Raisecom
ISCOM2600G-HI (A) Series Configuration Guide
Raisecom Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd.
2.8 MRSTP
2.8.1 Introduction
RSTP aims to trims a bridged LAN to a logical single spanning tree. A tree network must have
a root, so the concept of the root bridge is introduced. There is only one root bridge on the
entire network while other devices are called leaf nodes.
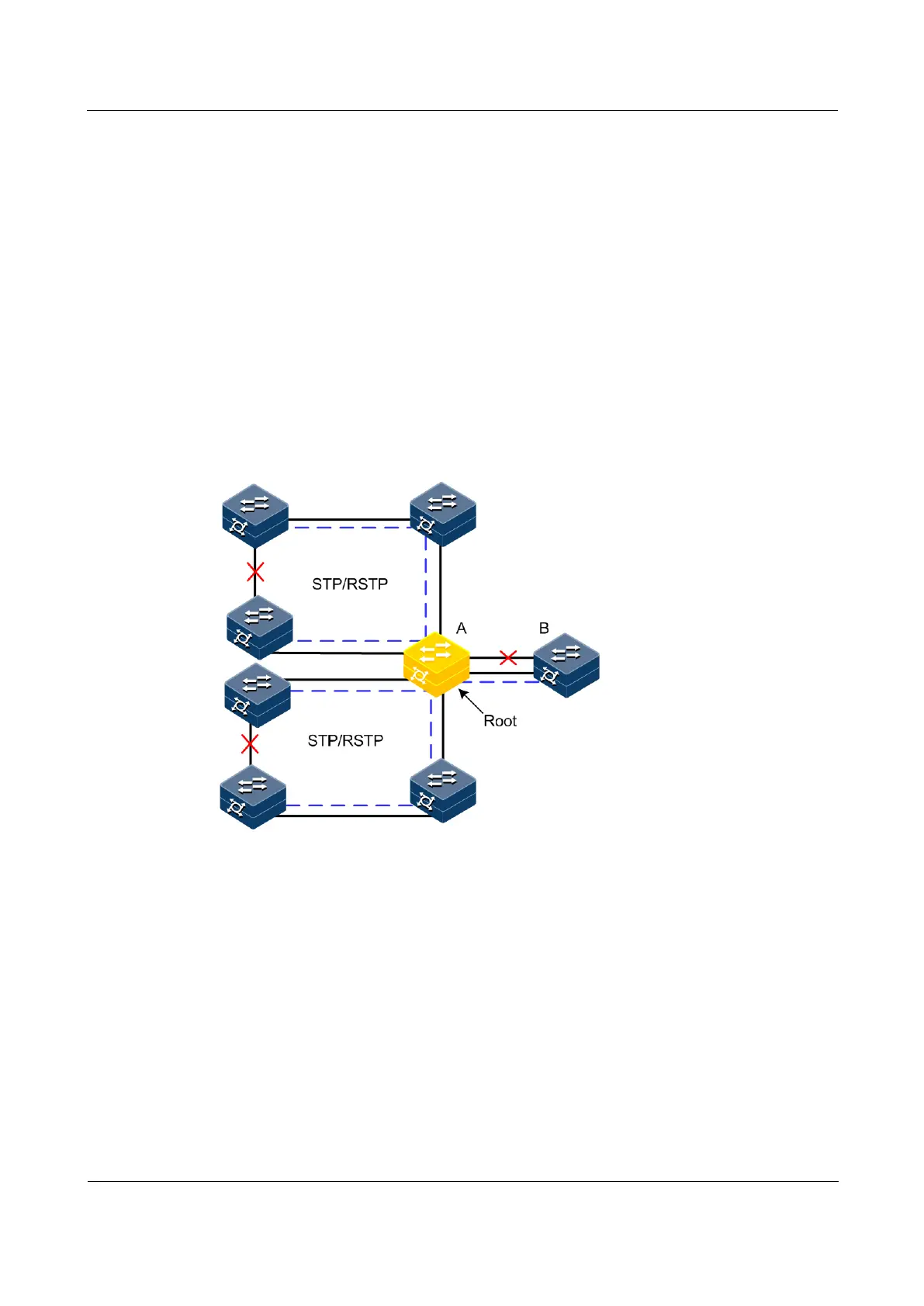
As shown in Figure 2-19, when running RSTP, device B is generally elected as the root bridge.
When these ring networks do not want or fit to run MSTP, device A is specified as the root
bridge of the ring network while device B is the root bridge of device A. You can create
multiple MRSTP processes on device A and bind the interfaces connecting these ring
networks to the specified processes. In this case, when devices on these ring networks, they
will elect device A as the root bridge of each ring network while device A will elect device B
as its root bridge.
Figure 2-19 Configuring MRSTP for specifying root bridge
2.8.2 Preparing for configurations
Scenarios
When device A is connected upstream to device B which has a higher priority, device B will
be elected as the root bridge. Device A is concurrently connected to multiple ring networks
which run STP/RSTP only, so device A is expected to be specified as the root bridge of
devices of multiple ring networks, to forward all traffic, and to choose device B as the root
bridge.
Prerequisite
N/A

 Loading...
Loading...










