Optimizing Cache Usage 6
6-35
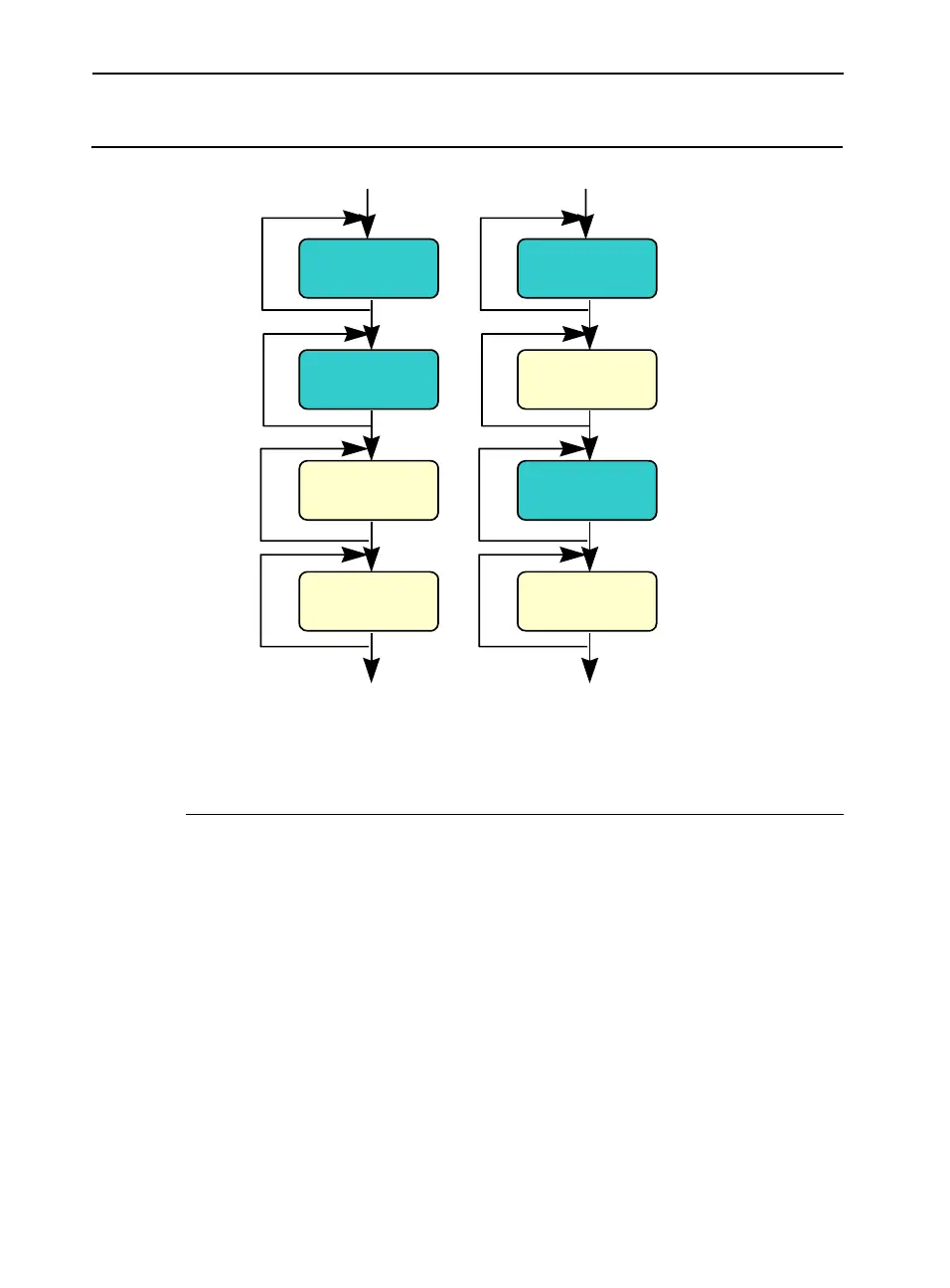
In the temporally-adjacent scenario, subsequent passes use the same
data and find it already in second-level cache. Prefetch issues aside, this
is the preferred situation. In the temporally non-adjacent scenario, data
used in pass m is displaced by pass (m+1), requiring data re-fetch into
the
first level cache and perhaps the second level cache if a later pass
reuses the data. If both data sets fit into the second-level cache, load
operations in passes 3 and 4 become less expensive.
Figure 6-6 Cache Blocking – Temporally Adjacent and Non-adjacent Passes
Dataset A
Dataset B
Dataset B
Dataset
A
Dataset A
Dataset A
Dataset B
Dataset B
Pass 1
Pass 2
Pass 3
Pass
Temporally
adjacent passes
Temporally
non-adjacent
passes

 Loading...
Loading...