IA-32 Intel® Architecture Optimization
E-10
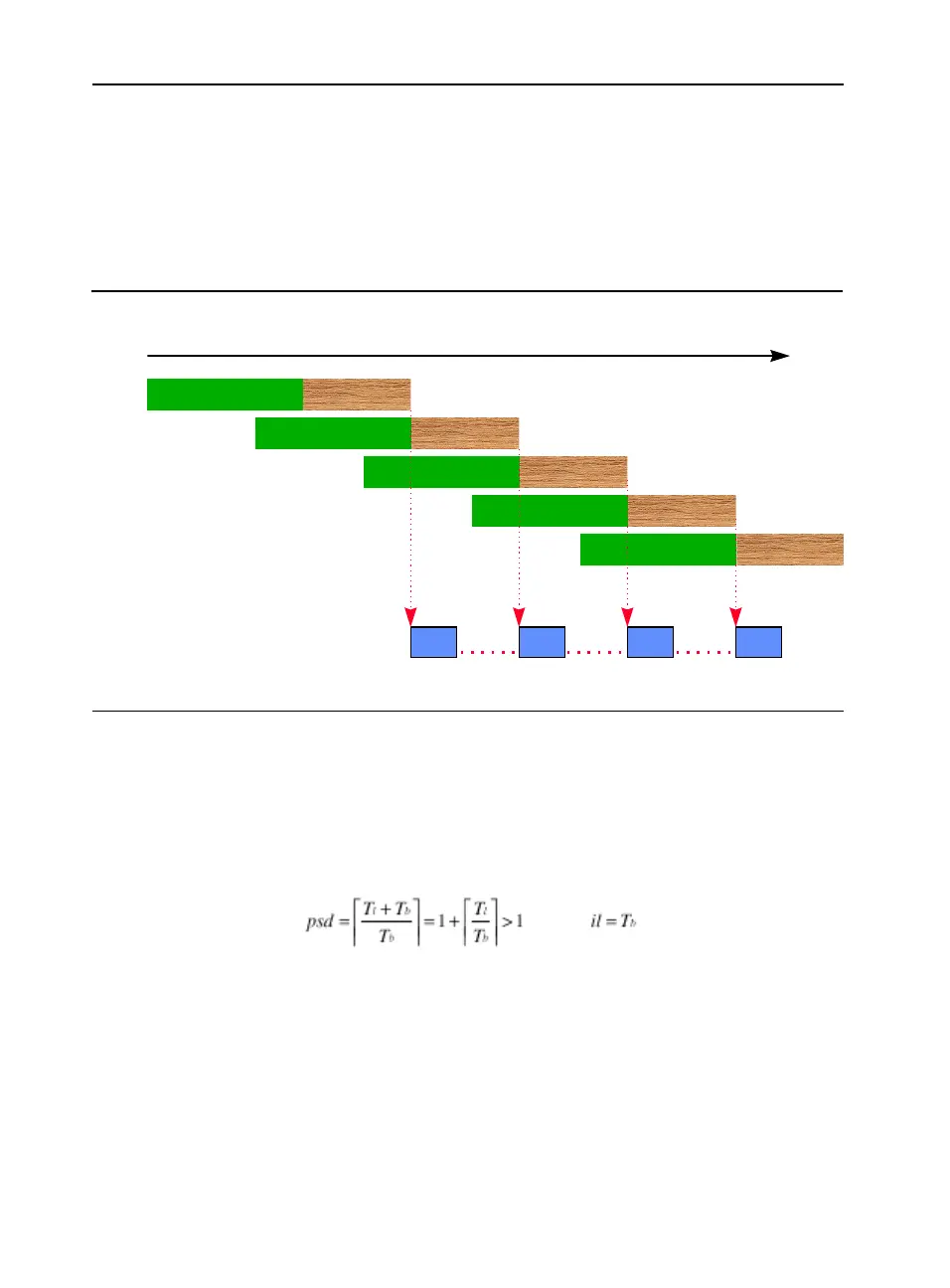
Memory Throughput Bound (Case: T
b
>= T
c
)
When the application or loop is memory throughput bound, the memory
latency is no way to be hidden. Under such circumstances, the burst
latency is always greater than the compute latency. Examine Figure E-5.
The following relationship calculates the prefetch scheduling distance
(or prefetch iteration distance) for the case when memory throughput
latency is greater than the compute latency.
Apparently, the iteration latency is dominant by the memory throughput
and you cannot do much about it. Typically, data copy from one space to
another space, for example, graphics driver moving data from writeback
Figure E-5 Memory Throughput Bound Pipeline
i
Execution cycles
Execution pipeline
i+pid
T
c
δ
f
T
c
T
c
T
c
i+pid+1 i+pid+2 i+pid+3
Front-Side Bus
T
l
T
b
T
l
T
b
T
l
T
b
T
l
T
b
T
l
T
b
δ
f
δ
f
δ
f

 Loading...
Loading...