Concepts and Features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
111User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 55
●
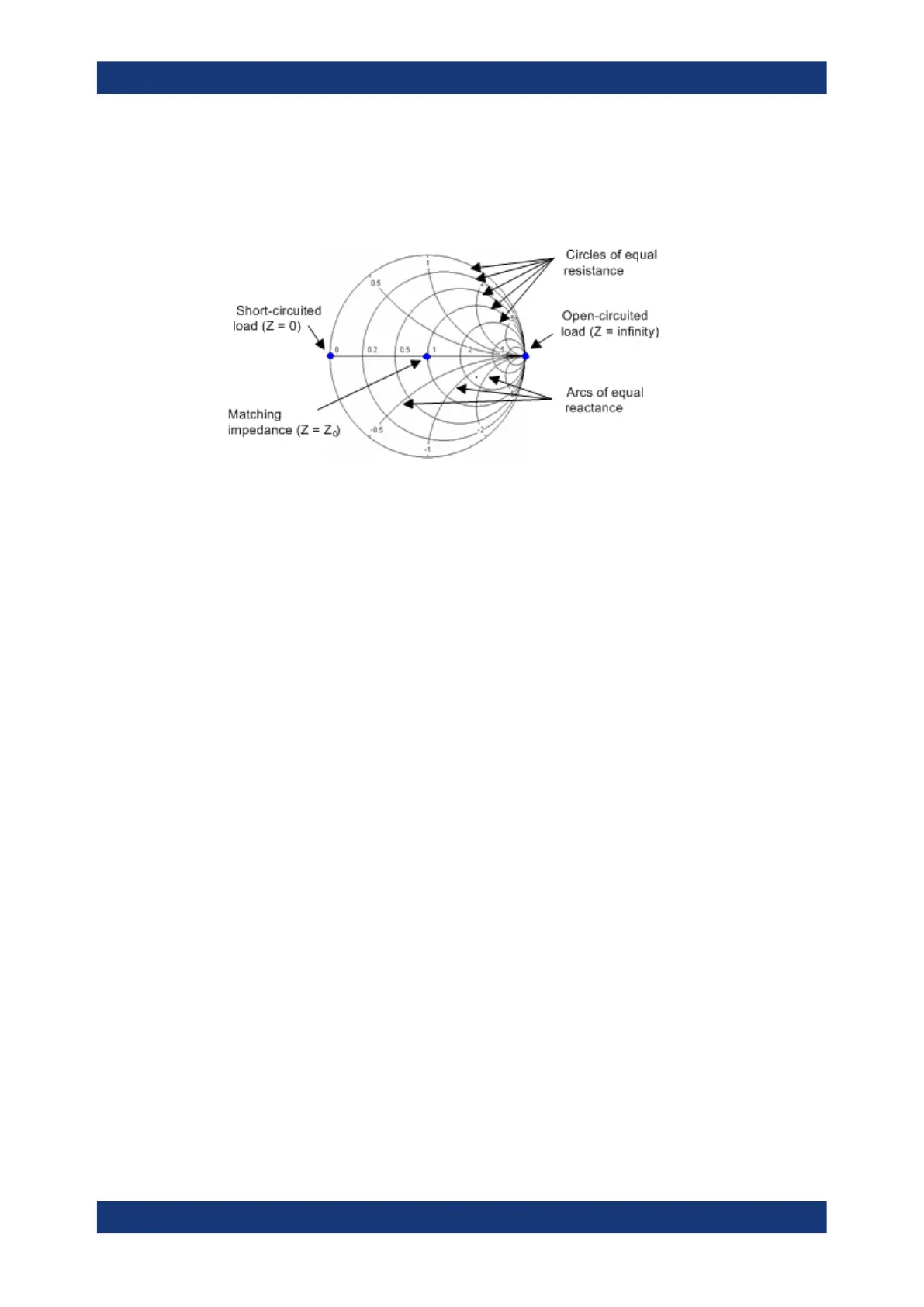
The circles for the points of equal resistance are centered on the real axis and
intersect at Z = infinity. The arcs for the points of equal reactance also belong to
circles intersecting at Z = infinity (open circuit point (1, 0)), centered on a straight
vertical line.
Examples for special points in the Smith chart:
●
The magnitude of the reflection coefficient of an open circuit (Z = infinity, I = 0) is
one, its phase is zero.
●
The magnitude of the reflection coefficient of a short circuit (Z = 0, U = 0) is one, its
phase is –180 deg.
Inv Smith
For "Inv Smith" formatted traces, the response values are interpreted as complex
reflection coefficients S
ii
and represented in terms of their corresponding complex
admittance Y(S
ii
) = G(S
ii
) + j B(S
ii
).
In a diagram, the grid lines overlaid to a "Smith" trace correspond to points of equal
conductance G and susceptance B:
●
Points with the same conductance are located on circles.
●
Points with the same susceptance produce arcs.
The following example shows an inverted Smith chart with a marker used to display the
stimulus value, the complex admittance Y = G + j B and the equivalent inductance L.
Screen Elements

 Loading...
Loading...