System Arbitration
Élan™SC520 Microcontroller User’s Manual 8-15
■ Clock #4: The cpu_hlda signal is deasserted by the Am5
x
86 CPU to take ownership of
the CPU bus, and cpu_ads
is asserted to begin a cycle to PCI.
■ Clock #5: The CPU bus arbiter samples cpu_ads asserted and rearbitrates. In this
example, a higher priority master is requesting the bus, so cpu_hold is asserted to the
Am5
x
86 CPU. The Am5
x
86 CPU maintains ownership of the CPU bus until it completes
its cycle and asserts cpu_hlda.
■ Clock #9: The host bridge asserts its req to the PCI bus arbiter in response to the Am5
x
86
CPU bus cycle to PCI.
■ Clock #10: The PCI bus arbiter asserts gnt to the host bridge. The assertion of gnt would
be delayed if the bus was not idle or if another higher priority master was requesting the
PCI bus.
■ Clock #11: The host bridge samples gnt asserted and begins the PCI transaction.
■ Clock #17: The PCI transaction is complete and the host bridge returns cpu_rdy to the
Am5
x
86 CPU ending the Am5
x
86 CPU-to-PCI cycle.
■ Clock #18: The Am5
x
86 CPU samples cpu_rdy asserted ending the current cycle and
asserts cpu_hlda to allow the next CPU bus master access to the CPU bus.
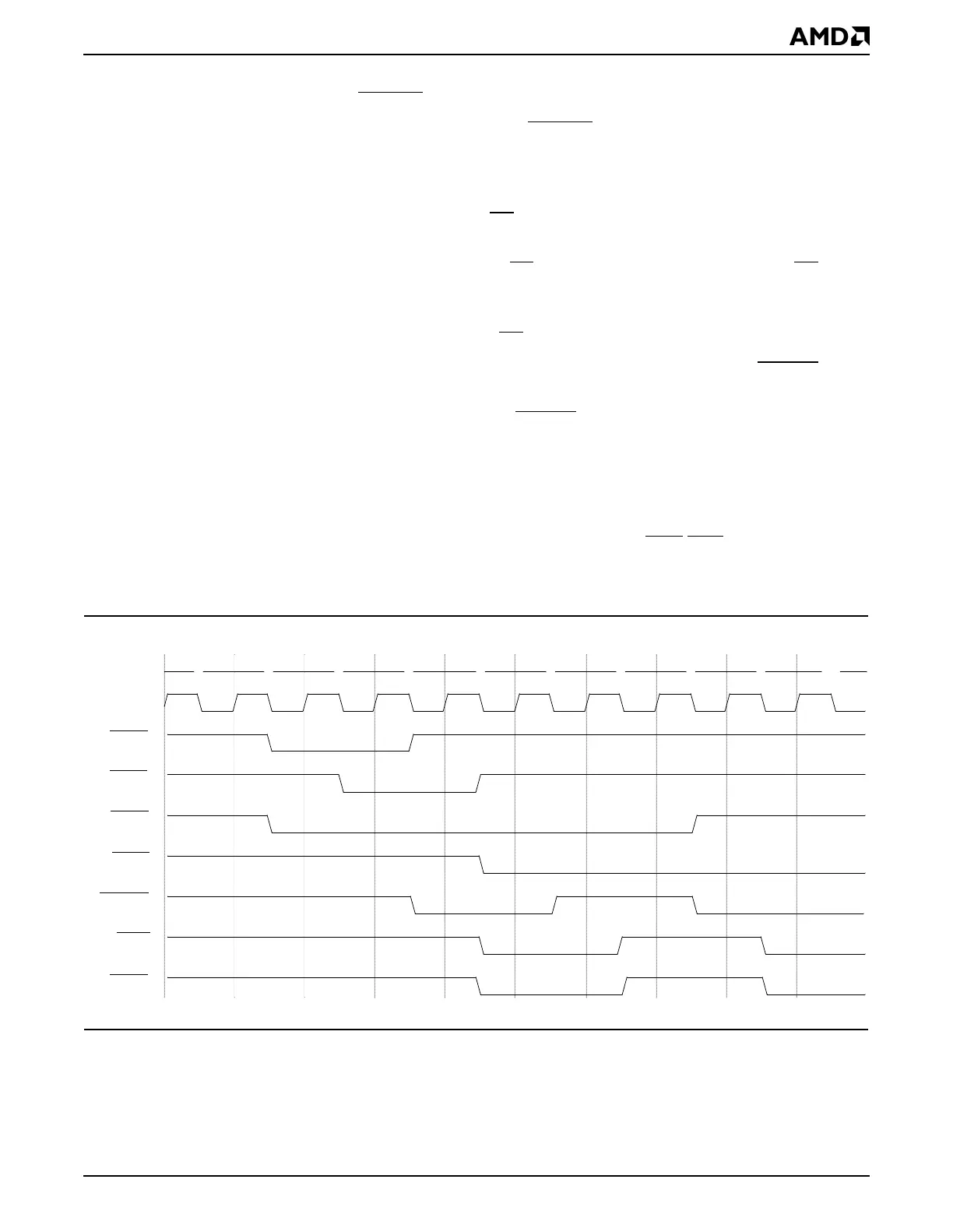
8.4.4.4 PCI Bus Arbitration
Figure 8-9 shows how the PCI bus arbiter arbitrates between two masters. Although there
are only two PCI masters in this example, the mechanism is the same when there are more
PCI masters. The differences are that there would be more REQ
/GNT signal pairs and
more than one PCI bus transaction could take place before an individual PCI master is
granted the bus.
Figure 8-9 PCI Bus Arbitration
The following sequence annotates the PCI bus arbitration cycle shown in Figure 8-9.
■ Clock #2: Master 0 and master 1 simultaneously request access to the bus.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
CLKPCIIN
REQ0
GNT0
REQ1
GNT1
FRAME
IRDY
TRDY
 Loading...
Loading...