Concepts and Features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
179User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 55
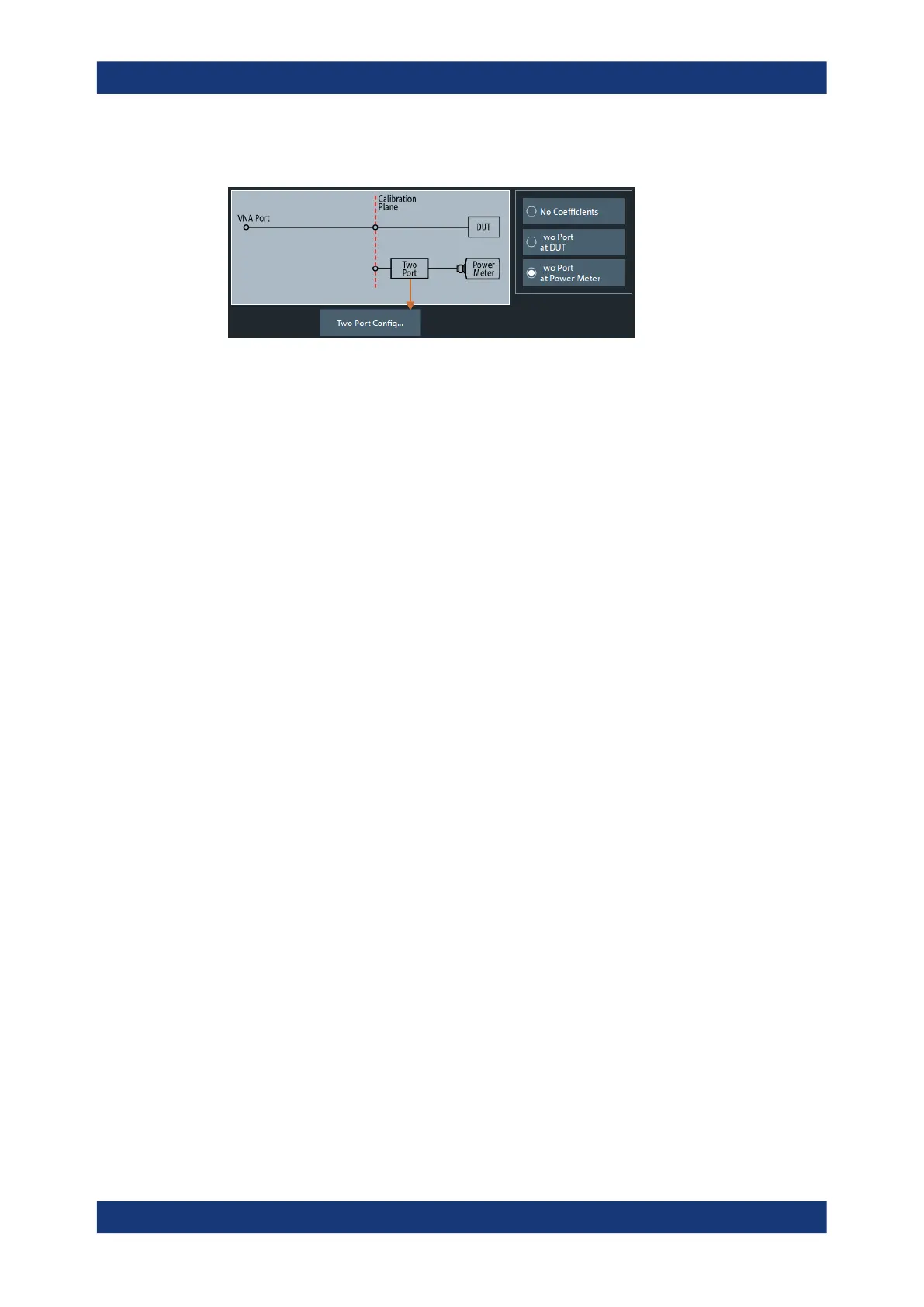
B: Two-port at power meter (during calibration)
Test and measurement procedure:
1. Perform the calibration with the additional two-port between the analyzer port and
the power sensor. During the calibration, the analyzer increases the power sensor
values by the 2-port transmission coefficients to move the calibration plane of the
power calibration towards the input of the DUT. The calibration plane corresponds
to the input of the additional 2-port.
2. Perform the measurement without the additional two-port.
Practical example: An adapter or attenuator with known attenuation is needed to con-
nect the power sensor to the test port of the network analyzer. The transmission coeffi-
cients of the adapter are used for the power meter correction.
5.5.7 SMARTerCal
A SMARTerCal (smarter calibration) is a combination of a full n-port system error cor-
rection (TOSM, UOSM, Adapter Removal, TRL, TNA ...) for two or more ports with a
(scalar) receiver power calibration at a single port. The two calibration methods serve
different purposes:
●
The system error correction requires a set of calibration standards; it provides vec-
tor error-corrected S-parameters. For equal port frequencies, the n-port calibration
types provide the full set of error terms. For frequency conversion measurements,
a source match correction and (optional) load match correction is calculated.
●
The receiver power calibration requires an external power meter; it corrects the
power readings of the reference and measurement receivers according to the mea-
sured absolute power at the calibration plane. This does not include a readjust-
ment of the actual source power (flatness calibration).
Example: Channel base power: –10 dBm; the test setup involves a 3-dB attenua-
tion between the source port and the calibration plane. After the power calibration
is applied, the analyzer indicates an output power (a-wave) of –13 dBm, although
the actual source power remains at –10 dBm.
The SMARTerCal is also applied to ratios and wave quantities. For measurements on
linear DUTs, SMARTerCal is sufficient. Non-linear measurements can be further
improved by a combination of a SMARTerCal plus a scalar power calibration. See
Combining SMARTerCal with Scalar Power Calibration.
Calibration

 Loading...
Loading...