DGS-3630 Series Layer 3 Stackable Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide
294
Parameter Description
Source Network
Enter the source IPv4 network address and mask length here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Show All button to display all the entries.
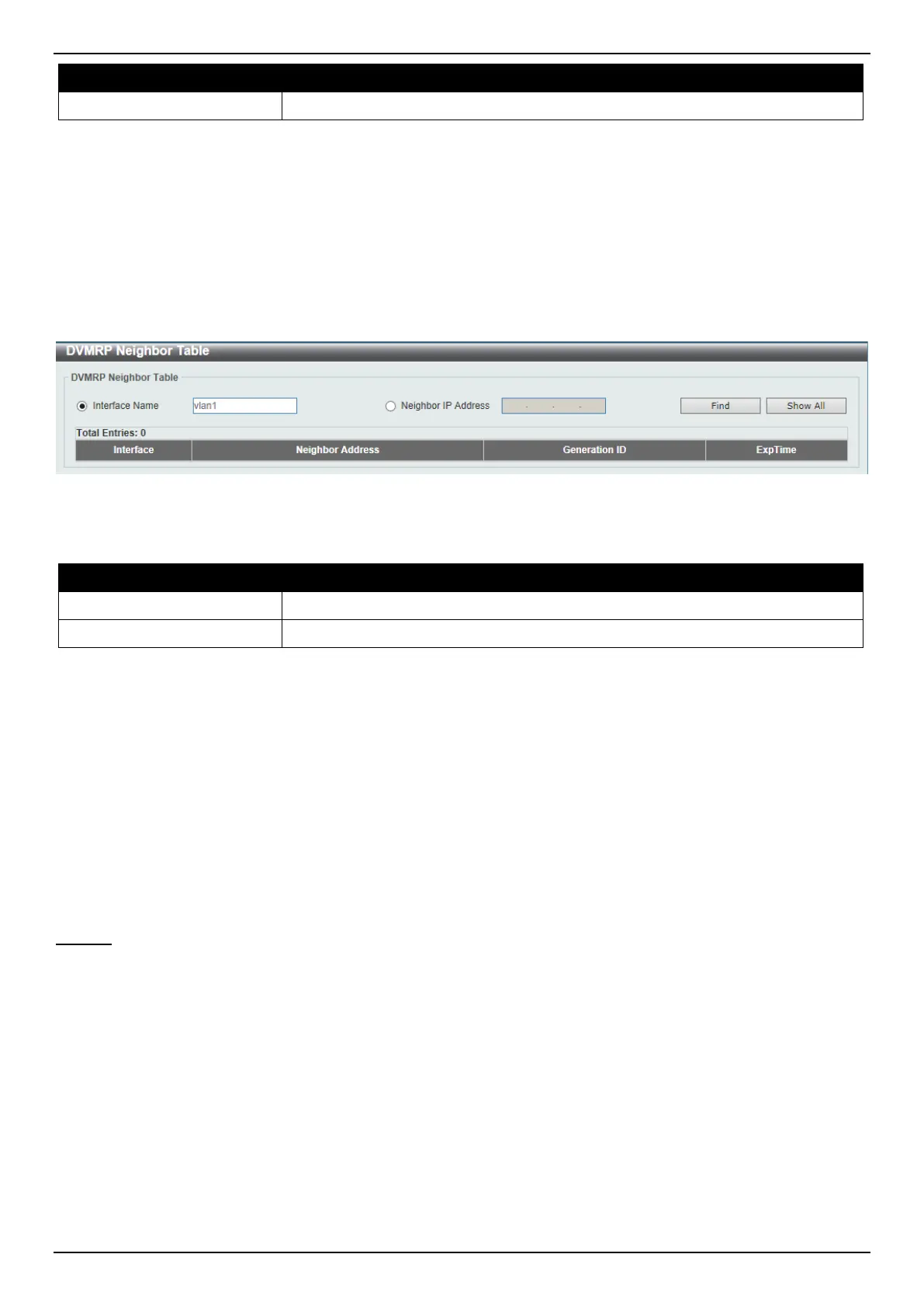
DVMRP Neighbor Table
This window is used to find and display DVMRP neighbor information.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IP Multicast Routing Protocol > DVMRP > DVMRP Neighbor
Table, as shown below:
Figure 6-115 DVMRP Neighbor Table Window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Interface name
Enter the VLAN interface name here.
Neighbor IP Address
Select and enter the IPv4 address of the neighbor here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Show All button to display all the entries.
PIM
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is a family of multicast routing protocols for Internet Protocol (IP) networks that
provide one-to-many and many-to-many distribution of data over a LAN, WAN or the Internet. PIM is protocol-
independent as it does not include its own topology discovery mechanism, but uses routing information supplied by
other routing protocols, such as RIP or OSPF. The Switch supports four types of PIM, Dense Mode (PIM-DM), Sparse
Mode (PIM-SM), PIM Source Specific multicast (PIM-SSM), and Sparse-Dense Mode (PIM-DM-SM).
PIM-SM
Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) is a multicast routing protocol that can use the underlying
unicast routing information base or a separate multicast-capable routing information base. It builds unidirectional
shared trees rooted at a Rendezvous Point (RP) per group, and optionally creates shortest-path trees per source.
Unlike most multicast routing protocols which flood the network with multicast packets, PIM-SM will forward traffic to
routers who are explicitly a part of the multicast group through the use of a Rendezvous Point (RP). This RP will take
all requests from PIM-SM enabled routers, analyze the information and then return multicast information it receives
from the source to requesting routers within its configured network. Through this method, a distribution tree is created,
with the RP as the root. This distribution tree holds all PIM-SM enabled routers within which information collected from
these routers is stored by the RP.
When many routers are a part of a multiple access network, a Designated Router (DR) will be elected. The DR’s
primary function is to send Join/Prune messages to the RP. The router with the highest priority on the LAN will be
selected as the DR. If there is a tie for the highest priority, the router with the higher IP address will be chosen.

 Loading...
Loading...










