Inter-integrated circuit (I
2
C) interface RM0008
730/1096 Doc ID 13902 Rev 12
Address matched: the interface generates in sequence:
● An acknowledge pulse if the ACK bit is set
● The ADDR bit is set by hardware and an interrupt is generated if the ITEVFEN bit is
set.
● If ENDUAL=1, the software has to read the DUALF bit to check which slave address
has been acknowledged.
In 10-bit mode, after receiving the address sequence the slave is always in Receiver mode.
It will enter Transmitter mode on receiving a repeated Start condition followed by the header
sequence with matching address bits and the least significant bit set (11110xx1).
The TRA bit indicates whether the slave is in Receiver or Transmitter mode.
Slave transmitter
Following the address reception and after clearing ADDR, the slave sends bytes from the
DR register to the SDA line via the internal shift register.
The slave stretches SCL low until ADDR is cleared and DR filled with the data to be sent
(see Figure 270 Transfer sequencing EV1 EV3).
When the acknowledge pulse is received:
● The TxE bit is set by hardware with an interrupt if the ITEVFEN and the ITBUFEN bits
are set.
If TxE is set and some data were not written in the I2C_DR register before the end of the
next data transmission, the BTF bit is set and the interface waits until BTF is cleared by a
read to I2C_SR1 followed by a write to the I2C_DR register, stretching SCL low.
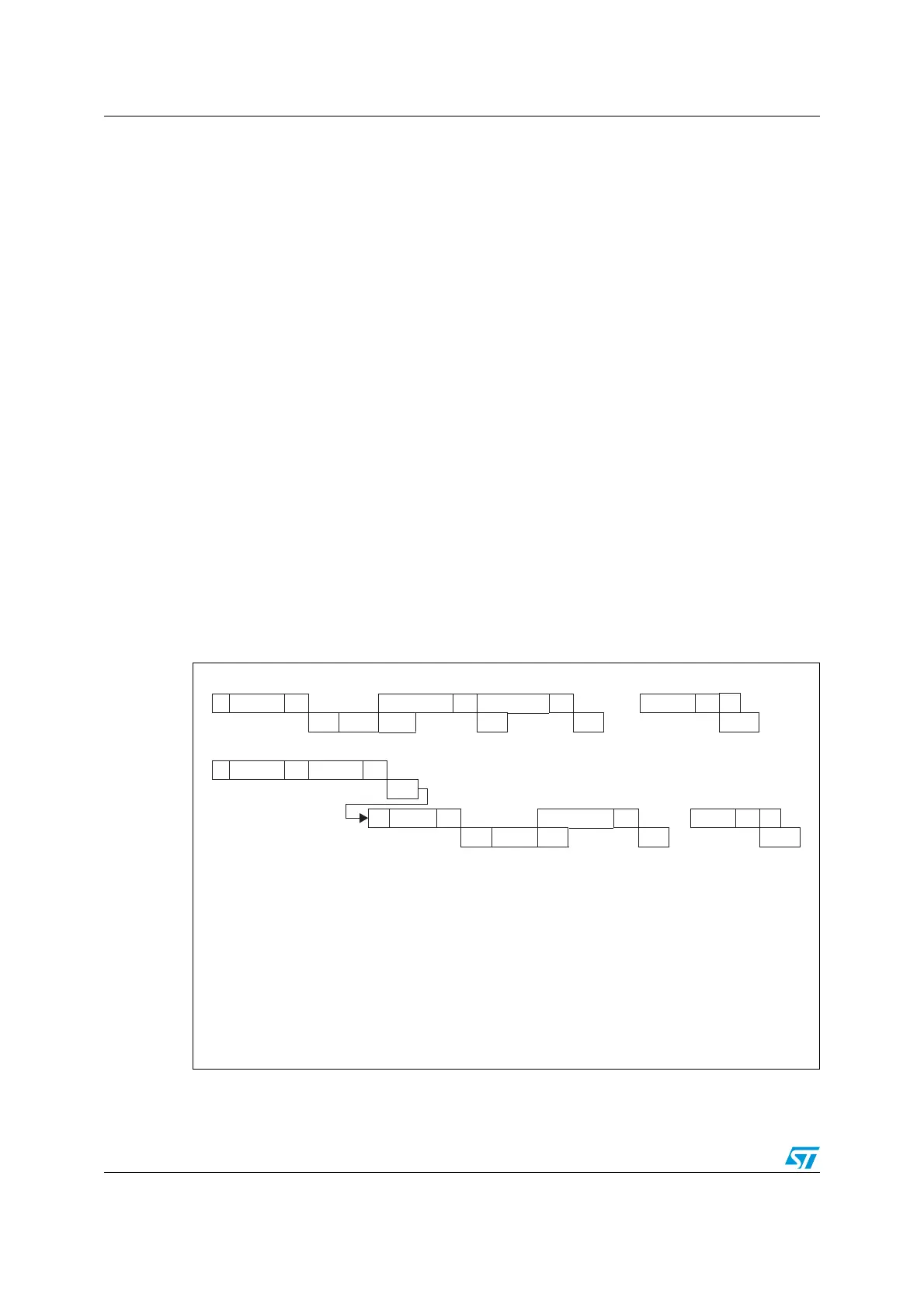
Figure 270. Transfer sequence diagram for slave transmitter
7-bit slave transmitter
10-bit slave transmitter
Legend: S= Start, S
r
= Repeated Start, P= Stop, A= Acknowledge, NA= Non-acknowledge,
EVx= Event (with interrupt if ITEVFEN=1)
EV1: ADDR=1, cleared by reading SR1 followed by reading SR2
EV3-1: TxE=1, shift register empty, data register empty, write Data1 in DR.
EV3: TxE=1, shift register not empty, data register empty, cleared by writing DR
EV3-2: AF=1; AF is cleared by writing ‘0’ in AF bit of SR1 register.
S Address AData1A Data2A
.....
DataNNAP
EV1 EV3-1 EV3 EV3 EV3 EV3-2
S Header A Address A
EV1
S
r
Header A Data1A
....
DataNNA
P
EV1 EV3_1 EV3 EV3 EV3-2
ai15883b
Notes: 1- The EV1 and EV3_1 events stretch SCL low until the end of the corresponding software sequence.
2- The EV3 software sequence must complete before the end of the current byte transfer. In case
the EV3 software sequence can not be managed before the current byte end of transfer,
it is recommended to use BTF instead of TXE with the drawback of slowing the communication.

 Loading...
Loading...