PROGRAM > Basic/X-Y/Controllers 1–5: X-Y Control
43
Each of the four directions of the Vector can send a different
CC, including left (–X), right (+X), up (+Y), and down (–Y).
You can choose between several different patterns
combining these four directions by using the X-Y X Mode
and X-Y Y Mode parameters.
You can either use the X-Y CCs to automate existing
modulation routings, such as the X-Y-panel knobs, or as
distinct modulation sources. The X-Y CC is transmitted as
MIDI control change messages on the global MIDI channel.
This means that it controls all voices of the program, not
individual voices.
Note: A Global parameter allows you to enable or disable
MIDI output for the CC Control. By default, this is disabled.
This setting does not affect the internal Programs, which can
always receive the X-Y CCs.
Enable CC Control [Off, On]
When this box is checked, the X-Y position will control the
CCs assigned to +X, –X, +Y, and –Y, as set below.
When this box is not checked, the X-Y position will not
affect these CCs. However, the joystick will still send and
receive its dedicated MIDI CCs, just like other physical
controllers. See “Vector and MIDI,” above, for more
information.
X-Y X Mode [Positive, Negative, Xfade, Split]
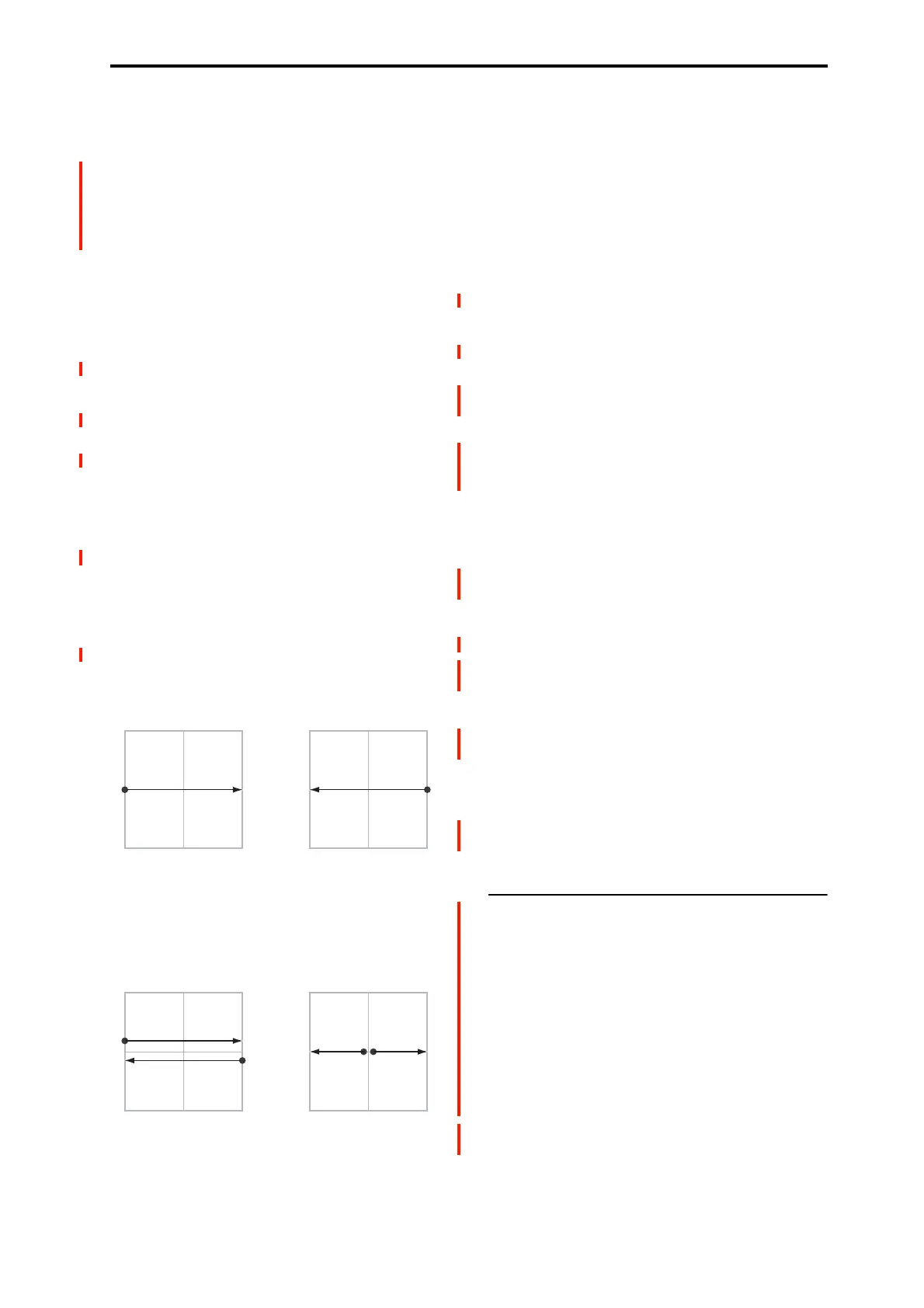
You can set up the Vector to send out CCs in several
different patterns, as shown in the graphic below. This
controls the pattern for the X axis. Note that this setting
affects only CC Control; it has no effect on Volume Control.
X-Y CC Modes
Positive sends out only +X, starting at 0 at the far left, and
increasing to 127 at the far right. –X is disabled in this mode.
Negative sends out only –X, starting at 0 at the far left, and
increasing to 127 at the far right. In this mode, +X is grayed
out.
Xfade sends out both +X and –X, overlapping throughout
the X axis. As one increases, the other decreases.
Split sends out both +X and –X, with a split in the center. +X
is sent when the point moves to the right of the center, and –
X is sent when the point moves to the left of center.
+X [Off…MIDI CC#119]
This assigns the controller sent by the +X X-Y. You can use
this as an AMS source to control Program parameters, or as a
DMod source to control Effects parameters. It will be grayed
out if the X-Y X Mode, above, is set to Negative.
In addition to the standard list of MIDI controllers, you can
also assign the +X X-Y to duplicate the function of several
front-panel controllers, including JS X, JS+X, JS-X, and SW
1–2.
For instance, if you assign +X to Knob 6, the X-Y’s +X will
use the controller assigned to Knob 6 on the Basic/X-
Y/Controllers– Controllers page.
Finally, you can also assign +X to control the Master
Vo l u m e .
–X [Off…MIDI CC#119]
This assigns the controller sent by the –X X-Y. It will be
grayed out if the X-Y X Mode, above, is set to Positive.
The selections are the same as for +X, above.
X-Y Y Mode [Positive, Negative, Xfade, Split]
This controls the X-Y CC pattern for the Y axis. For more
information, see the description under X-Y X Mode, above.
+Y [Off…MIDI CC#119]
This assigns the controller sent by the +Y X-Y. It will be
grayed out if the X-Y Y Mode, above, is set to Negative.
The selections are the same as for +X, above.
–Y [Off…MIDI CC#119]
This assigns the controller sent by the +Y X-Y. It will be
grayed out if the X-Y Y Mode, above, is set to Positive.
The selections are the same as for +X, above.
1–5c: X-Y Graphic
X-Y Graphic
This is a diagram of the X-Y Control, including the five
points of the X-Y Envelope (labeled 0–4) and the current
position of the X-Y Control (labeled J).
The transitions between the EG’s points are shown by white
lines.
Touch this area to control the vector by moving the X-Y
point.
Show Volume Image [Off, On]
The X-Y Control includes an image representing the current
X-Y Volume Control settings. You can use the Show Volume
Image check-box to toggle this part of the graphic on and
off.
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Positive
+X CC0 127
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Negative
–X CC127 0
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Xfade
+X CC0 127
–X CC0 127
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Split
+X CC
0 127
–X CC
127 0
Generates only +X,
increasing from left to right.
Generates both +X and –X.
One increases as the other
decreases.
Generates both +X and -X.
Both are 0 in the center.
+X increases to the right;
–X increases to the left.
Generates only –X,
increasing from right to left.

 Loading...
Loading...