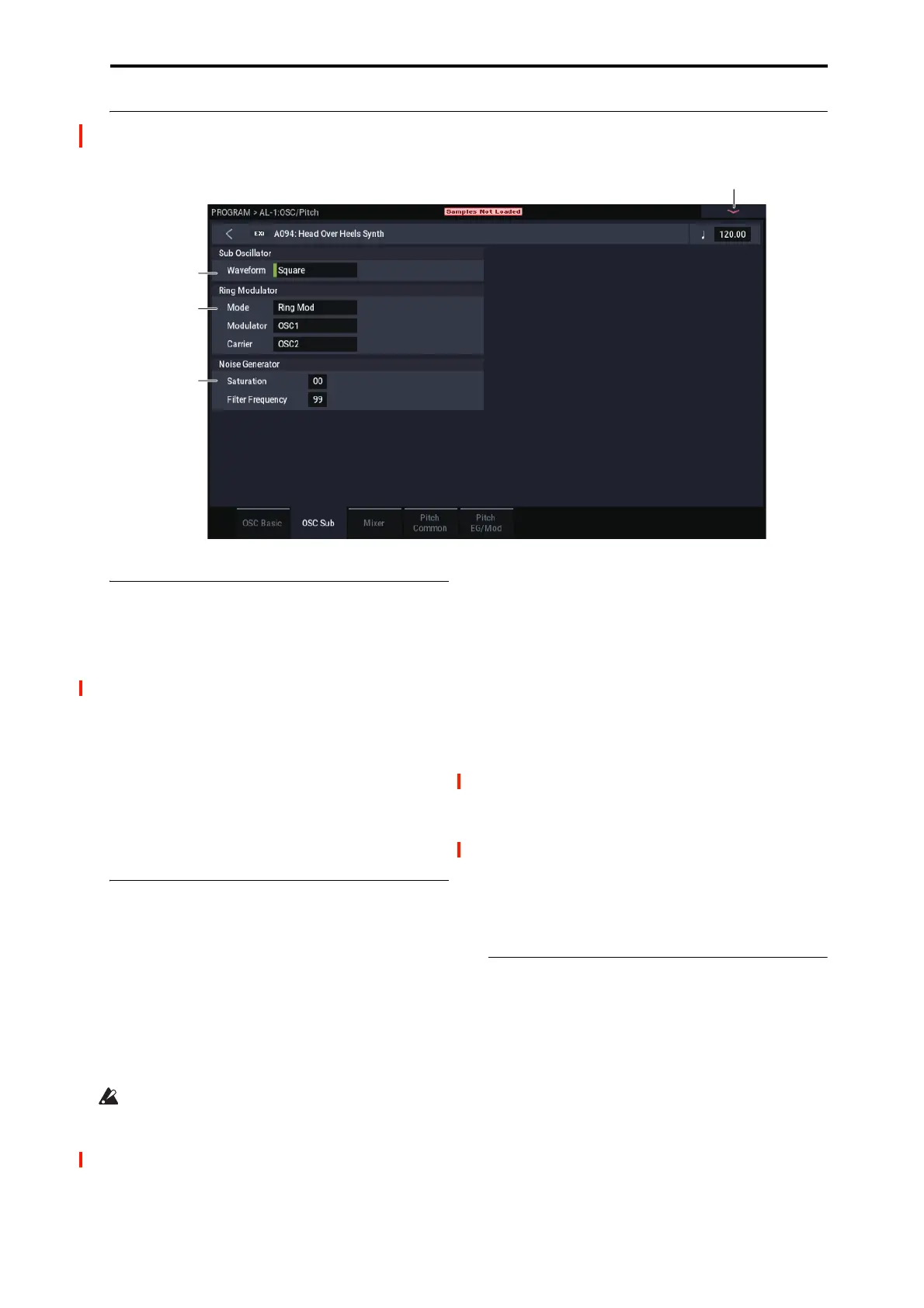
4–2a: Sub Oscillator
The Sub Oscillator plays exactly one octave below
Oscillator 1. All Oscillator 1 pitch mod effects the Sub
Oscillator as well.
Waveform [Square, Triangle]
This selects the basic waveform of the Sub-Oscillator. The
Triangle waveform’s amplitude is three times that of the
square, to compensate for the difference in perceived
loudness. This means that similar Level settings at the mixer
result in similar amounts of “boom.”
Note that this is different from Oscillator 1’s Triangle wave.
In Oscillator 1, the Triangle amplitude is the same as that of
the other waveforms, resulting in a lower perceived volume
(just like on classic analog synths).
4–2b: Ring Modulator
The Ring Modulator has its own input to the Mixer section.
The default volume is 0, so to hear it, you’ll need to turn it
up!
When the frequencies of the Carrier and the Modulator are
the same, the Ring Modulator produces steady, constant
waveforms. When the two are detuned, it produces more
movement and overtones.
Note that FM, Sync, and Ring Mod can all be used
simultaneously.
Even though the oscillators themselves have extremely
low aliasing, Ring Mod can produce aliasing - especially
at higher frequencies.
Mode [Ring Mod, AM, Rectify, Clip]
This selects between four different variations of ring
modulation.
Ring Mod produces the traditional ring modulation effect.
AM includes both the traditional ring modulation effect and
the dry signal of the Carrier input.
Rectify means that any negative parts of the Modulator’s
waveform are flipped around to be positive instead. If the
Modulator is a square wave, this mode sounds pretty much
like just listening to the Carrier alone.
Clipped means that the Modulator input is clipped to
positive values before going into the Ring Mod; any
negative parts of the waveform are chopped off and thrown
away.
Modulator [OSC 1, Noise]
This selects the modulator source for the Ring Modulator.
Rectify and Clip, above, both affect the Modulator signal.
Carrier [OSC 2, Ext Input]
Selects the carrier source for the ring modulator.
Ext Input uses the audio input selected under Sub
OSC/Audio Input, on the Mixer page. For more information,
see “4–3c: Sub OSC/Audio Input” on page 149.
4–2c: Noise Generator
The noise generator includes Saturation, for creating unique
and chaotic noise effects, and a dedicated 1-pole filter to
control noise color.
For standard white noise, set the Saturation to 0, and the
Filter Frequency to 99.
For colored noise (such as pink noise), set the Saturation to
0, and reduce the Filter Frequency as desired.
To create “speckled noise” such as rocket sounds and
thunder, set Saturation to 99, and Filter Frequency to 10.
To create key contact noise (such as you might find on
vintage analog synths), create speckled noise as described
above, and then use a fast EG to control its volume in the
mixer.
 Loading...
Loading...