Mathematics of Prefetch Scheduling Distance E
E-7
The iteration latency is approximately equal to the computation latency
plus the memory leadoff latency (includes cache miss latency, chipset
latency, bus arbitration, and so on.) plus the data transfer latency where
transfer latency= number of lines per iteration * line burst latency.
This means that the decoupled memory and execution are ineffective to
explore the parallelism because of flow dependency. That is the case
where prefetch can be useful by removing the bubbles in either the
execution pipeline or the memory pipeline.
With an ideal placement of the data prefetching, the iteration latency
should be either bound by execution latency or memory latency, that is
il = maximum(T
c
, T
b
).
Compute Bound (Case:Tc >= T
l
+ T
b
)
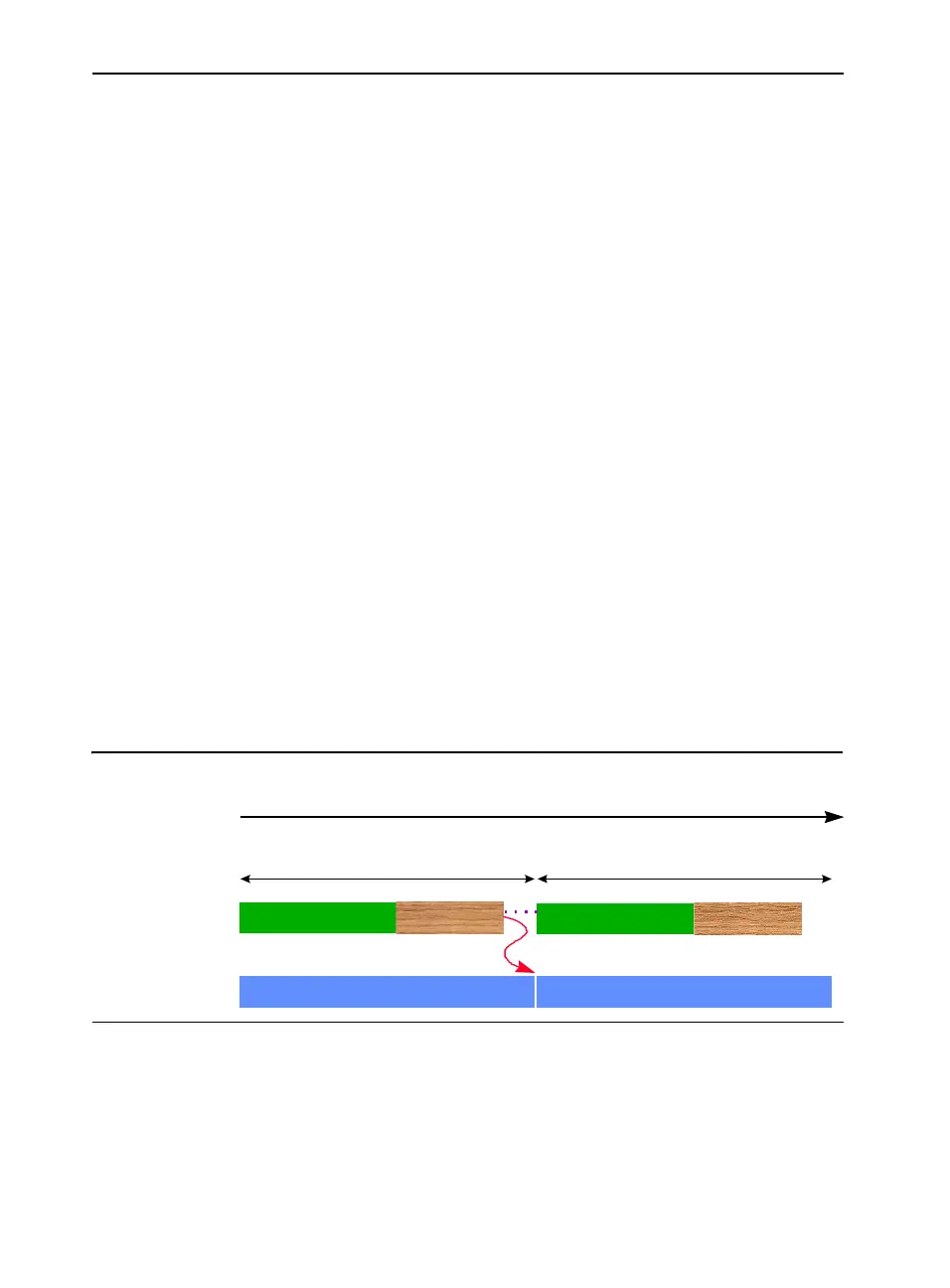
Figure E-3 represents the case when the compute latency is greater than
or equal to the memory leadoff latency plus the data transfer latency. In
this case, the prefetch scheduling distance is exactly 1; i.e., prefetch data
one iteration ahead is good enough. The data for loop iteration i can be
prefetched during loop iteration i-1, the δ
f
symbol between front-side
bus and execution pipeline indicates the data flow dependency.
Figure E-3 Compute Bound Execution Pipeline
Front-Side Bus
Execution pipeline
T
c
T
l
T
b
Iteration i
Iteration i+1
T
c
T
l
T
b
Execution cycles
δ
f

 Loading...
Loading...