IA-32 Intel® Architecture Optimization
E-4
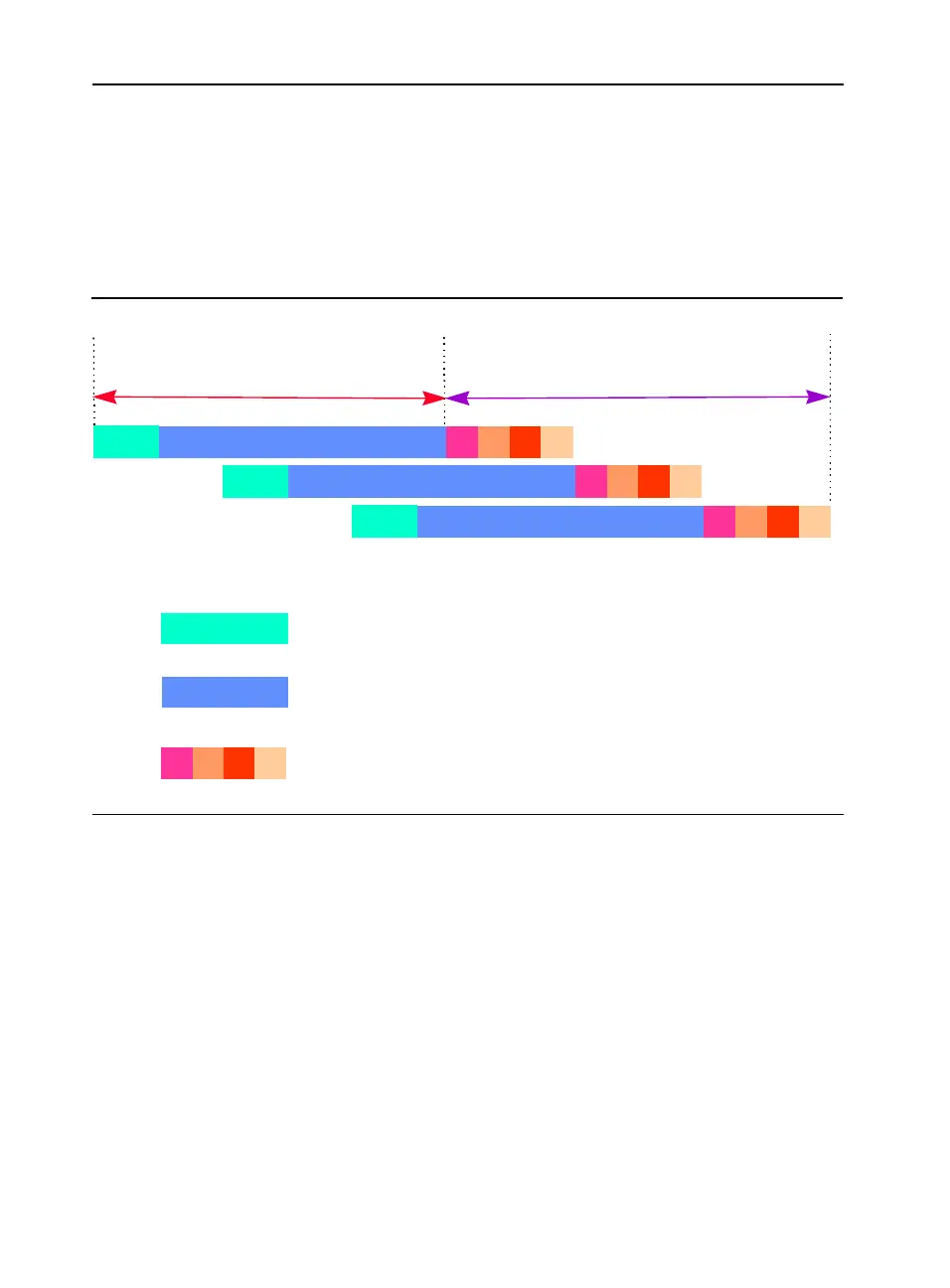
Memory access plays a pivotal role in prefetch scheduling. For more
understanding of a memory subsystem, consider Streaming SIMD
Extensions and Streaming SIMD Extensions 2 memory pipeline
depicted in Figure E-1.
Assume that three cache lines are accessed per iteration and four chunks
of data are returned per iteration for each cache line. Also assume these
3 accesses are pipelined in memory subsystem. Based on these
assumptions,
T
b
= 3 * 4 = 12 FSB cycles.
Figure E-1 Pentium II, Pentium III and Pentium 4 Processors Memory Pipeline
Sketch
1 2 3 4
1
1 2 3 4
1
1
2
3
4
1
T
l
T
b
:
L2 lookup miss latency
:
Memory page access leadoff latency
:
Latency for 4 chunks returned per line
2
3
1
4

 Loading...
Loading...