IA-32 Intel® Architecture Processor Family Overview
1-35
In the first implementation of HT Technology, the physical execution
resources are shared and the architecture state is duplicated for each
logical processor. This minimizes the die area cost of implementing HT
Technology while still achieving performance gains for multithreaded
applications or multitasking workloads.
The performance potential due to HT Technology is due to:
• the fact that operating systems and user programs can schedule
processes or threads to execute simultaneously on the logical
processors in each physical processor
• the ability to use on-chip execution resources at a higher level than
when only a single thread is consuming the execution resources;
higher level of resource utilization can lead to higher system
throughput
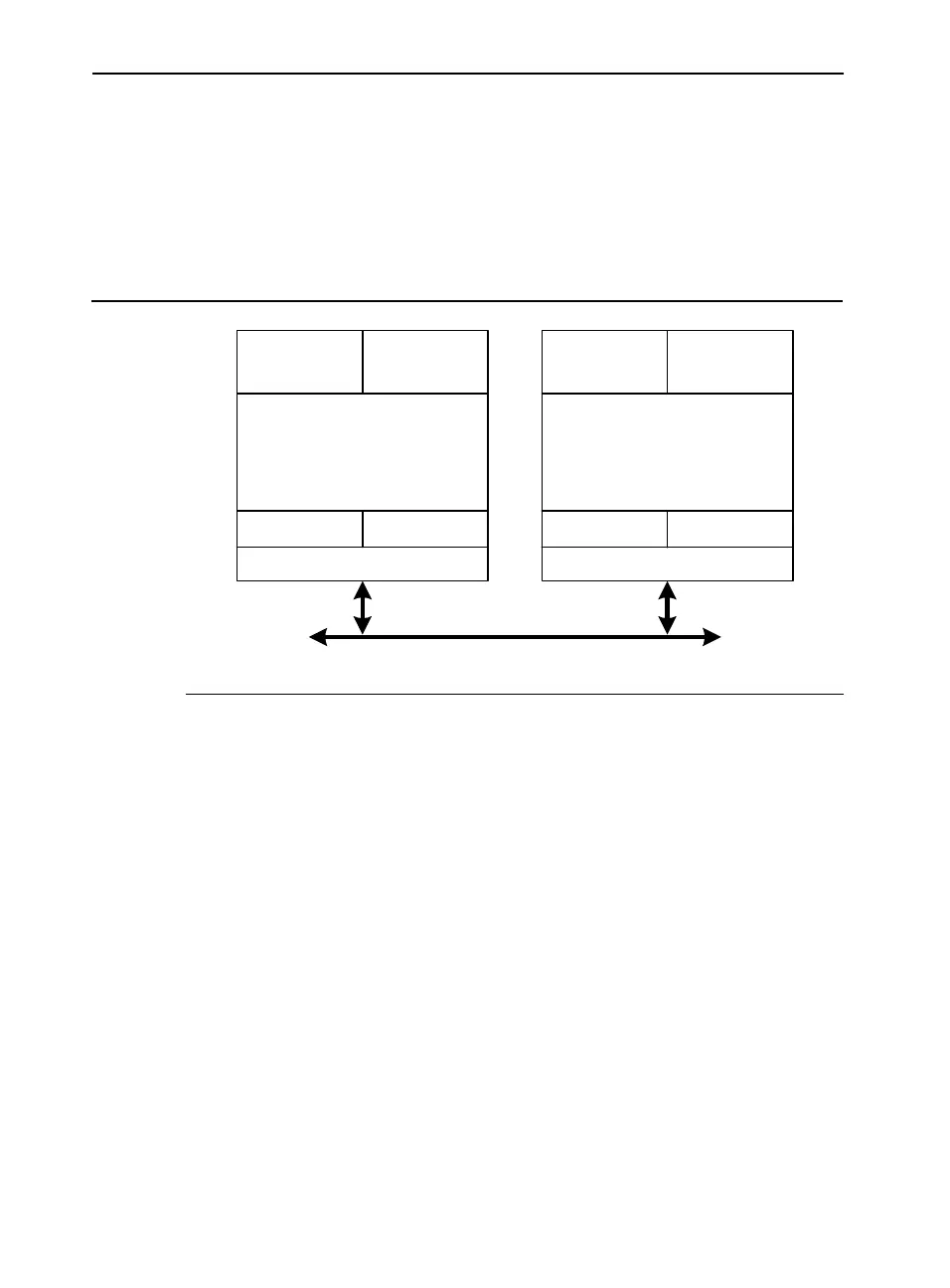
Figure 1-6 Hyper-Threading Technology on an SMP
OM15152
Bus Interface
Execution Engine
Architectural
State
Architectural
State
Local APIC
Local APIC
System Bus
Execution Engine
Architectural
State
Architectural
State
Local APIC
Local APIC
Bus Interface

 Loading...
Loading...