CHAPTER16 Services
Mediant 1000 Gateway & E-SBC | User's Manual
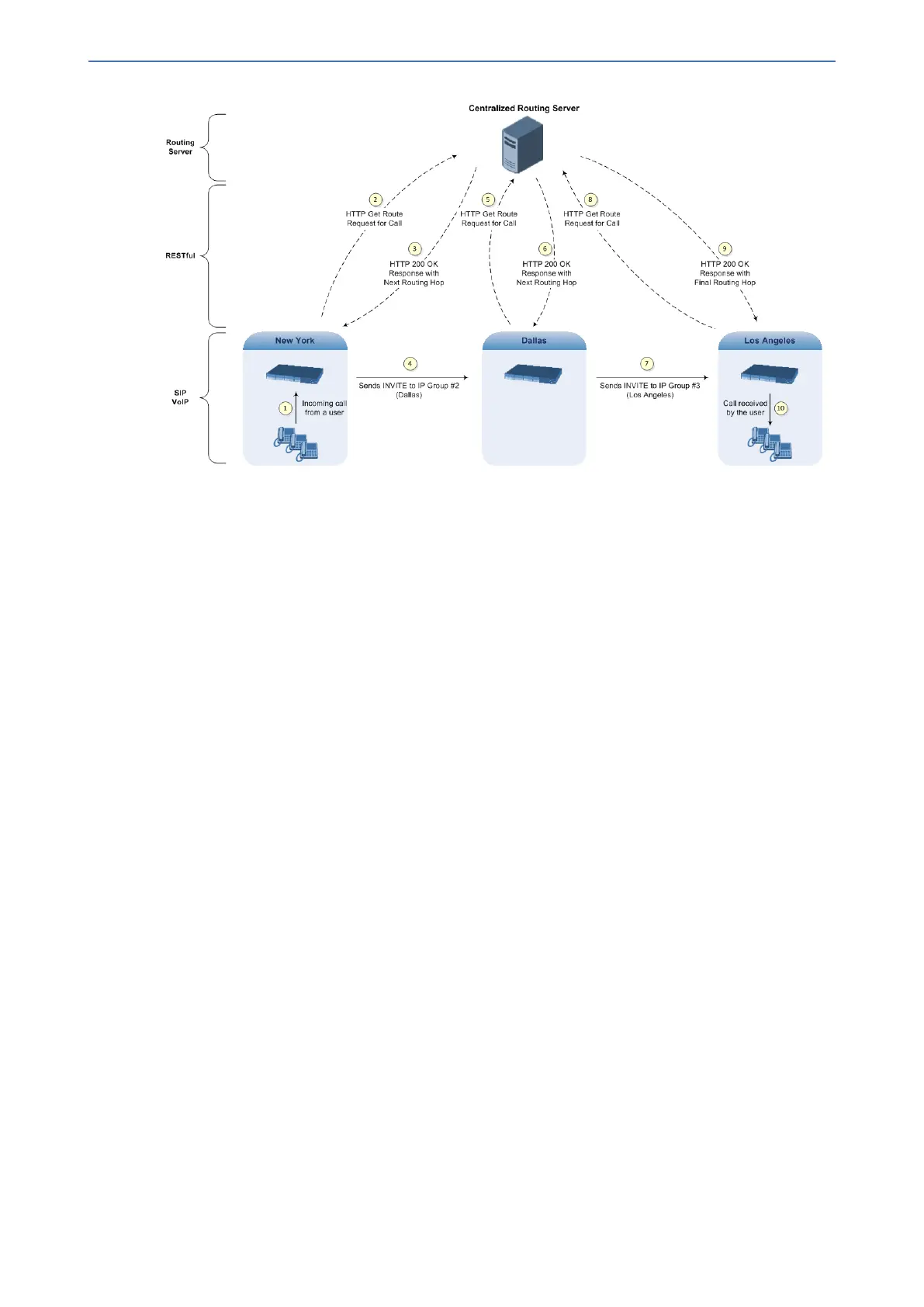
The Routing server can also manipulate call data such as calling name, if required. It can also
create new IP Groups and associated configuration entities, if necessary for routing. Multiple
Routing servers can also be employed, whereby each device in the chain path can use a specific
Routing server. Alternatively, a single Routing server can be employed and used for all devices
("stateful" Routing server).
The device automatically updates (sends) the Routing server with its' configuration topology
regarding SIP routing-related entities (Trunk Groups, SRDs, SIP Interfaces, and IP Groups) that
have been configured for use by the Routing server. For example, if you add a new IP Group and
enable it for use by the Routing server, the device sends this information to the Routing server.
Routing of calls associated with routing-related entities that are disabled for use by the Routing
server (default) are handled only by the device (not the Routing server).
In addition to regular routing, the Routing server also supports the following:
■ Alternative Routing: If a call fails to be established, the device "closest" to the failure and
configured to send "additional" routing requests (through REST API - "additionalRoute"
attribute in HTTP Get Route request) to the Routing server, sends a new routing request to the
Routing server. The Routing server may respond with a new route destination, thereby
implementing alternative routing. Alternatively, it may enable the device to return a failure
response to the previous device in the route path chain and respond with an alternative route to
this device. Therefore, alternative routing can be implemented at any point in the route path. If
the Routing server sends an HTTP 404 "Not Found" message for an alternative route request,
the device rejects the call. If the Routing server is configured to handle alternative routing, the
device does not make any alternative routing decisions based on its alternative routing tables.
■ Call Forking: The device can fork calls according to the Routing server. When the device
finds a matching routing rule in the IP-to-IP Routing table that is configured with the Routing
Server destination, it sends an HTTP Get Route request to the Routing server. When it
receives a successful response from the server, the device sends an INVITE message to a
destination based on the response. If the routingMethod in the response from the Routing
server is "fork", the device sends another HTTP Get Route request to the server and upon a
successful response, sends another INVITE to another destination based on the response,
and so on. This call forking process continues until no routingMethod is received from the
server or it is set to “seq”, or there is a failed response from the server. If all the contacts fail
(4xx), the device falls back to an alternative route, if exists, from the Routing server. If 3xx is
received for any of the forked destinations, the device handles it after all the forked INVITEs
have been terminated.
- 253 -
 Loading...
Loading...











