Concepts and Features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
122User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 55
DUT
VNA
1 2
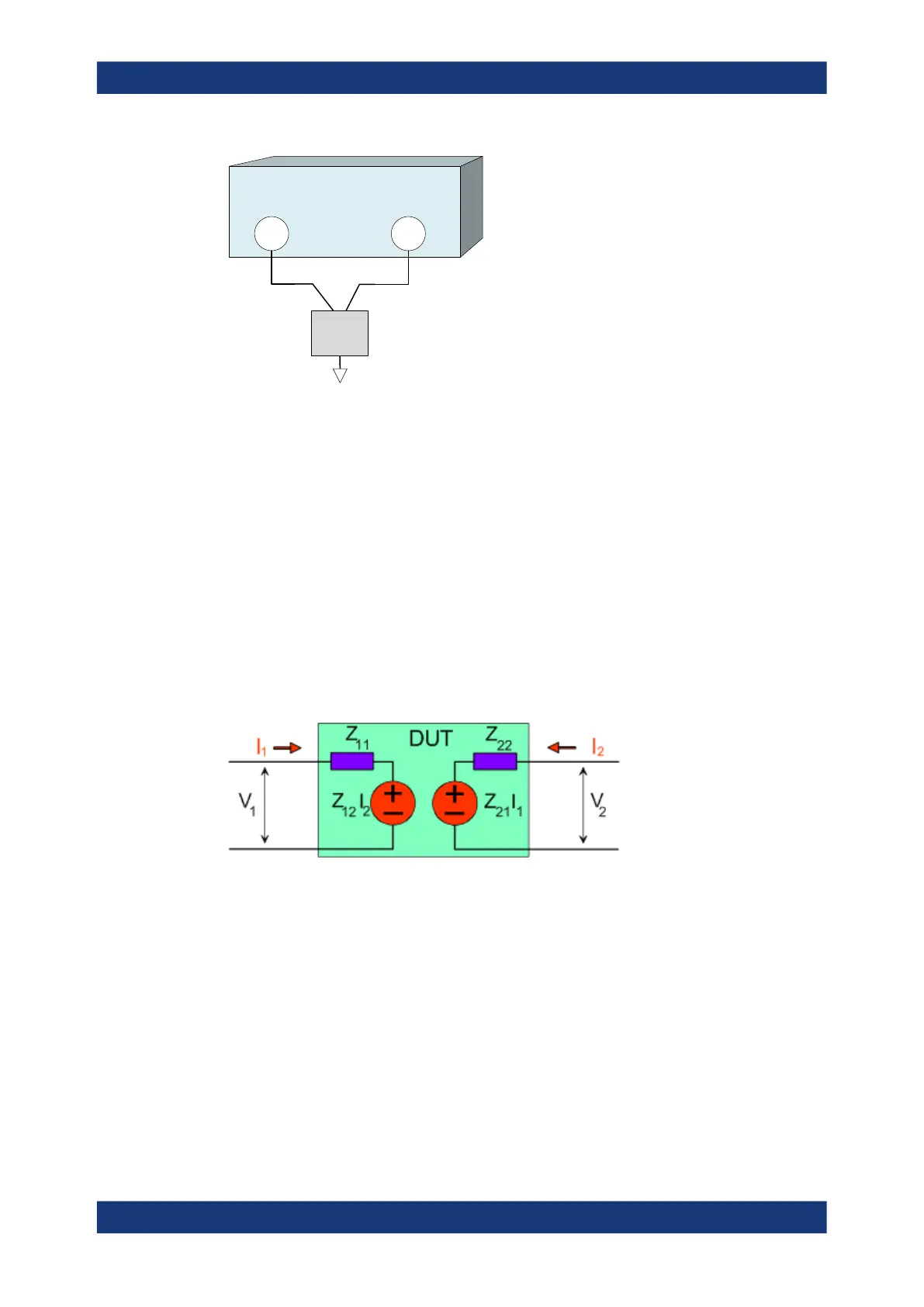
5.3.3.2 Z-Parameters
The Z-parameters describe the impedances of a DUT with open output ports (impe-
dance = 0). The analyzer provides the full set of Z-parameters including the transfer
impedances (i.e. the complete nxn Z-matrix for an n port DUT).
This means that Z-parameters can be used as an alternative to S-parameters (or Y-
parameters) to characterize a linear n-port network completely.
2-Port Z-Parameters
In analogy to S-parameters, Z-parameters are expressed as Z
ij
, where i denotes the
measured and j the stimulated port.
The Z-parameters for a two-port are based on a circuit model that can be expressed
with two linear equations:
2221212
2121111
IZIZV
IZIZV
Meaning of Z-parameters
The four 2-port Z-parameters can be interpreted as follows:
●
Z
11
is the input impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
1
to the current I
1
,
measured at port 1 (forward measurement with open output, I
2
= 0).
●
Z
21
is the forward transfer impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
2
to the
current I
1
(forward measurement with open output, I
2
= 0).
●
Z
12
is the reverse transfer impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
1
to the
current I
2
(reverse measurement with open input, I
1
= 0).
Measurement Results

 Loading...
Loading...