SHOP MANUAL
DRIVE LINE
Ch 3 page 72 Ch 3 page 73
DRIVE LINE
General function
With a hypoid crownwheel and pinion arrangment the
pinion centre is below the centre of the crowwheel, which
provides the teeth with increased strength by
extended sliding mesh and more tooth overlap.
Distance “a” is known as offset
Under heavy load the gearwheel set is exposed to
forces which both tend to push the pinion forward
(front diff.) / backward (rear diff.), as well as pressing
the crownwheel and pinion apart.
To prevent this, the pinion runs in robust roller
bearings.
The rear diff. has a support bearing which is cylindrical
and seated in the gear housing inside the crownwheel
circumference.
The other two bearings are taper roller bearings and
absorb the axial and radial forces in the pinion.
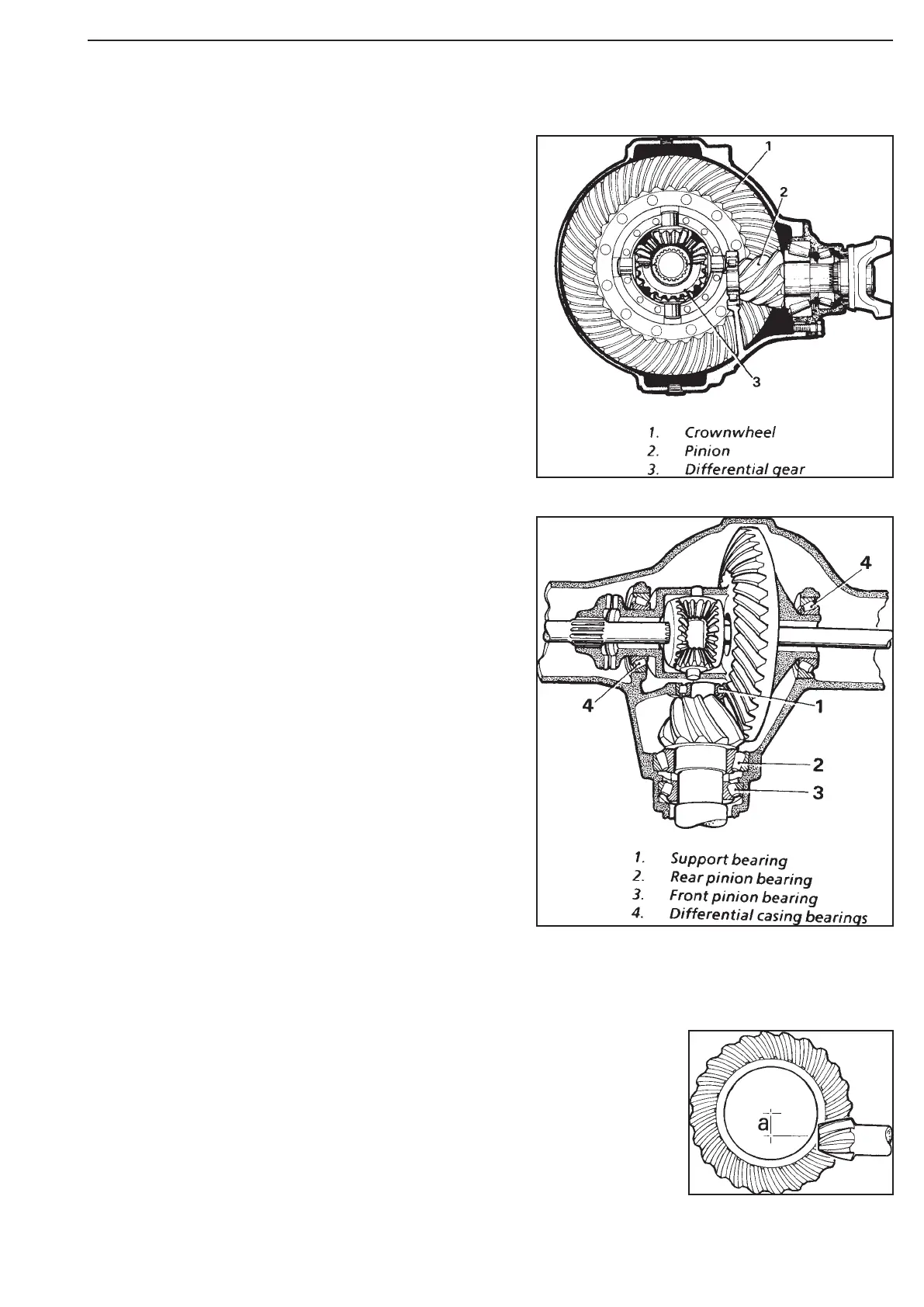
The crownwheel is attached to the differential casing,
which runs in two robust taper roller bearings in the
differential housing.
The differentials transmit the torque of the transmission
output propeller shafts to the wheels.
The differential contains one crownwheel and one pinion,
as well as a differential gear.
The teeth of the crownwheel and pinion are cut in
a special way to provide proper mesh and high strength.
As heavy torque has to be transmitted, the fit between
crown wheel and pinion has to be accurate and therefore
the parts are lapped together as a pair in manufacturing.
When changing crownwheel or pinion, both parts have to
be changed.
Figure 190
Figure 189
Figure 191
 Loading...
Loading...