1-4
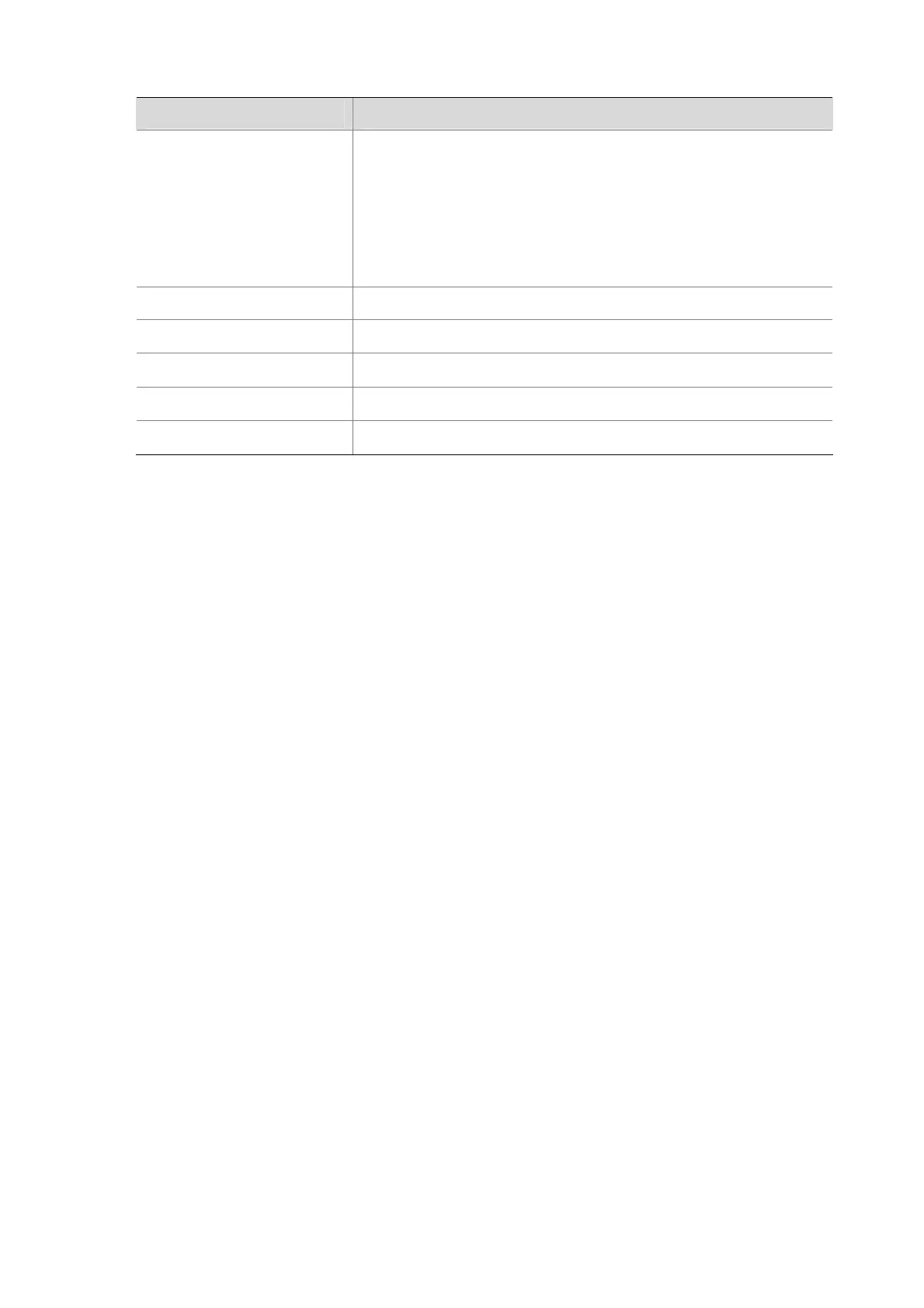
Table 1-2 display mac-address statistics command output description
Field Description
MAC TYPE
MAC address type:
z Dynamic Unicast
z Static Unicast
z Total Unicast
z Dynamic Multicast
z Static Multicast
z Total Multicast
LEARNED Dynamically learned MAC addresses
USER-DEFINED User defined MAC addresses (dynamic and static)
SYSTEM-DEFINED MAC addresses generated by the system (for example, 802.1x)
IN-USE Number of existing MAC addresses of a specific type
AVAILABLE Maximum number of MAC addresses supported by the system
mac-address (Interface view)
Syntax
mac-address { dynamic | static } mac-address vlan vlan-id
undo mac-address { dynamic | static } mac-address vlan vlan-id
View
Ethernet interface view, Layer 2 aggregate interface view
Default Level
2: System level
Parameters
dynamic: Dynamic MAC address entries. Aging time is set for these entries.
static: Static MAC address entries. They do not age but you can add or remove them.
mac-address: Specifies a MAC address in the format of H-H-H, where 0s at the beginning of each H
(16-bit hexadecimal digit) can be omitted; for example, inputting “f-e2-1” indicates that the MAC address
is “000f-00e2-0001”.
vlan vlan-id: Specifies an existing VLAN to which the Ethernet interface belongs, where vlan-id is the
specified VLAN ID, in the range 1 to 4094.
Description
Use the mac-address command to add or modify a MAC address entry on a specified interface.
Use the undo mac-address command to remove a MAC address entry on the interface.
Note that, as your MAC address entries configuration cannot survive a reboot, save it after completing
the configuration. The dynamic MAC address table entries however will be lost whether you save the
configuration or not.

 Loading...
Loading...















