Control method
160
PARAMETERS
PM sensorless vector control
• Highly efficient motor control and highly accurate motor speed control can be performed by using the inverter with a PM
(permanent magnet embedded) motor, which is more efficient than an induction motor.
• The motor speed is calculated based on the output voltage and current from the inverter. It does not require a speed
detector such as an encoder. The inverter drives the PM motor with the least required current when a load is applied in
order to achieve the highest motor efficiency.
• Performing the IPM parameter initialization makes the IPM motor MM-CF ready for the PM sensorless vector control.
POINTPOINT
• The PM sensorless vector control requires the following conditions.
• The motor used are described in the table below.
• For the motor capacity, the rated motor current should be equal to or less than the rated inverter current. (It must be 0.4 kW
or higher.)
Using a motor with the rated current substantially lower than the rated inverter current will cause torque ripples, etc. and
degrade the speed and torque accuracies. As a reference, select the motor with the rated motor current that is about 40% or
higher of the rated inverter current.
• Single-motor operation (one motor to one inverter) is preformed.
• The overall wiring length with the motor is 100 m or less. (Refer to page 43.) (Even with the IPM motor MM-CF, when the
wiring length exceeds 30 m, perform offline auto tuning.)
• A surge voltage suppression filter (FR-ASF/FR-BMF) or sine wave filter (MT-BSL/BSC) is not used.
Motor Condition
Mitsubishi IPM motor (MM-CF) Offline auto tuning is not required
IPM motor (other than MM-CF), SPM motor Offline auto tuning is required
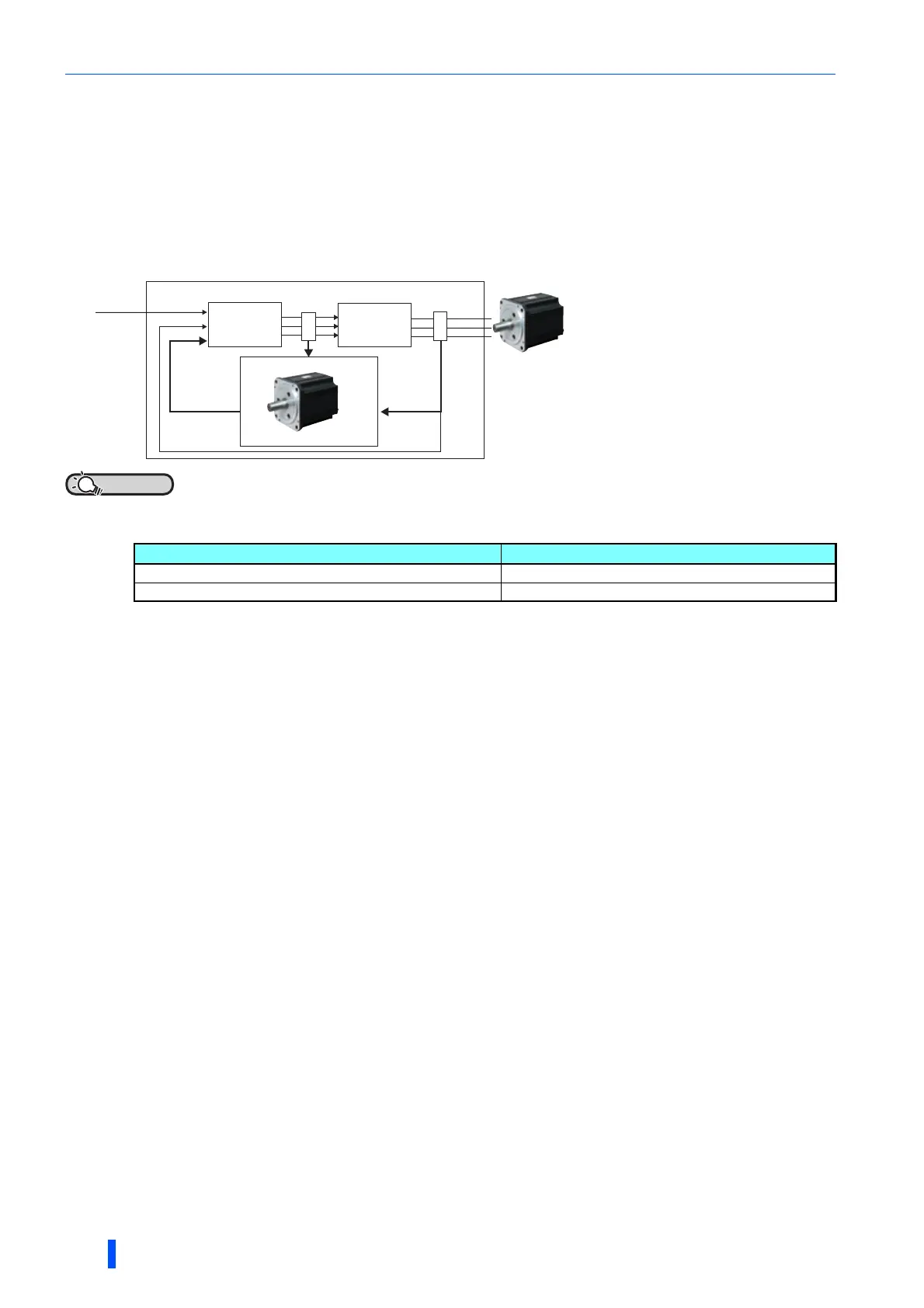
PM sensorless vector control image
Inverter
circuit
Controller
Output
current
Ooutput
voltage
Inverter
Virtual motor
Magnetic field observer
Speed
command
Speed/magnetic
pole position
∗1 A magnetic field observer is a control
method that calculates the motor
speed/magnetic pole position based
on the motor voltage and current of a
virtual motor which is set up in the
drive unit.
∗1

 Loading...
Loading...











