7065DS3KBasicConfig.fm Draft Document for Review August 30, 2007 12:59 am
48 IBM System Storage DS3000: Introduction and Implementation Guide
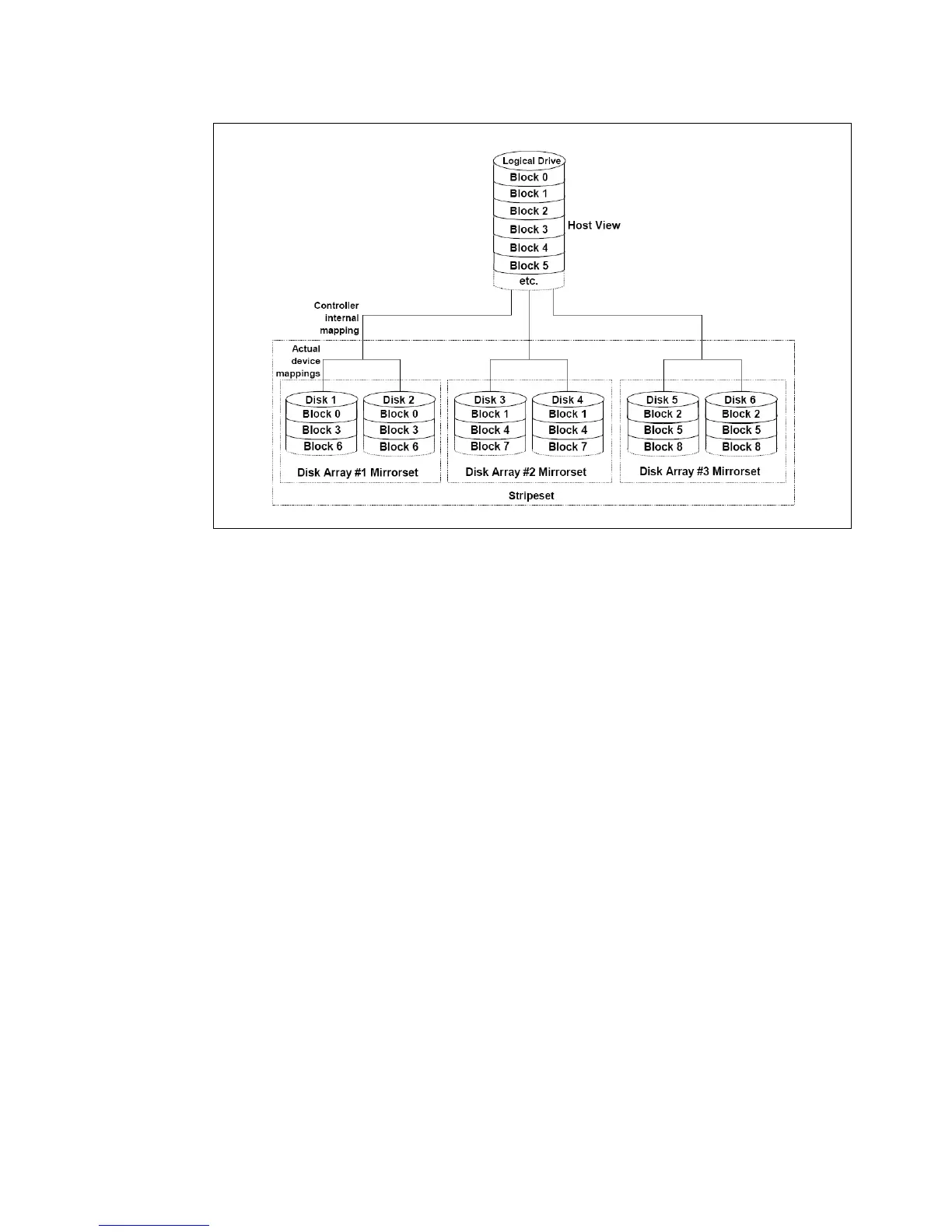
Figure 4-5 RAID 10
4.1.2 Arrays and logical drives
Before the host servers can start using the disk drives on the DS3000, you have to create at
least one array and logical drive. An array is simply a set of physical disk drives. Each array
has to be carved into one or more logical drives. Finally, you have to assign the logical drives
to the host servers. Host servers see the logical drives as physical disk drives.
The RAID level is defined per array. This means all logical drives inside an array will use the
same RAID level.
Figure 4-6 illustrates the concept of arrays and logical drives. It shows nine physical disk
drives, labeled
Drive 1 through Drive 9. Disk drives 1 to 4 are grouped into Array 1 and set to
operate as RAID level 10. Drives 5 to 9 operate as RAID 5 and are members of
Array 2.
Array 1 is carved into two logical drives (1 and 2) and there is some free space left. Array 2 is
split into logical drives 3, 4, 5 and 6, which take up entire array space.
Logical drives 1 through 6 are now ready to be assigned to the host servers.
 Loading...
Loading...











