CHAPTER13 Network
Mediant 1000 Gateway & E-SBC | User's Manual
If a static route is required to access OAMP applications (for remote management, for
example) and the route is not configured correctly, the route is not added and the device
is not accessible remotely. To restore connectivity, the device must be accessed
locally from the OAMP subnet and the required routes be configured.
Network Address Translation Support
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a mechanism that maps internal IP addresses (and ports)
used within a private network to global IP addresses and vice versa, providing transparent routing
to end hosts. The primary advantages of NAT include (1) reduction in the number of global IP
addresses required in a private network (global IP addresses are only used to connect to the
Internet) and (2) better network security by hiding the internal architecture.
The design of SIP creates a problem for VoIP traffic to pass through NAT. SIP uses IP addresses
and port numbers in its message body. However, the NAT server is unable to modify the SIP
messages and thus, can’t change local addresses to global addresses.
This section discusses the device's solutions for overcoming NAT traversal issues.
Device Located behind NAT
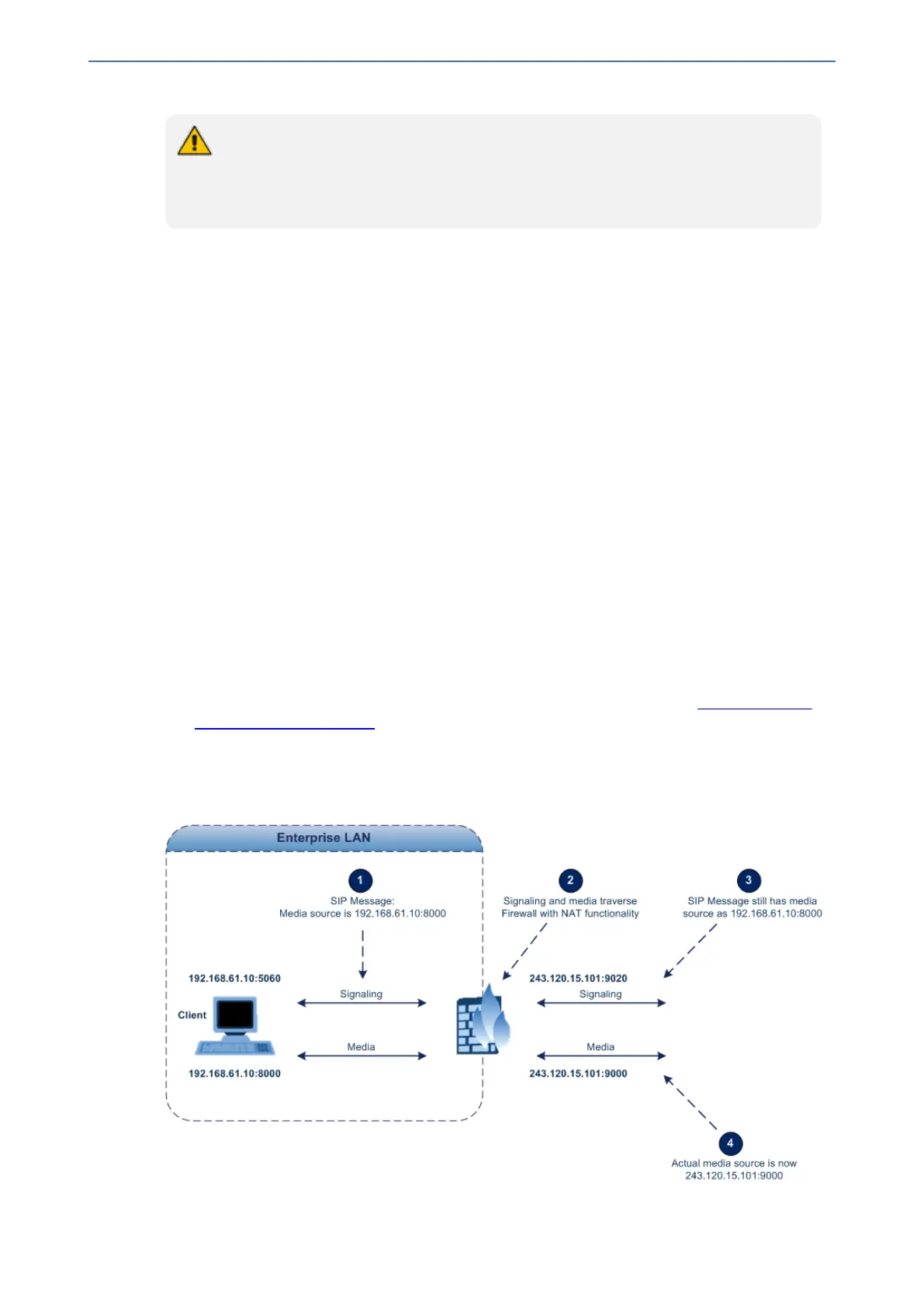
Two different streams of traffic traverse through NAT - signaling and media. A device located
behind NAT that initiates a signaling path has problems receiving incoming signaling responses, as
they are blocked by the NAT server. Therefore, the initiating device must inform the receiving
device where to send the media. To resolve this NAT problem, the device provides the following
solutions (listed in priority of the method used):
■ (Gateway Application Only) If configured, uses the single Static NAT IP address for all
interfaces - see Configuring a Static NAT IP Address for All Interfaces on the next page
■ NAT Translation table, which configures NAT per IP network interface - see Configuring NAT
Translation per IP Interface.
If NAT is not configured, the device sends the packet according to its IP address configured in the
IP Interfaces table.
The figure below illustrates the NAT problem faced by SIP networks when the device is located
behind a NAT:
- 108 -

 Loading...
Loading...











