137
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
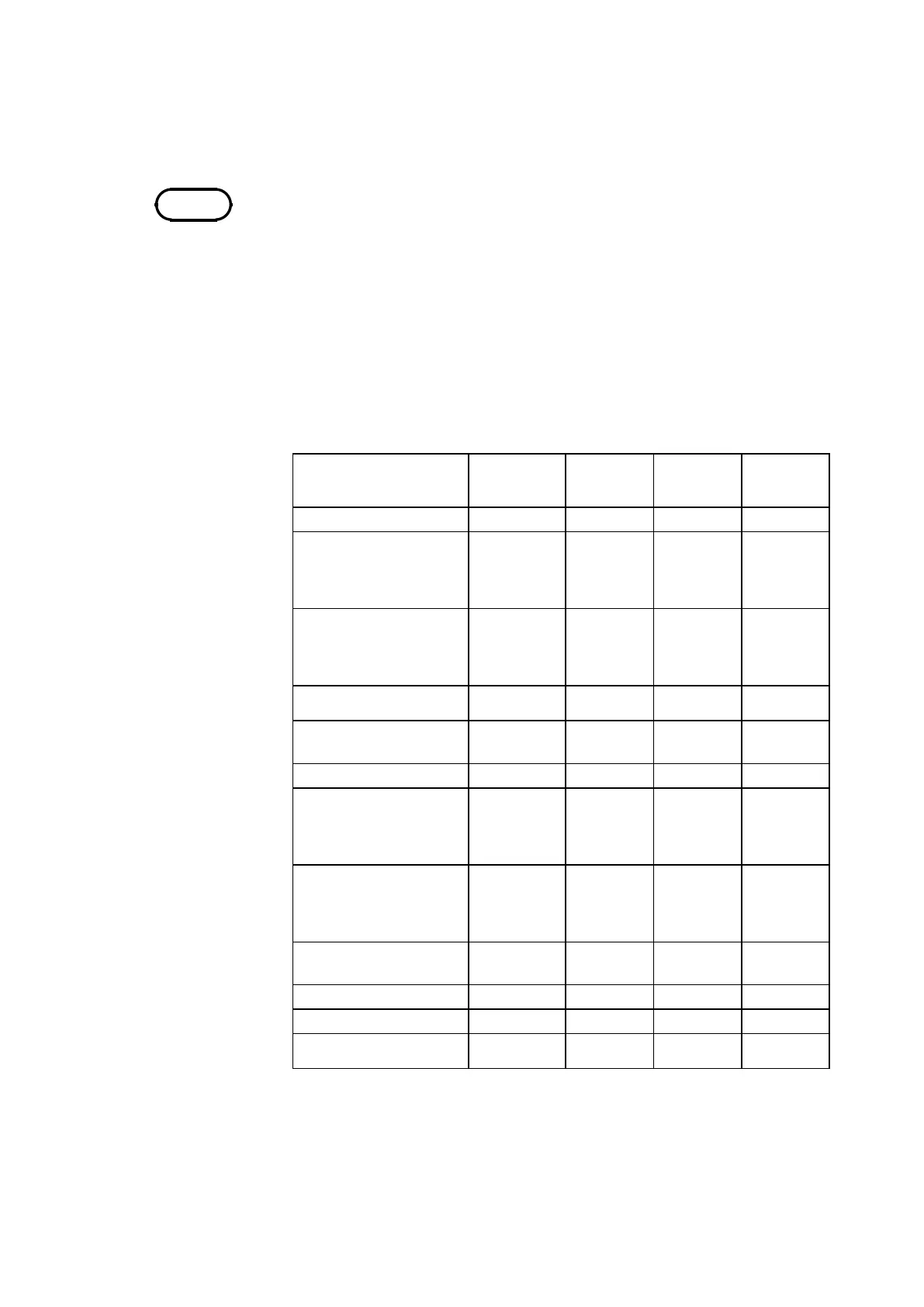
8.4 STATUS2 Settings (FFT)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
NOTE
FFT analysis mode Y-axis
Time axis
averaging
Frequency
axis
averaging
Peak hold
Storage waveform
(
Linear
)
● ● −
Linear spectrum
LIN-REAL
LIN-IMAG
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
PHASE
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
−
−
−
●
●
−
RMS spectrum
LIN-REAL
LIN-IMAG
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
PHASE
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
−
−
−
●
●
−
Power spectrum
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
●
●
●
●
●
●
Auto correlation
function
(
Linear
)
● ● ●
Histogram
(
Linear
)
● − −
Transfer function
LIN-REAL
LIN-IMAG
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
PHASE
●
●
●
●
●
−
−
●
●
−
−
−
●
●
−
Cross power spectrum
LIN-REAL
LIN-IMAG
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
PHASE
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
−
−
−
●
●
−
Cross correlation
function
(
Linear
)
● ● ●
Unit impulse response
(
Linear
)
● ● ●
Coherence function
(
Linear
)
● ● ●
Octave analysis
LIN-MAG
LOG-MAG
●
●
●
●
●
●
Frequency axis peak hold
The specified number of samples are captured, and the peak value is held
(stored) for each frequency.
・ For details on summing averaging and exponential averaging, refer to
Appendix 3.6.
・ When averaging is used together with the waveform evaluation function,
waveform evaluation is carried out after the specified averaging count is
completed.
・ After calculating the average, changing the analysis channel does not cause
recalculation.
FFT analysis mode and averaging
●: Setting is valid
−: Setting is invalid (has no effect)
Same for linear spectrum, transfer function, and cross-power spectrum with
Nyquist display.
 Loading...
Loading...