Concepts and Features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
173User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 55
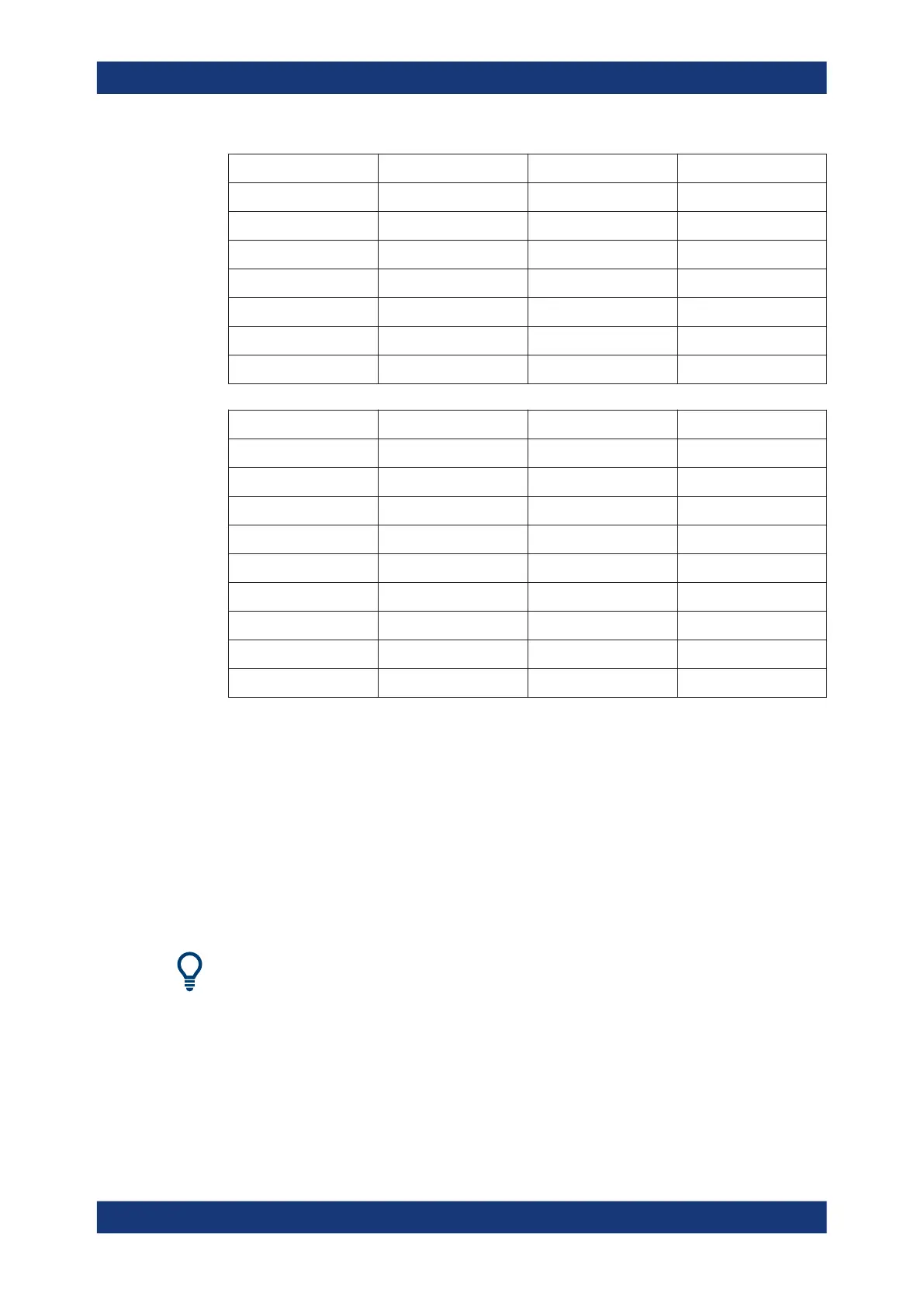
Test Port Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Assignment 3
3 Cal Unit Port 3 - -
4 Cal Unit Port 4 - -
5 - Cal Unit Port 2 -
6 - Cal Unit Port 3 -
7 - Cal Unit Port 4 -
8 - - Cal Unit Port 2
9 - - Cal Unit Port 3
Table 5-12: Full n-port: Line-shaped optimum solution
Test Port Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Assignment 3
1 Cal Unit Port 1 - -
2 Cal Unit Port 2 - -
3 Cal Unit Port 3 - -
4 Cal Unit Port 4 Cal Unit Port 4 -
5 - Cal Unit Port 1 -
6 - Cal Unit Port 2 -
7 - Cal Unit Port 3 Cal Unit Port 3
8 - - Cal Unit Port 1
9 - - Cal Unit Port 2
5.5.6 Scalar Power Calibration
The purpose of a scalar power calibration is to ensure accurate source power levels
and power readings at a particular position (calibration plane) in the test setup. Scalar
power calibration is different from the system error correction described in Chapter 5.5,
"Calibration", on page 147.
A power calibration is required for accurate measurement of wave quantities or ratios
(see section Chapter 5.1.5, "Data Flow", on page 89). For best accuracy, choose a cali-
bration method according to the table below.
Calibration of S-parameters
S-parameters are not affected by a scalar power calibration. S-parameters are ratios of
incident and outgoing waves: for linear DUTs, they do not depend on the absolute
power. For measurements on non-linear DUTs, a SMARTerCal is recommended.
A SMARTerCal is also appropriate for frequency conversion measurements. For
detailed information, refer to Chapter 5.5.7, "SMARTerCal", on page 179.
Calibration

 Loading...
Loading...