Description of function
The priority determines whether a stop response or a stop function inuences another active
Safety Integrated Function.
The stop responses and stop functions have a higher priority than all other Safety Integrated
Functions.
Amongst themselves, the stop responses and stop functions have dierent priorities.
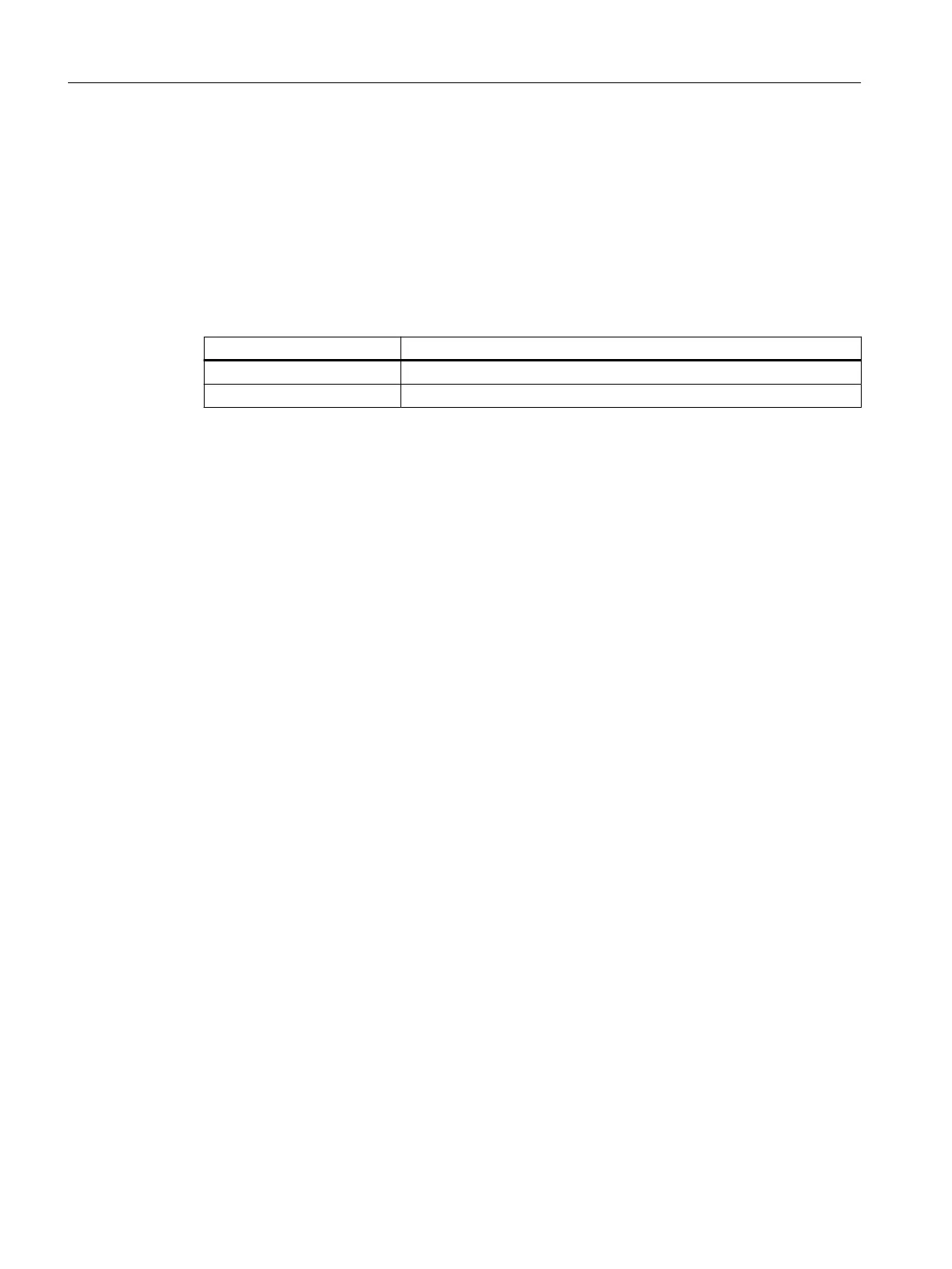
Table 14-95 Priority of stop responses and stop functions
Priority Stop response or stop function
High Safe Torque O (STO)
Low Safe Stop 1 (SS1)
A stop response or stop function with a higher priority inuences an active stop response or
stop function with a lower priority.
A stop response or stop function with a lower priority has no inuence on an active stop
response or stop function with a higher priority.
Example
Examples of the behavior of the motor if a stop response is active or if a stop function is selected:
• Safely-Limited Speed (SLS) is active and Safe Stop 1 (SS1) is selected.
Result: The converter brakes the motor because the stop function Safe Stop 1 (SS1) has a
higher priority than Safely-Limited Speed (SLS).
• Safely-Limited Speed (SLS) is active and the converter detects a limit value violation.
Safe Torque O (STO) is set as the stop response to a limit value valuation.
During the stop response, the stop function Safe Stop 1 (SS1) is selected.
Result: The selection of Safe Stop 1 (SS1) has no inuence on the behavior of the motor. The
motor coasts down because Safe Torque O (STO) has a higher priority than Safe Stop 1 (SS1).
14.12.11.3 Fail-safe acknowledgment of safety messages
Overview
In the event of safety messages, e.g. due to limit value violations of the motor with active Safety
Integrated Functions, the converter detects an internal event.
A safety message requires a failsafe acknowledgement.
Requirement
You checked and eliminated the cause of the internal event.
Functions
14.12Safety Integrated
SINAMICS G220 converter
710 Operating Instructions, 04/2024, FW V6.2, A5E51781573B AB

 Loading...
Loading...











