186
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
9.8 Scaling Function (SYST EM2)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
9.8.2 Scaling Setting Example
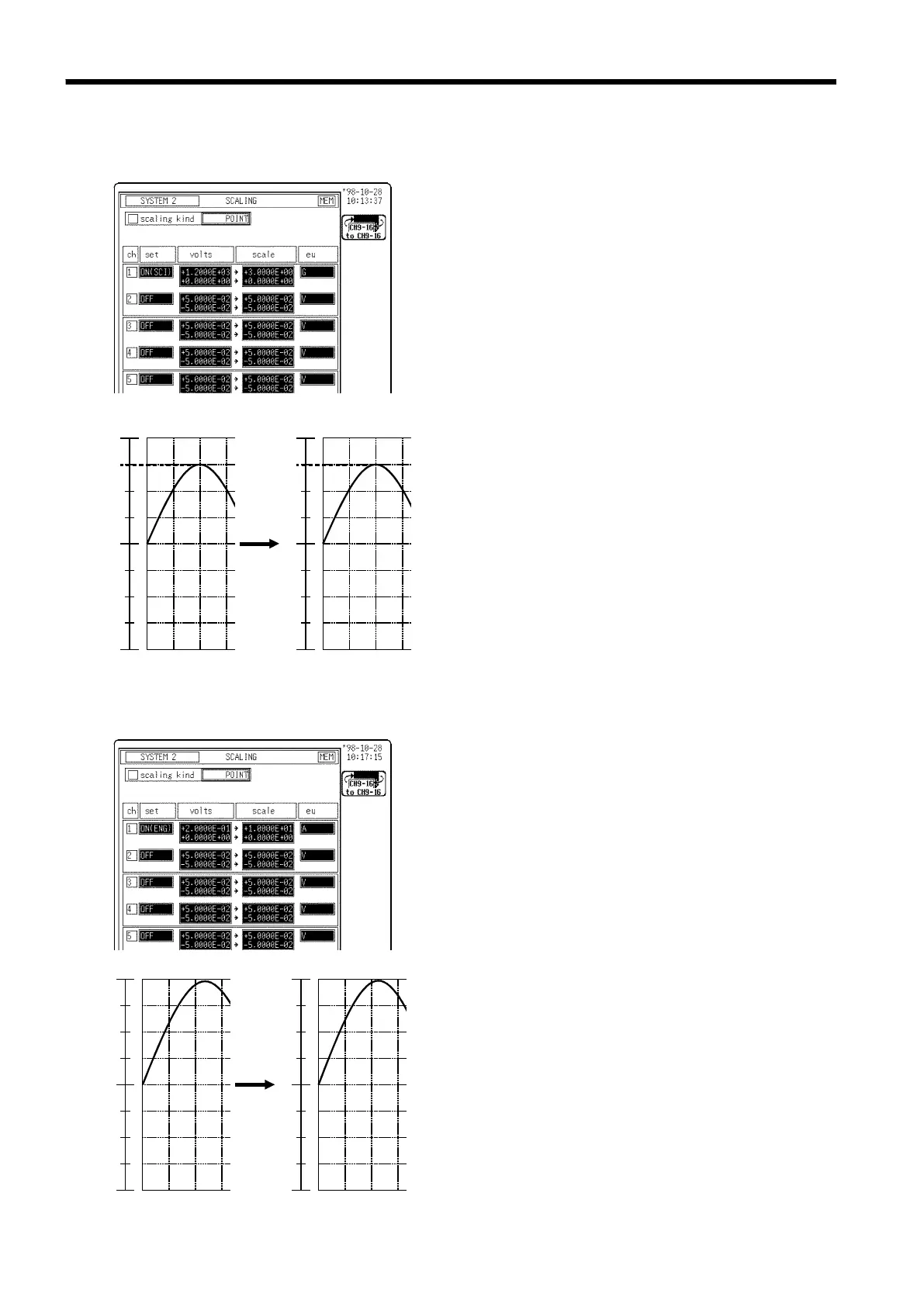
The example below shows the scaling function
of the strain unit.
When a sensor (the conversion ratio is
characterized as "3G = 1200
με
(micro
strain)") is used:
Scaling method: 2-point method
Setting: SCI or ENG
Converting value: 1200 (
με
)
→
3 (scale),
0(
με
)
→
0 (scale)
unit (eu): G
Through the use of the scaling function, the
signal from the sensor can be obtained in the
form of a physical quantity.
Cursor values A and B, respectively, show the
physical quantities.
If the gauge is turned on before the printout is
made, the gauge is output in a physical
quantity.
1200
1600
800
-800
-1600
2
3
-2
-4
V
G
00
0.2
0.1
-0.1
-0.2
5.0
10
-5.0
-10
V
A
00
The example below shows the type of scaling
when the measurement range is set to 10 A
using the 9018 CLAMP ON PROBE.
Through the use of the scaling function, the
signal from the sensor can be obtained in the
form of a current value.
Cursor values A and B, respectively, show the
current values.
If the gauge is turned on before the printout is
made, the gauge is output in a current value.
Scaling method: 2-point method
Setting: SCI or ENG
Converting value: 0.2 (V)
→
10 (scale),
0
(
V
)→
10
(
scale
)
unit (eu): A
 Loading...
Loading...