MPC5604B/C Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 8
Freescale Semiconductor 65
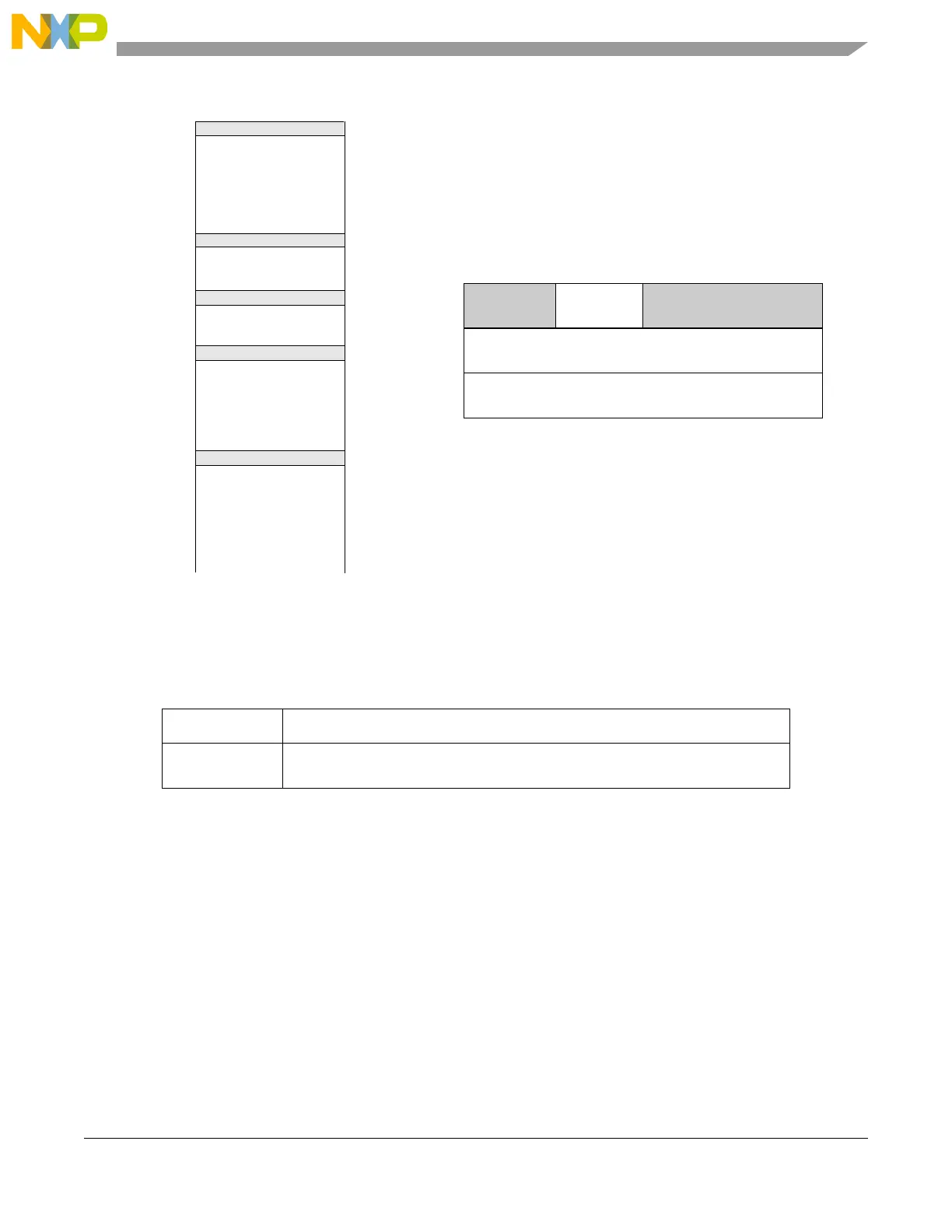
Figure 5-2. Boot sector structure
The RCHW fields are described in Table 5-2.
The SSCM performs a sequential search of each boot sector (starting at sector 0) for a valid BOOT_ID
within the RCHW. If a valid BOOT_ID is found, the SSCM reads the boot vector address. If a valid
BOOT_ID is not found, the SSCM starts the process of putting the microcontroller into static mode.
Finally, the SSCM sets the e200z0h core instruction pointer to the reset vector address and starts the core
running.
5.1.1.1 Static mode
If no valid BOOT_ID within the RCHW was found, the SSCM sets the CPU core instruction pointer to the
BAM address and the core starts to execute the code to enter static mode as follows:
• The core executes the "wait" instruction which halts the core.
The sequence is illustrated in Figure 5-3.
Table 5-2. RCHW field descriptions
Field Description
BOOT_ID Boot identifier.
If BOOT_ID = 0x5A, the boot sector is considered valid and bootable.
32 KB
Boot sector 0
16 KB
16 KB
32 KB
0x0000_0000
0x0000_8000
0x0000_C000
0x0001_0000
Code flash memory
32 KB
0x0001_8000
Boot sector 1
Boot sector 2
Boot sector 3
Boot sector 4
Boot sector structure
Bit 0 Bit 31
Reserved Reserved
78 1516
BOOT_ID
(0x5A)
0x0
(RCHW)
0x4
32-bit reset vector (points to start address of application code)
0x8
Application code (from offset 0x8 and onward)
 Loading...
Loading...