Coding for SIMD Architectures 3
3-13
Coding Methodologies
Software developers need to compare the performance improvement
that can be obtained from assembly code versus the cost of those
improvements. Programming directly in assembly language for a target
platform may produce the required performance gain, however,
assembly code is not portable between processor architectures and is
expensive to write and maintain.
Performance objectives can be met by taking advantage of the different
SIMD technologies using high-level languages as well as assembly. The
new C/C++ language extensions designed specifically for SSE2, SSE,
and MMX technology help make this possible.
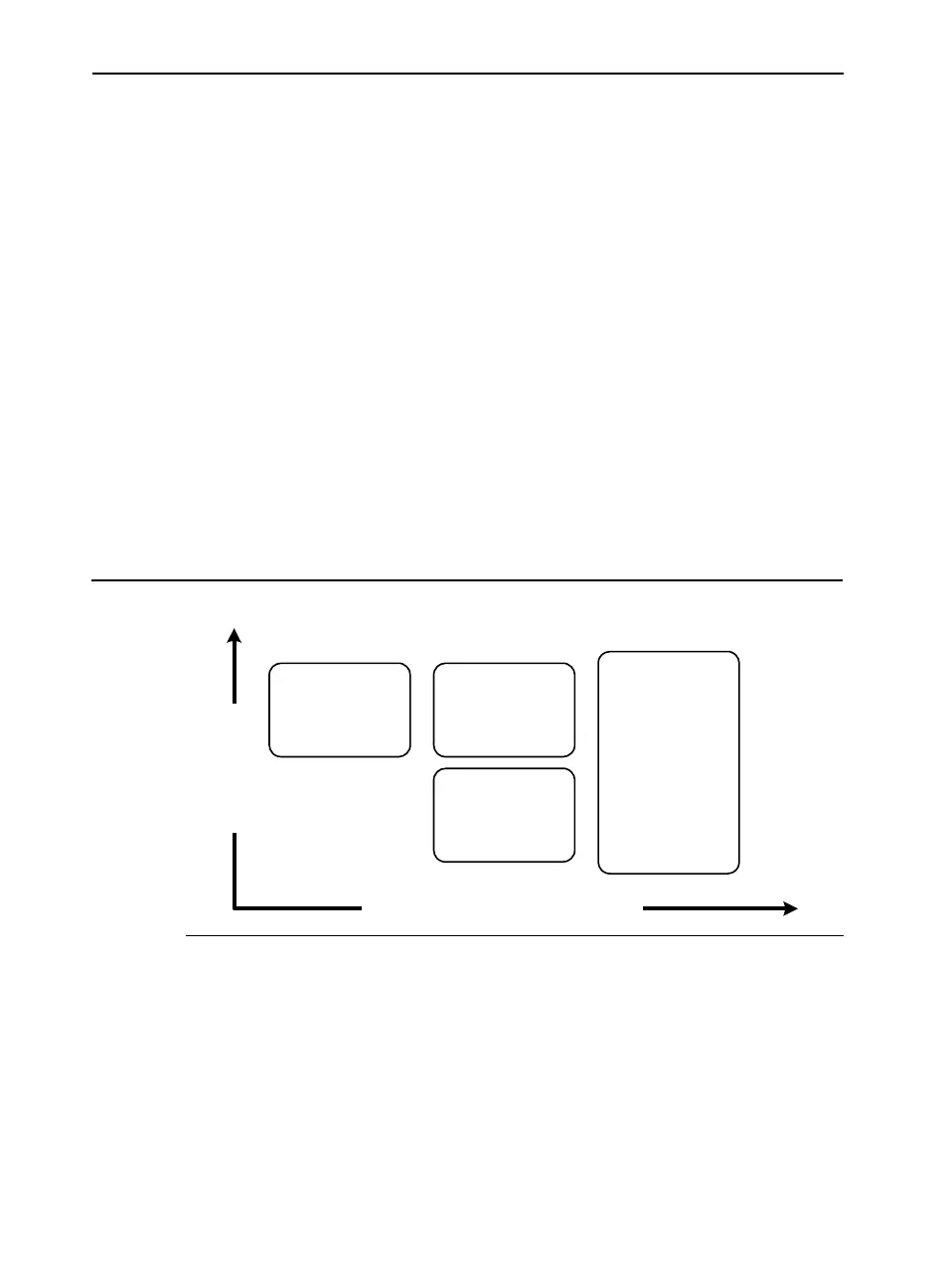
Figure 3-2 illustrates the trade-offs involved in the performance of
hand-coded assembly versus the ease of programming and portability.
Figure 3-2 Hand-Coded Assembly and High-Level Compiler Performance
Trade-offs
Performance
Ease of Programming/Portability
InstrinsicsAssembly
C/C++/Fortran
Automatic
Vectorization

 Loading...
Loading...