IA-32 Intel® Architecture Optimization
2-20
Assembly/Compiler Coding Rule 3. (M impact, H generality) Arrange
code to be consistent with the static branch prediction algorithm: make the
fall-through code following a conditional branch be the likely target for a
branch with a forward target, and make the fall-through code following a
conditional branch be the unlikely target for a branch with a backward target.
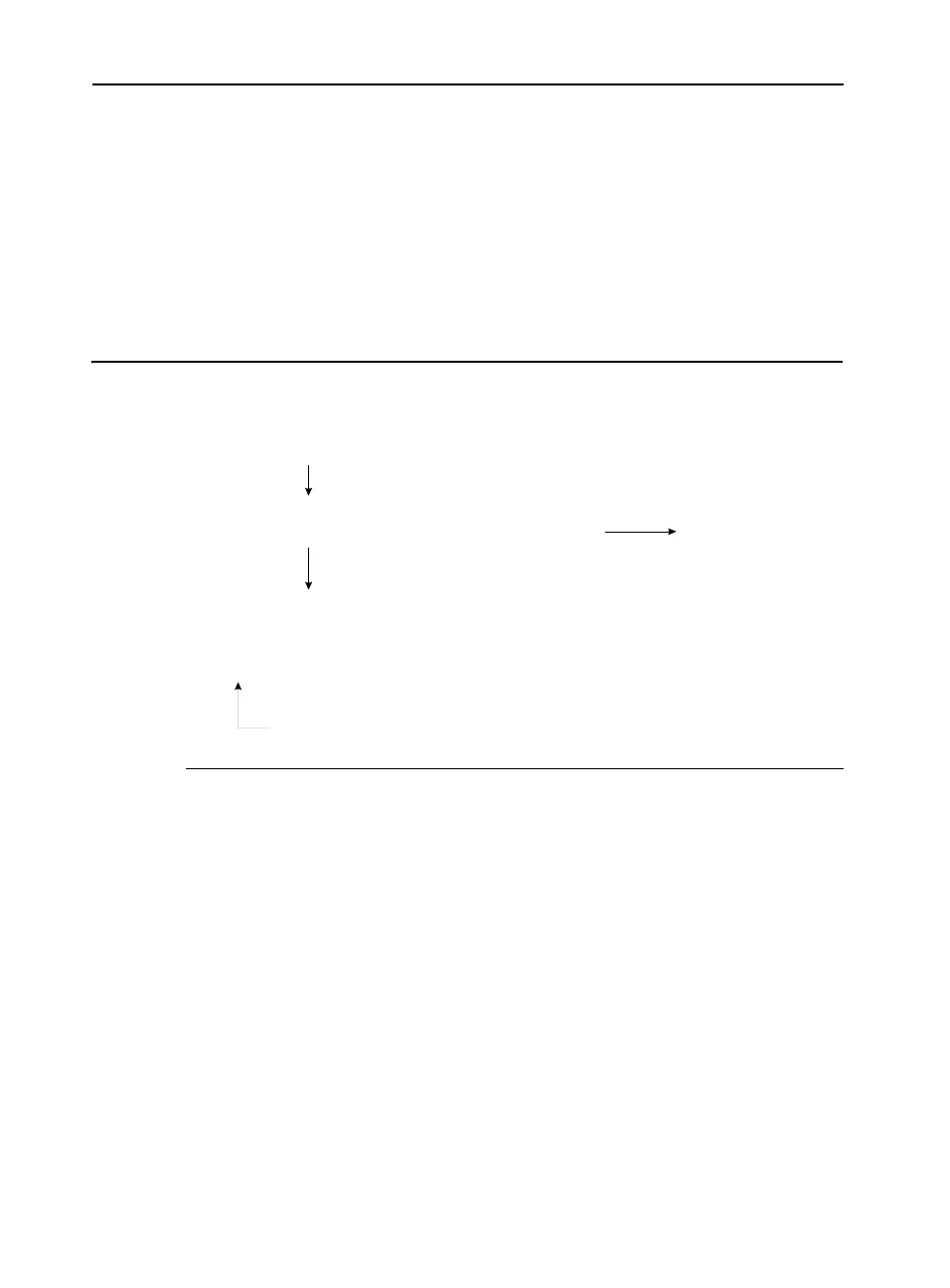
Example 2-5 illustrates the static branch prediction algorithm. The body
of an
if-then conditional is predicted to be executed.
Example 2-5 Pentium 4 Processor Static Branch Prediction Algorithm
forw ard conditional branches not taken (fall through)
If <condition> {
...
}
Unconditional Branchestaken
JM P
for <condition> {
...
}
Backward Conditional Branchesaretaken
loop {
}<condition>

 Loading...
Loading...