Chapter 2 95
Agilent VEE Programming Techniques
General Techniques
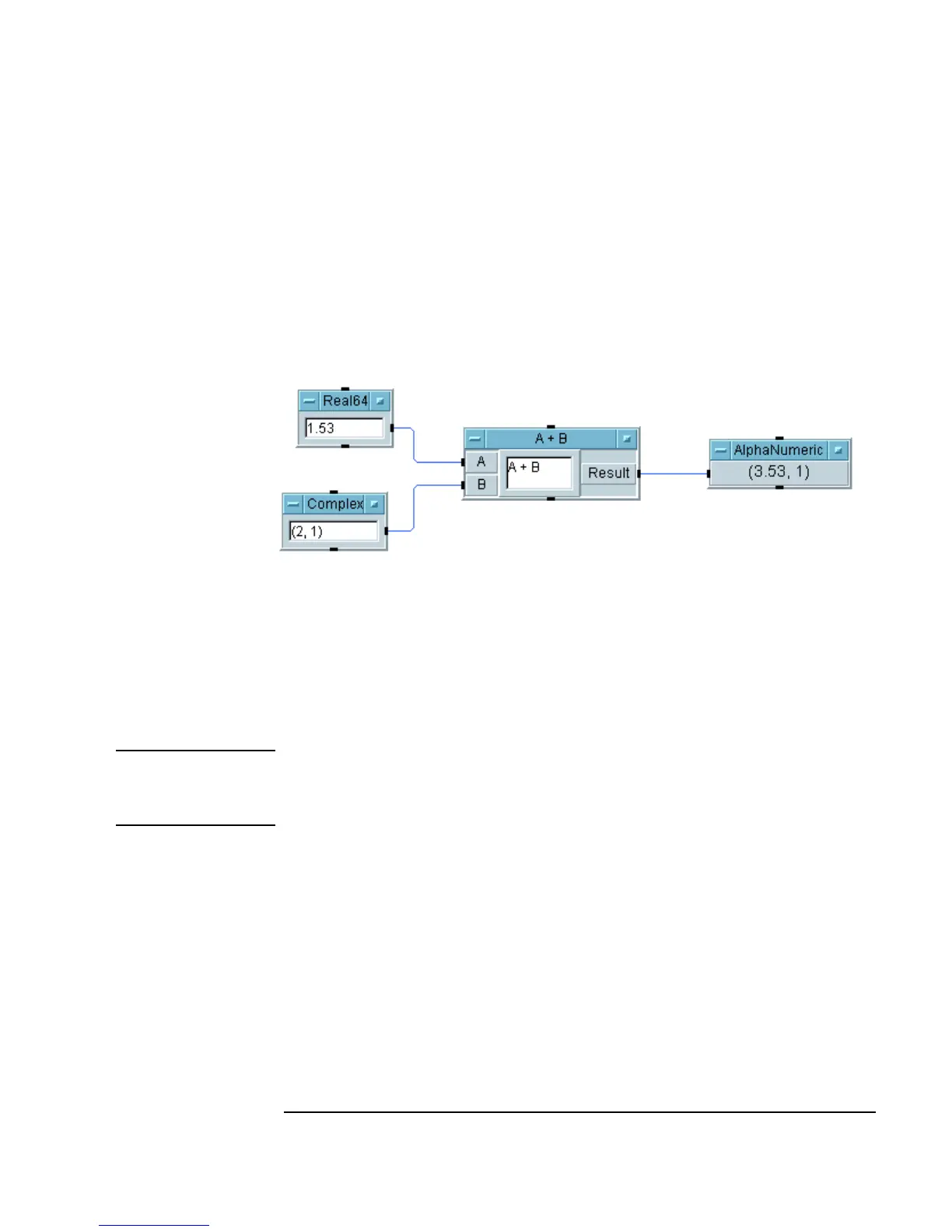
5. Add an AlphaNumeric object by selecting Display ⇒
AlphaNumeric. Connect the objects as shown in Figure 2-15. Type in
the value
1.53 in the data entry field of the Real64 Constant object
and the complex value
(2,1) in the Complex object. Run the program
and you should get the result shown in Figure 2-15.
Figure 2-15. Using Data Types
VEE automatically converts the data as needed and then performs the
addition in the
A+B object. The real value 1.53 is converted to the complex
value
(1.53,0), which is then added to the complex value (2,1). The
result,
(3.53,1) (a complex number), is displayed in the AlphaNumeric
object.
Note Normally, VEE automatically handles all data type conversions. For more
information, select
Help ⇒ Contents and Index from the VEE menu
bar. Then, browse How Do I..., Tell Me About..., or Reference.
Using Data Shapes VEE supports a variety of data shapes, such as scalars and arrays. Unlike
most programming languages, VEE objects can operate on an entire array,
rather than on only one element.
The following program creates a one-dimensional, ten-element array,
calculates the median of the 10 values, and then displays the median value.
1. Select
File ⇒ New to clear the work area.
2. Add a
For Range object, by selecting Flow ⇒ Repeat ⇒ For Range.

 Loading...
Loading...