2-92 Phaser 6180MFP Multifunction Printer Service Manual
Theory of Operation
Analog and Digital Signals
An analog signal is an electrical signal generated by the telephone’s
microphone. The waveform of this analog signal fluctuates responsive to the
voice volume. When the voice is loud, the amplitude (voltage) increases;
when the voice is soft, the amplitude decreases. When the voice is high-
pitched, the frequency (number of vibrations) increases; when low-pitched,
the frequency decreases.
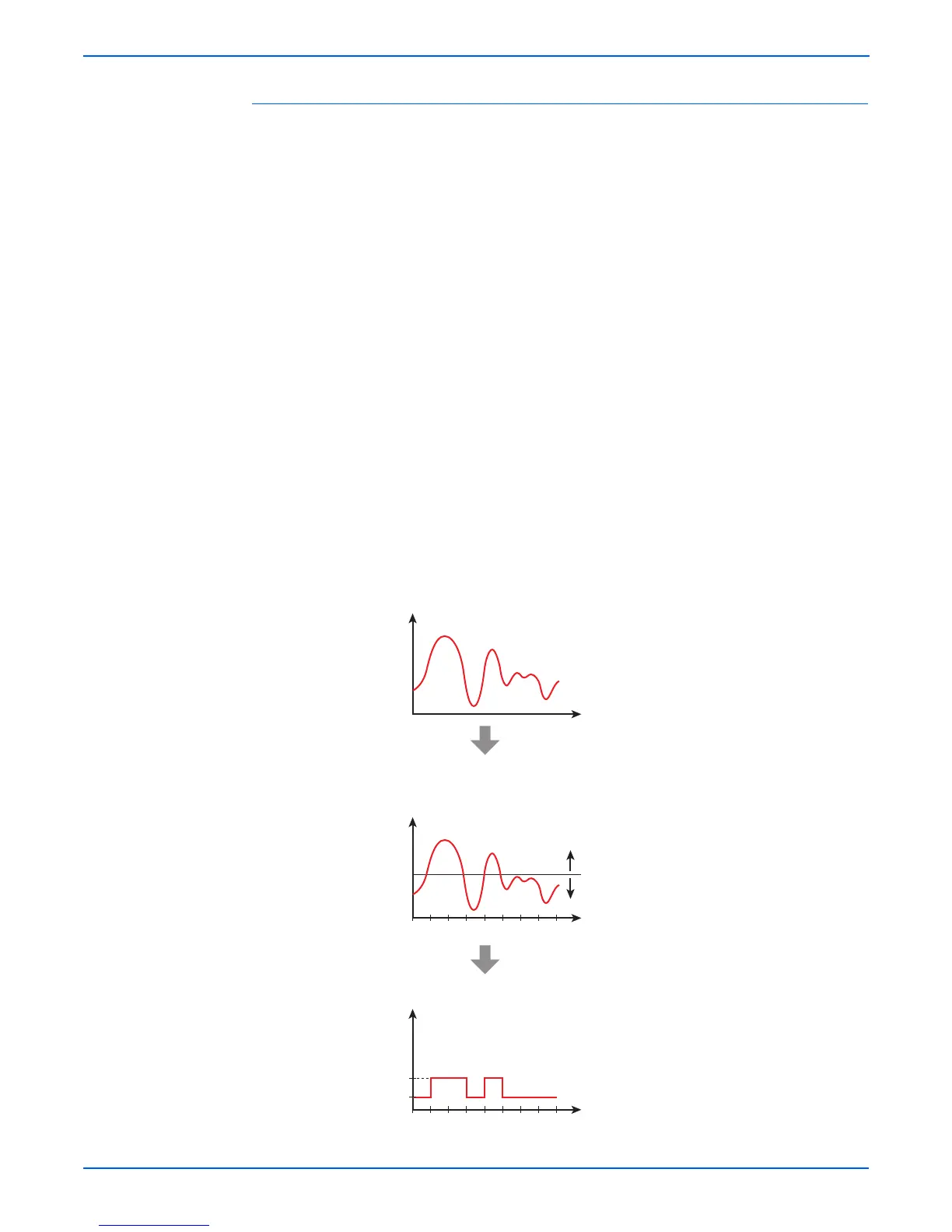
A signal whose values change in a continuous manner with time like this is
called an analog signal. In contrast, a digital signal is a set of values that
change with time in a discrete instead of continuous manner. In other words,
an analog signal is like a hill. A digital signal is like stairs.
A digital signal is a series of values obtained by sampling a continuous analog
signal at a certain required rate. For example, when sampling is by time, the
rate is once a second, millisecond, etc. Because the sampling reduces the
amount of data along the time axis, the converted signal is compressed and
smaller in data size. Thus, once digitized, the signal information is spread out
compared to the original analog signal.
Moreover, digital signal transmission is performed by dividing a continuously
changing electrical signal according to a certain rate of time, then converting
each division to a value of 1 or 0, depending on whether it is greater or less
than a specified threshold value. Compared to an analog signal, a digital
signal offers precise data exchange because the only change that must be
handled is that between 1 (high-voltage) and 0 (low-voltage) with respect to a
standard value (the threshold value).
s6180mfp-100
01101000
0
0
1
1101000
Analog signal
Digital signal
Voltage
Time
Voltage
Time
Voltage
Time
The signal is converted to 1 or 0 depending on
whether it is higher or lower than a threshold value.
In other words, the waveform is quantified.
Threshold
Value
Higher = 1
Lower = 0

 Loading...
Loading...
















