CHAPTER13 Network
Mediant 1000 Gateway & E-SBC | User's Manual
SIP Signaling Messages
By default, the device resolves NAT issues for SIP signaling, using its NAT Detection mechanism.
The NAT Detection mechanism checks whether the endpoint is located behind NAT by comparing
the source IP address of the incoming UDP/TCP packet (in which the SIP message is received)
with the IP address in the SIP Contact header. If the packet's source IP address is a public address
and the Contact header's IP address is a local address, the device considers the endpoint as
located behind NAT. In this case, the device sends the SIP messages to the endpoint using the
packet's source IP address. Otherwise (or if you have disabled the NAT Detection mechanism),
the device sends the SIP messages according to the SIP standard (RFC 3261), where requests
within the SIP dialog are sent using the IP address in the Contact header and responses to
INVITEs are sent using the IP address in the Via header.
If necessary, you can also configure the device to always consider incoming SIP INVITE
messages as sent from endpoints that are located behind NAT. When this is enabled, the device
sends responses to the INVITE (to the endpoint) using the the source IP address of the packet
(INVITE) initially received from the endpoint. This is useful in scenarios where the endpoint is
located behind a NAT firewall and the device (for whatever reason) is unable to identify NAT using
its regular NAT Detection mechanism. This feature is enabled per specific calls using the 'Always
Use Source Address' parameter in the IP Groups table (see Configuring IP Groups). If this feature
is disabled, the device's NAT detection is according to the settings of the global parameter, 'SIP
NAT Detection' parameter (see below procedure).
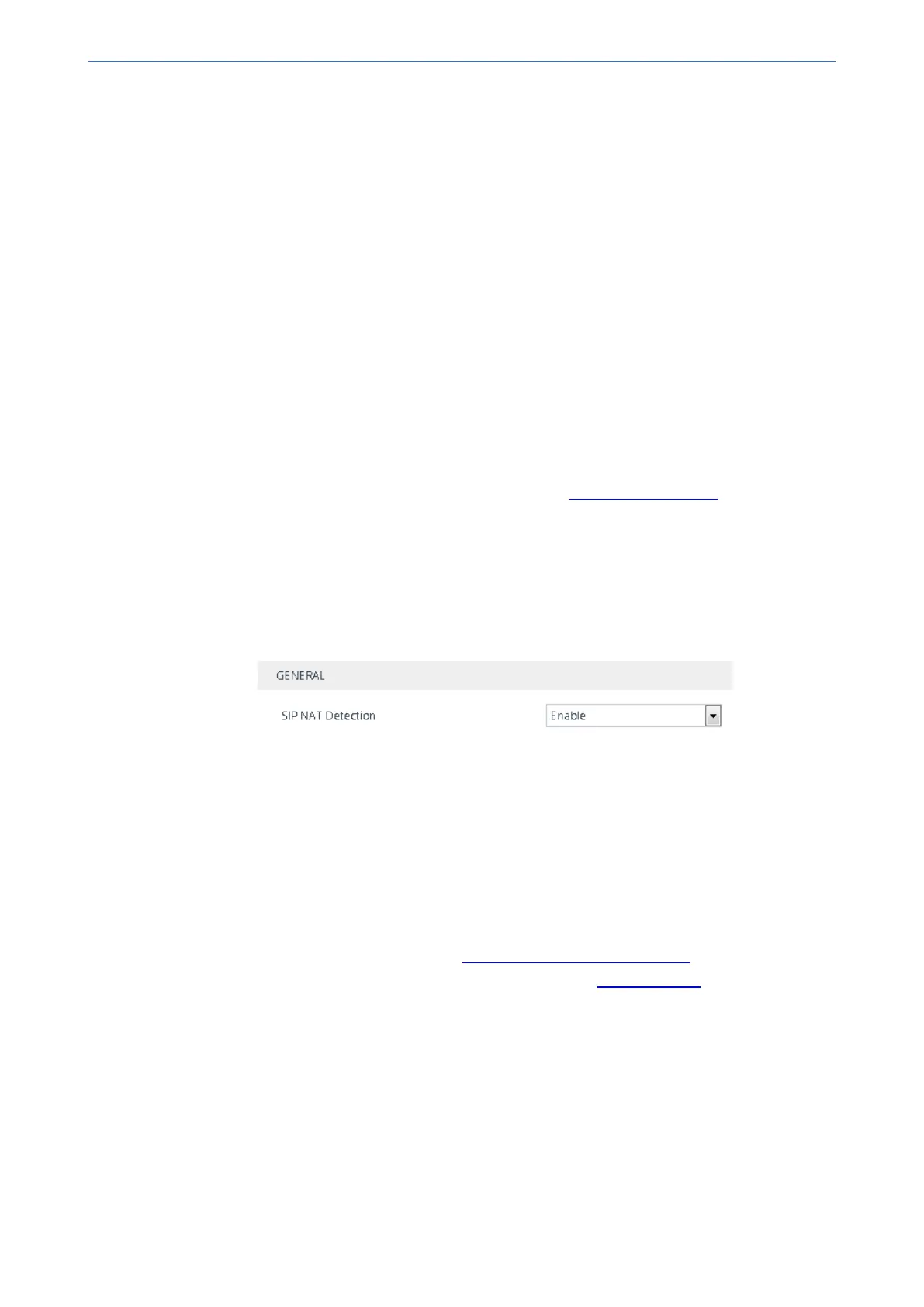
➢ To enable the NAT Detection feature (global):
1. Open the Transport Settings page (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > SIP Definitions
folder > Transport Settings).
2. From the 'SIP NAT Detection' drop-down list (SIPNatDetection), select Enable:
3. Click Apply.
Media (RTP/RTCP/T.38)
When a remote UA initiates a call and is not located behind a NAT server, the device sends the
media (RTP, RTCP, and T.38) packets to the remote UA using the IP address:port (UDP) indicated
in the SDP body of the SIP message received from the UA. However, if the UA is located behind
NAT, the device sends the RTP with the IP address of the UA (i.e., private IP address) as the
destination instead of that of the NAT server. Thus, the RTP will not reach the UA. To resolve this
NAT traversal problem, the device offers the following features:
■ First Incoming Packet Mechanism - see First Incoming Packet Mechanism
■ RTP No-Op packets according to the avt-rtp-noop draft - see No-Op Packets
The figure below illustrates a typical network architecture where the remote UA is located behind
NAT:
- 111 -
 Loading...
Loading...











