EXi: STR-1 Plucked String
234
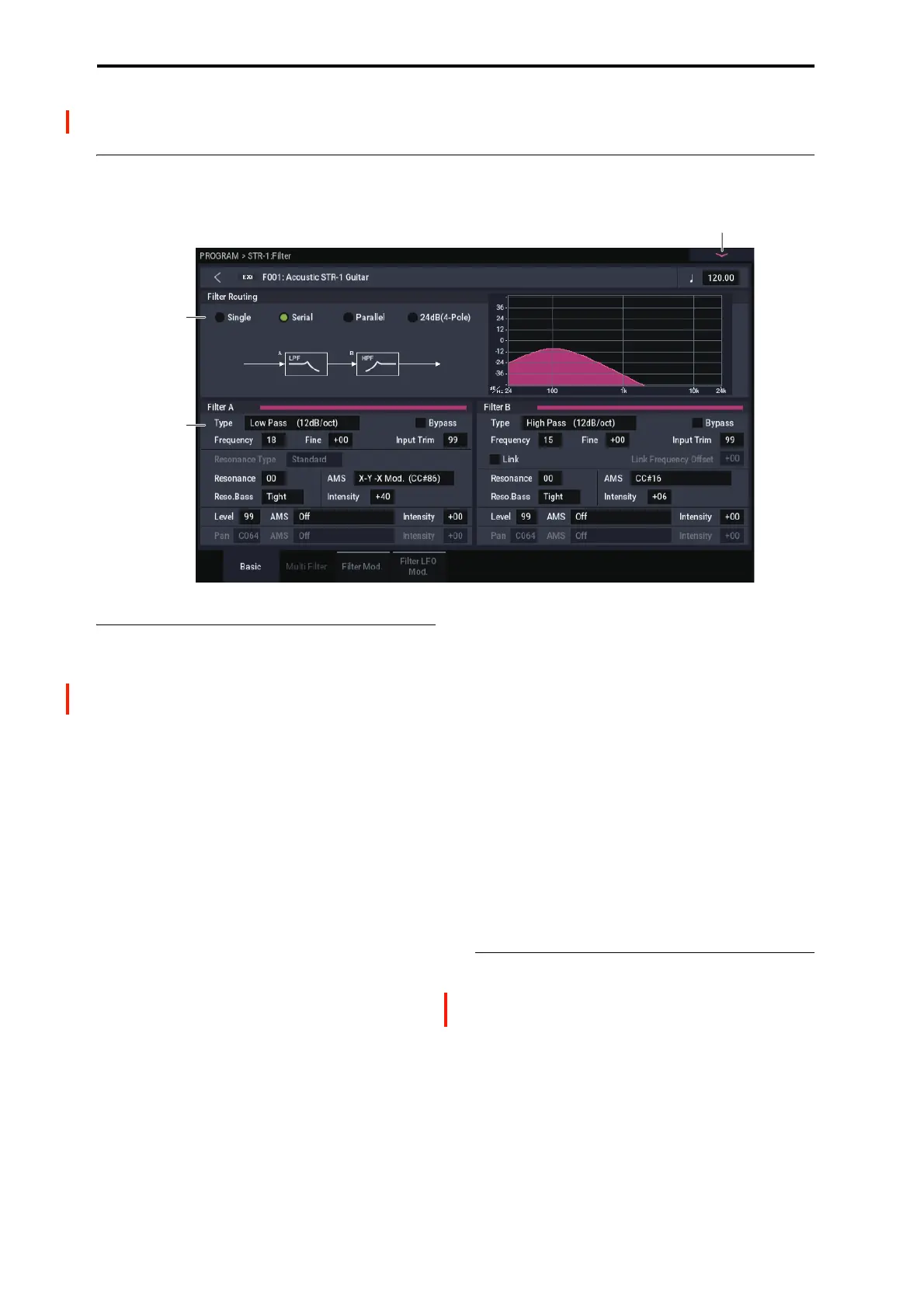
PROGRAM > STR-1: Filter
5–1: Basic
Interaction between the filters and the
mixer
When the Filter Routing is set to either Single or 24dB (4-
Pole), the routing from the String section into the Filter
section is fairly simple. There’s only a single filter, and that
filter processes the entire sound.
Things can get more interesting when the Filter Routing is
set to Serial or Parallel. In these modes, The Mixer page’s
Balance parameters let you separately control the filter
routing for each of the five inputs: the String, the PCM
Oscillator, the Noise Generator, Pickup1, and Pickup2.
When an input’s Balance is set to 0, it goes into Filter A.
(Note that if the Filter Routing is set to Serial, the signal
will also pass through Filter B.)
If the input’s Balance is set to 99, it goes directly into Filter
B, regardless of whether the routing is set to Serial or
Parallel.
Standard serial configuration
To create a standard serial filter configuration:
1. Set the Filter Routing to Serial.
This connects the output of Filter A to the input of Filter B.
2. Set all of the mixer’s Balance controls to 0.
This makes all of the inputs go to Filter A first, and then
through Filter B.
Standard parallel configuration
To create a standard parallel filter configuration:
1. Set the Filter Routing to Parallel.
2. Set all of the mixer’s Balance controls to 50.
This routes all of the inputs to both filters, at equal volumes.
Dual signal paths
You can also send the String through Filter A, and the PCM
Oscillator through Filter B (or vice-versa), to create a
layered sound. For instance:
1. Set the Filter Routing to Parallel.
2. Set the String’s Balance to 0.
This routes the String to Filter A.
3. Set the PCM Oscillator’s Balance to 99.
This routes the PCM Oscillator to Filter B.
Anywhere in-between
If an input’s Balance is set between 1 and 98, it will go to a
combination of both filters–so that many “in between” filter
effects are available.
Finally, by modulating an input’s Balance via AMS, you can
crossfade between routing through Filter A and Filter B.
5–1a: Routing
Filter Routing
[Single, Serial, Parallel, 24dB (4-Pole)]
There are two filters, Filter A and Filter B. This parameter
controls whether one or both of the filters are used, and if
both are used, it controls how they are connected to each
other.
Single. This uses only Filter A as a single 2-pole,
12dB/octave filter (6dB for Band Pass and Band Reject).
When this option is selected, the controls for Filter B will be
grayed out.
Serial. This uses both filters. The output of Filter A is
processed through Filter B.

 Loading...
Loading...