USB on-the-go full-speed (OTG_FS) RM0090
1260/1749 RM0090 Rev 18
34.11.2 Peripheral Tx FIFOs
The core has a dedicated FIFO for each IN endpoint. The application configures FIFO sizes
by writing the non periodic transmit FIFO size register (OTG_FS_TX0FSIZ) for IN endpoint0
and the device IN endpoint transmit FIFOx registers (DIEPTXFx) for IN endpoint-x.
34.12 Host FIFO architecture
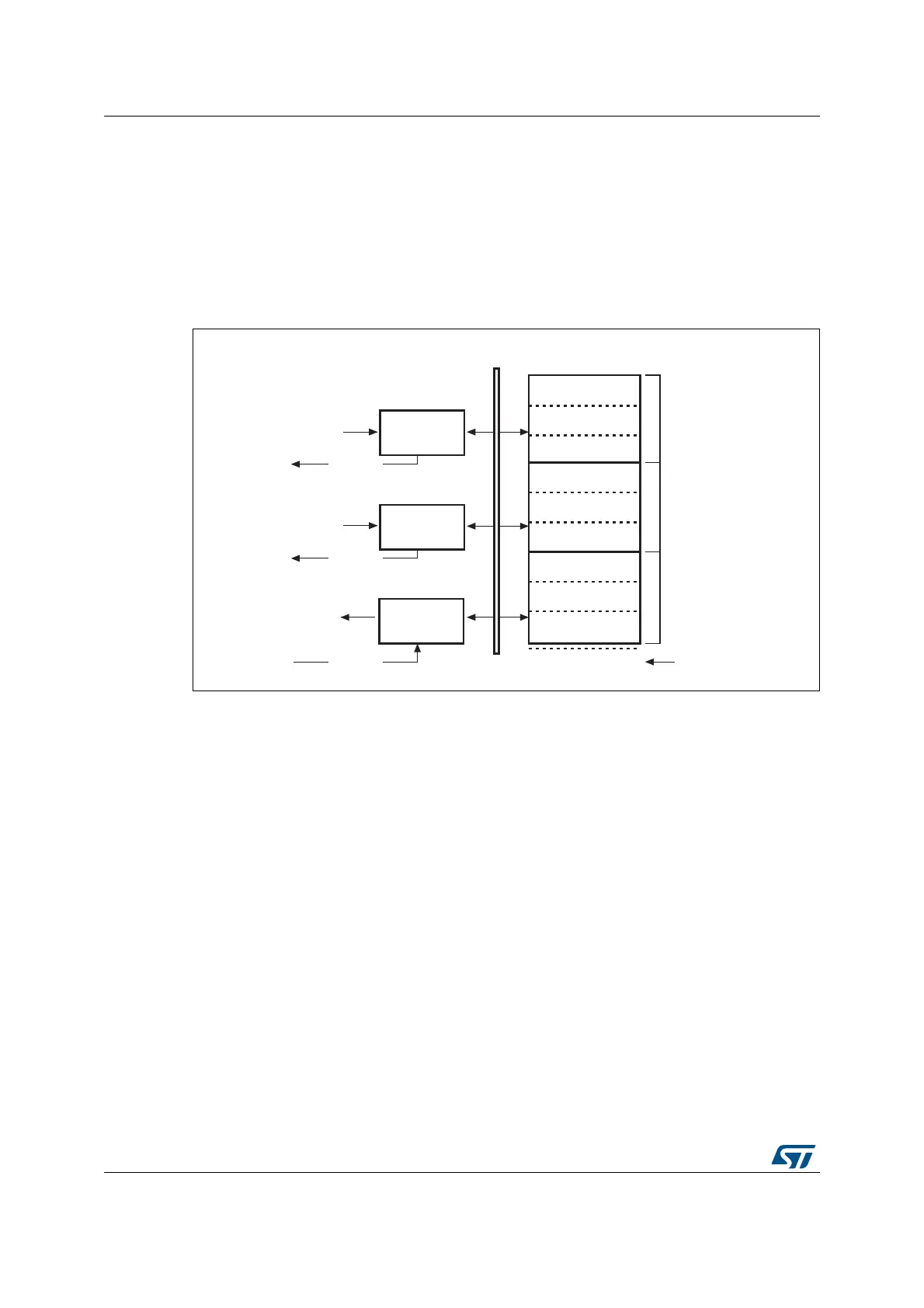
Figure 393. Host-mode FIFO address mapping and AHB FIFO access mapping
34.12.1 Host Rx FIFO
The host uses one receiver FIFO for all periodic and nonperiodic transactions. The FIFO is
used as a receive buffer to hold the received data (payload of the received packet) from the
USB until it is transferred to the system memory. Packets received from any remote IN
endpoint are stacked back-to-back until free space is available. The status of each received
packet with the host channel destination, byte count, data PID and validity of the received
data are also stored into the FIFO. The size of the receive FIFO is configured in the receive
FIFO size register (GRXFSIZ).
The single receive FIFO architecture makes it highly efficient for the USB host to fill in the
receive data buffer:
• All IN configured host channels share the same RAM buffer (shared FIFO)
• The OTG FS core can fill in the receive FIFO up to the limit for any sequence of IN
tokens driven by the host software
The application receives the Rx FIFO not-empty interrupt as long as there is at least one
packet available for download. It reads the packet information from the receive status read
and pop register and finally pops the data off the receive FIFO.
Any periodic channel
DFIFO push access
from AHB
Any channel DFIFO pop
access from AHB
Periodic Tx
FIFO control
(optional)
Non-periodic
Tx FIFO control
Rx FIFO control
Any non-periodic
channel DFIFO push
access from AHB
MAC pop
MAC pop
MAC push
Single data
FIFO
Periodic Tx packets
Periodic Tx packets
Rx packets
HPTXFSIZ[31:16]
HPTXFSIZ[15:0]
NPTXFSIZ[31:16]
NPTXFSIZ[15:0]
RXFSIZ[31:16]
Rx start address
fixed to 0
A1 = 0
ai15610

 Loading...
Loading...