Engine
SHOP MANUAL
Ch 1 page 31
Operation and reductant metering
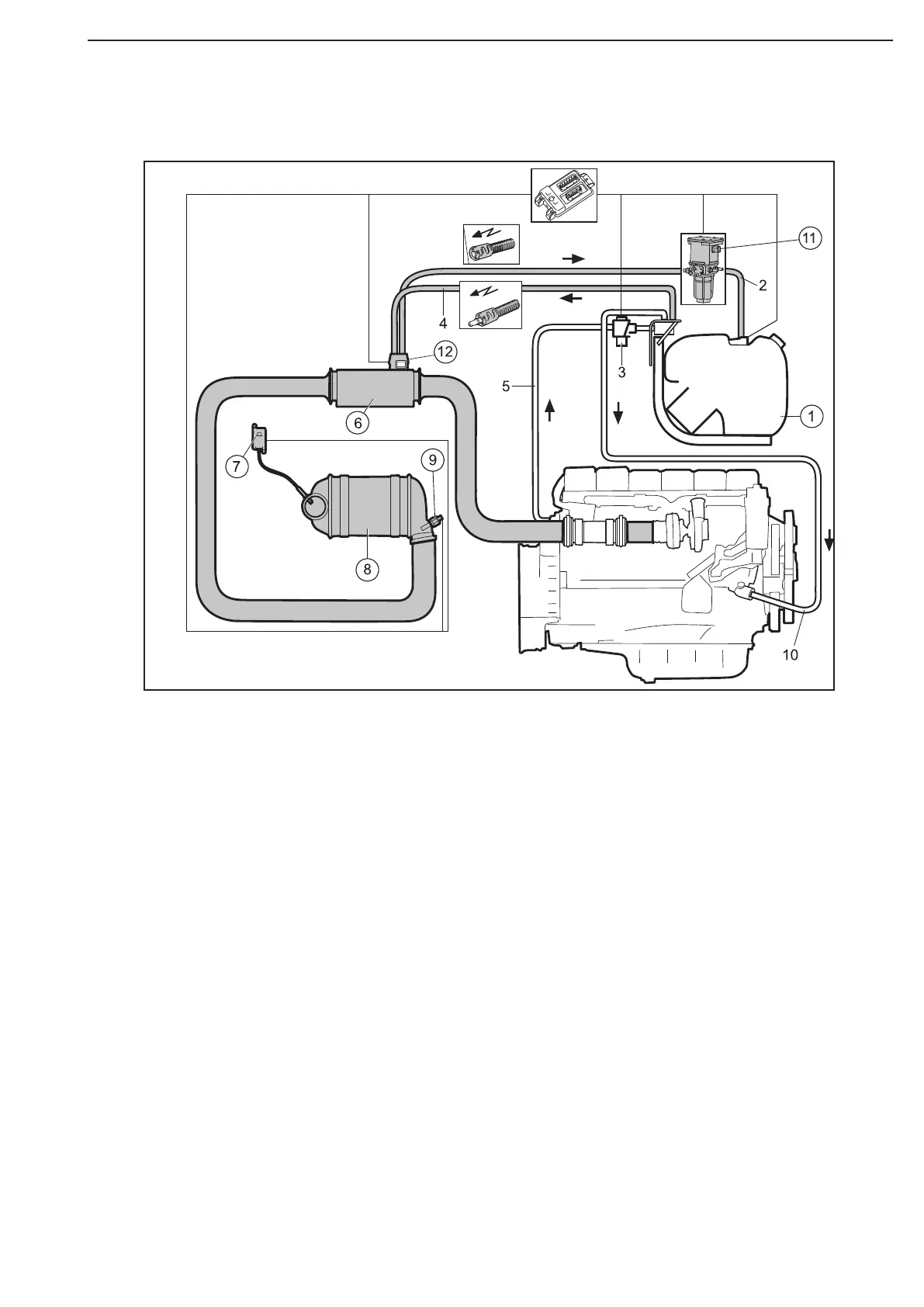
The exhaust gases are treated in a number of steps before being released via the tailpipe. These steps are
based on the combustion control mode of the engine control unit. First, the exhaust gases are mixed with reduc-
tant when they pass the hydrolysis catalytic converter (6). The process of hydrocarbon reduction begins in the
hydrolysis catalytic converter (6) and ends in the SCR catalytic converter (8).
Once the exhaust gases have passed the hydrolysis catalytic converter (6), the exhaust gas temperature is
measured using the temperature sensor (9). The value is read off by the EEC3 control unit and transmitted to
the engine control unit. The values from the temperature sensor (9) are used by the engine control unit to con-
trol the exhaust gas temperature, which should be between 200 and 250°C. This can be done with the exhaust
brake (if fitted), the injection system XPI or a combination of the two.
The exhaust gases then pass through the SCR catalytic converter (8) where most reduction of hydrocarbons
takes place by means of reductant injected in previously. NOx is converted into water, carbon dioxide and am-
monia.
The volume of reductant mixed with the exhaust gases in the hydrolysis catalytic converter (6) is determined by
the engine control unit, activated by the EEC3 control unit and carried out by the reductant doser (12). The dose
is determined by the engine control unit on the basis of the values from the NOx sensor (7), temperature sensor
(9) and the combustion control mode of the engine control unit.
The EEC3 control unit activates injection of reductant to the hydrolysis catalytic converter (6) from the reductant
tank (1) by means of the reductant pump (11) and the reductant doser (12).
Figure 44
 Loading...
Loading...