C
HAPTER
35
| ERPS Commands
– 1109 –
COMMAND USAGE
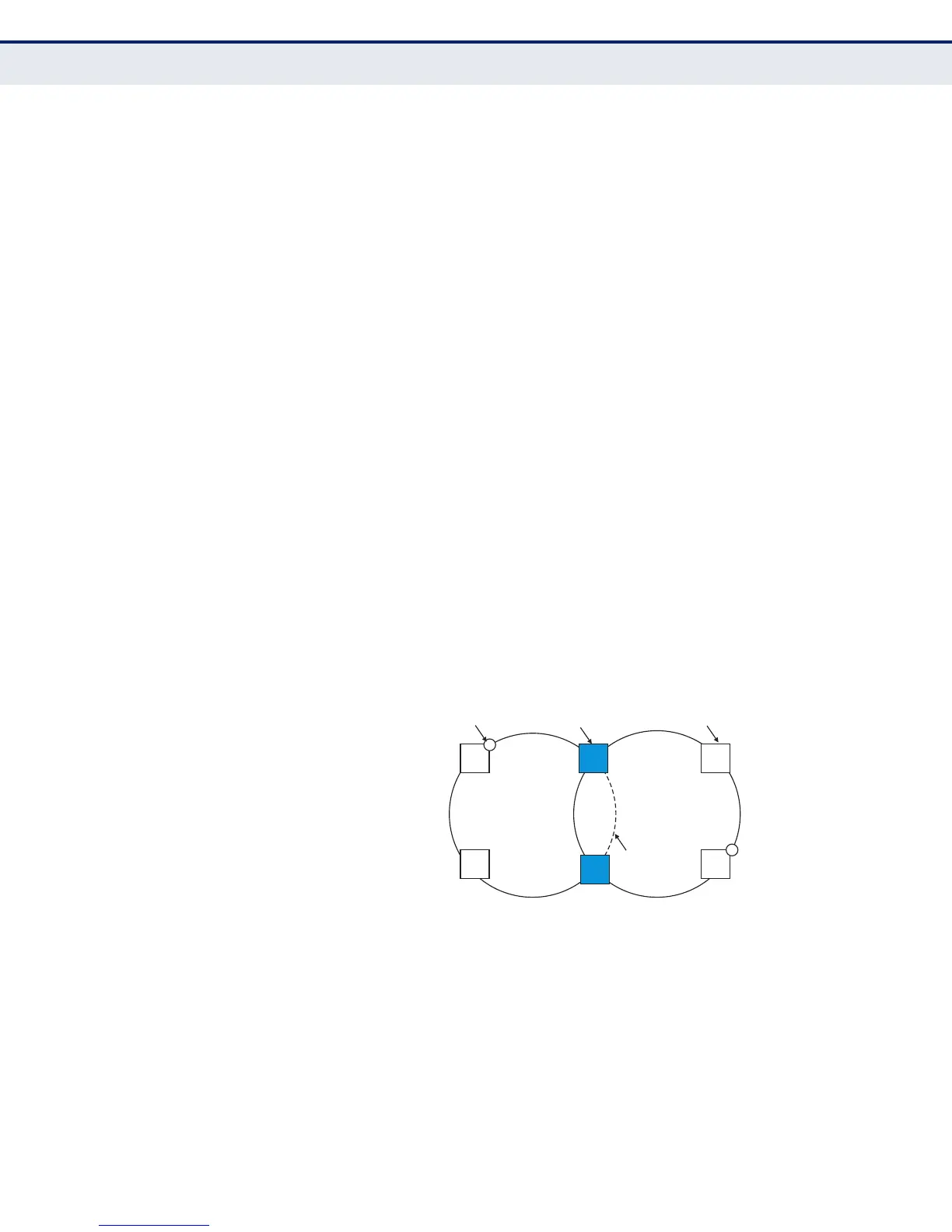
◆ A sub-ring may be attached to a primary ring with or without a virtual
channel. A virtual channel is used to connect two interconnection points
on the sub-ring, tunneling R-APS control messages across an arbitrary
Ethernet network topology. If a virtual channel is not used to cross the
intermediate Ethernet network, data in the traffic channel will still flow
across the network, but the all R-APS messages will be terminated at
the interconnection points.
◆ Sub-ring with R-APS Virtual Channel – When using a virtual channel to
tunnel R-APS messages between interconnection points on a sub-ring,
the R-APS virtual channel may or may not follow the same path as the
traffic channel over the network. R-APS messages that are forwarded
over the sub-ring’s virtual channel are broadcast or multicast over the
interconnected network. For this reason the broadcast/multicast
domain of the virtual channel should be limited to the necessary links
and nodes. For example, the virtual channel could span only the
interconnecting rings or sub-rings that are necessary for forwarding
R-APS messages of this sub-ring. Care must also be taken to ensure
that the local RAPS messages of the sub-ring being transported over
the virtual channel into the interconnected network can be uniquely
distinguished from those of other interconnected ring R-APS messages.
This can be achieved by, for example, by using separate VIDs for the
virtual channels of different sub-rings.
Note that the R-APS virtual channel requires a certain amount of
bandwidth to forward R-APS messages on the interconnected Ethernet
network where a sub-ring is attached. Also note that the protection
switching time of the sub-ring may be affected if R-APS messages
traverse a long distance over an R-APS virtual channel.
Figure 416: Sub-ring with Virtual Channel
◆ Sub-ring without R-APS Virtual Channel – Under certain circumstances
it may not be desirable to use a virtual channel to interconnect the sub-
ring over an arbitrary Ethernet network. In this situation, the R-APS
messages are terminated on the interconnection points. Since the sub-
ring does not provide an R-APS channel nor R-APS virtual channel
beyond the interconnection points, R-APS channel blocking is not
employed on the normal ring links to avoid channel segmentation. As a
result, a failure at any ring link in the sub-ring will cause the R-APS
channel of the sub-ring to be segmented, thus preventing R-APS
message exchange between some of the sub-ring’s ring nodes.
Sub-ring
with Virtual
Channel
Virtual
Channel
RPL Port
Interconnection Node
Ring Node
Major Ring
 Loading...
Loading...











