Optimizing for SIMD Floating-point Applications 5
5-23
SSE3 and Complex Arithmetics
The flexibility of SSE3 in dealing with AOS-type of data structure can
be demonstrated by the example of multiplication and division of
complex numbers. For example, a complex number can be stored in a
structure consisting of its real and imaginary part. This naturally leads to
the use of an array of structure. Example 5-11 demonstrates using SSE3
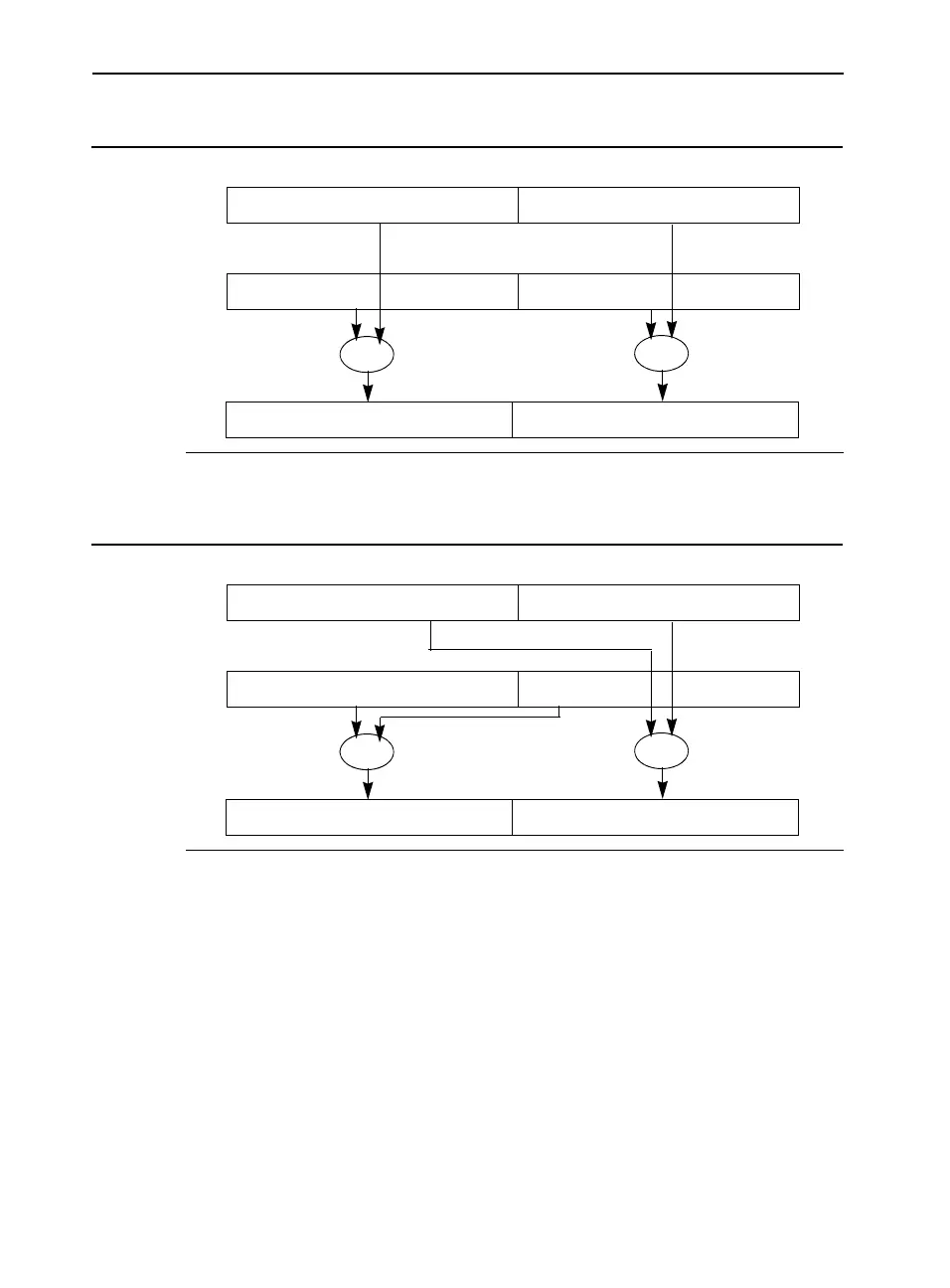
Figure 5-4 Asymmetric Arithmetic Operation of the SSE3 Instruction
Figure 5-5 Horizontal Arithmetic Operation of the SSE3 Instruction HADDPD
X1 X0
X1 + Y1 X0 -Y0
SUB
Y1 Y0
ADD
X1 X0
Y0 + Y1 X0 + X1
ADD
Y1 Y0
ADD

 Loading...
Loading...