Concepts and Features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
128User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 55
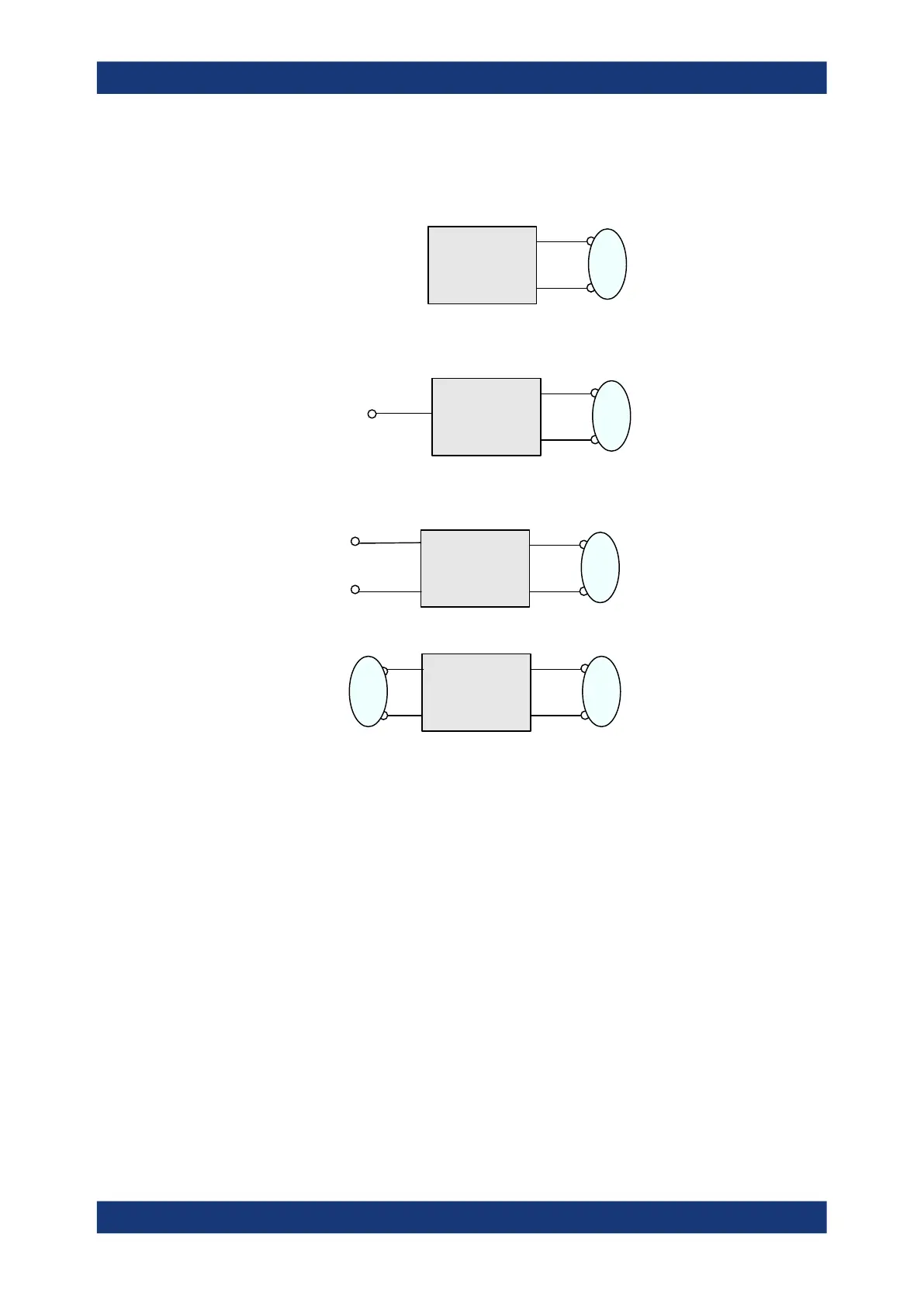
Example:
2 physical ports: Reflection measurements on 1 balanced port
Bal.
port
Differential mode
Z
ref
= Z
0d
Common mode
Z
ref
= Z
0c
DUT
Balanced port:
Log.
VNA
port
3 physical ports: Reflection and transmission measurements on 1 balanced port
Bal.
port
Differential mode
Z
ref
= Z
0d
Common mode
Z
ref
= Z
0c
DUT
Balanced port:
Log.
VNA
port
Single
ended
port
Single-ended
(unbalanced) port
Z
ref
= Z
connector
4 physical ports: Reflection and transmission measurements on 1 or 2 balanced ports
Bal.
port
Differential mode
Z
ref
= Z
0d
Common mode
Z
ref
= Z
0c
DUT
Balanced port:
Log.
VNA
port
Single
ended
ports
Single-ended
(unbalanced) ports
Z
ref1
= Z
connector1
Z
ref2
= Z
connector2
Bal.
port
Differential mode
Z
ref
= Z
0d
Common mode
Z
ref
= Z
0c
DUT
Balanced port:
Log.
VNA
port
Bal.
port
Differential mode
Z
ref
= Z
0d
Common mode
Z
ref
= Z
0c
Balanced port:
Log.
VNA
port
A balanced port configuration is defined in two steps: First, select the pairs of physical
ports that you want to combine to form balanced ports. Second, define the two refer-
ence impedances for the differential and common mode at each balanced port. Both
steps can be done in a single "Balanced Ports" dialog. The most commonly used bal-
anced port configurations and impedances are predefined and can be selected in the
"S-Parameter Wizard".
Depending on the test setup, the analyzer provides different types of mixed mode
parameters; refer to the following sections for details.
5.3.6.2 Mixed Mode Parameters
Mixed mode parameters are an extension of normal mode parameters (e.g. S-parame-
ters, impedances and admittances) for balanced measurements. The analyzer can
measure mixed mode parameters once a balanced port configuration is selected.
Mixed mode parameters are used to distinguish the following three port modes:
●
s: Single-ended (for unbalanced ports)
●
d: Differential mode (for balanced ports)
Measurement Results

 Loading...
Loading...